Social isolation significantly impacts mental and physical health, increasing risks of depression, anxiety, and cardiovascular problems. Understanding the causes and recognizing the signs of social isolation can help you take proactive steps to rebuild meaningful connections. Discover effective strategies and expert advice by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
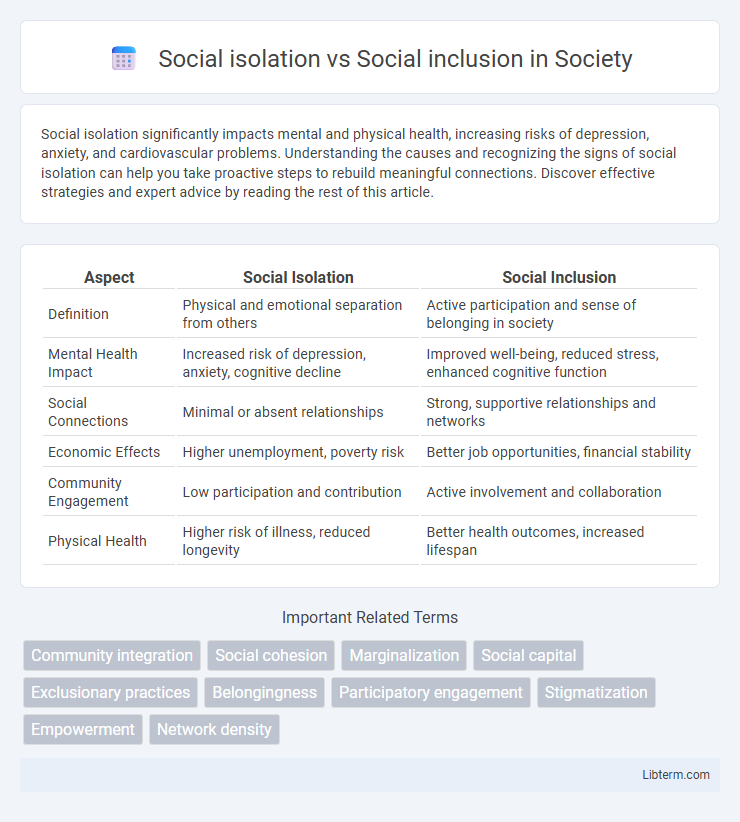
| Aspect | Social Isolation | Social Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical and emotional separation from others | Active participation and sense of belonging in society |
| Mental Health Impact | Increased risk of depression, anxiety, cognitive decline | Improved well-being, reduced stress, enhanced cognitive function |
| Social Connections | Minimal or absent relationships | Strong, supportive relationships and networks |
| Economic Effects | Higher unemployment, poverty risk | Better job opportunities, financial stability |
| Community Engagement | Low participation and contribution | Active involvement and collaboration |
| Physical Health | Higher risk of illness, reduced longevity | Better health outcomes, increased lifespan |
Understanding Social Isolation: Definitions and Causes
Social isolation refers to a lack of meaningful social connections and interactions, significantly impacting mental and physical health. Causes of social isolation include factors such as aging, chronic illness, disability, socioeconomic status, and geographic location. Understanding these causes helps target interventions aimed at fostering social inclusion and improving quality of life.
The Psychological and Physical Impact of Social Isolation
Social isolation significantly increases the risk of mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline, while also contributing to elevated stress hormone levels that impair immune function. Physically, prolonged social isolation is associated with higher rates of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and weakened recovery from illness. In contrast, social inclusion fosters psychological well-being, reduces stress, and supports healthier physiological responses through strengthened social networks and emotional support.
Social Inclusion: Meaning and Key Components
Social inclusion refers to the process of improving the terms of participation in society for individuals who are disadvantaged, ensuring equal access to opportunities and resources such as education, employment, healthcare, and social services. Key components of social inclusion include active engagement in community activities, recognition of diverse identities, and the removal of barriers related to discrimination, poverty, and marginalization. This approach fosters a sense of belonging, empowerment, and social cohesion that enhances individual well-being and societal resilience.
Benefits of Social Inclusion for Individuals and Communities
Social inclusion fosters improved mental health by reducing feelings of loneliness and depression, enhancing overall well-being. It promotes economic growth as diverse communities contribute varied skills and innovative ideas, boosting productivity and creativity. Strong social networks within inclusive communities support better access to resources, education, and healthcare, leading to increased social cohesion and resilience.
Major Factors Leading to Social Isolation
Major factors leading to social isolation include chronic health conditions, mobility limitations, and lack of access to transportation, which hinder individuals from engaging in social activities. Psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem contribute significantly to withdrawing from social interactions. Economic challenges, including poverty and unemployment, exacerbate isolation by restricting opportunities for participation in community events and social networks.
Barriers to Achieving Social Inclusion
Barriers to achieving social inclusion often stem from systemic issues such as discrimination, socioeconomic disparities, and limited access to education and healthcare. Social isolation is exacerbated by these factors, leading to exclusion of marginalized groups including the elderly, disabled, and minorities. Overcoming these barriers requires targeted policies that promote equal opportunities, enhance community engagement, and improve support networks.
Strategies to Reduce Social Isolation
Effective strategies to reduce social isolation include fostering community engagement through accessible social programs and support groups that enhance interpersonal connections. Implementing technology-based solutions, such as virtual meetups and online communities, provides inclusive platforms for isolated individuals to interact and build relationships. Collaboration between healthcare providers, local organizations, and policymakers is essential to develop targeted interventions that address the specific needs of vulnerable populations, including seniors and individuals with disabilities.
Promoting Social Inclusion: Effective Approaches
Promoting social inclusion involves strategies such as community engagement programs, inclusive education, and accessible public services designed to connect marginalized groups. Implementing these approaches reduces social isolation by fostering a sense of belonging and equal participation in society. Evidence from social policy research shows that targeted interventions in healthcare, employment, and civic activities significantly improve social cohesion and individual well-being.
The Role of Technology in Isolation and Inclusion
Technology shapes social dynamics by both amplifying social isolation and fostering social inclusion. Digital platforms and social media can create echo chambers that intensify feelings of loneliness, yet they also provide critical avenues for connection among marginalized groups and individuals with mobility challenges. Innovative tools like virtual reality and online support networks play a pivotal role in bridging social gaps, enabling greater participation and access to community resources.
Building Inclusive Societies: Policy and Community Solutions
Building inclusive societies requires targeted policies that promote social inclusion by addressing barriers such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to education and healthcare. Community solutions like local support networks, inclusive public spaces, and participatory decision-making empower marginalized groups and reduce social isolation. Evidence from social policy research indicates that integrated approaches combining government initiatives and grassroots efforts foster stronger social cohesion and improve overall well-being.
Social isolation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com