Government plays a crucial role in shaping policies that impact the economy, public services, and national security. Understanding how different branches and levels of government function can empower Your civic engagement and decision-making. Explore the rest of this article to uncover the complexities and importance of government in everyday life.
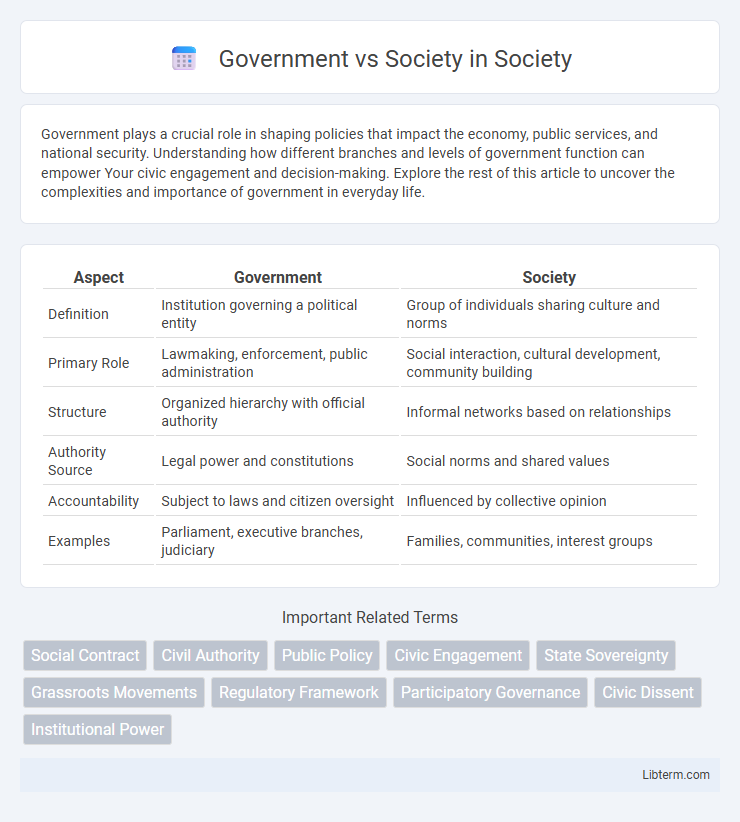
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Government | Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Institution governing a political entity | Group of individuals sharing culture and norms |
| Primary Role | Lawmaking, enforcement, public administration | Social interaction, cultural development, community building |
| Structure | Organized hierarchy with official authority | Informal networks based on relationships |
| Authority Source | Legal power and constitutions | Social norms and shared values |
| Accountability | Subject to laws and citizen oversight | Influenced by collective opinion |
| Examples | Parliament, executive branches, judiciary | Families, communities, interest groups |
Introduction: Defining Government and Society
Government refers to the organized system of authority and institutions responsible for creating and enforcing laws, policies, and regulations within a defined territory. Society encompasses the community of individuals connected through shared culture, values, and social structures that influence collective behavior and interactions. Understanding the distinct yet interdependent roles of government and society is crucial for analyzing governance, social order, and public welfare.
Historical Perspectives on Government-Society Relations
Historical perspectives on government-society relations reveal evolving dynamics between authority and social structures, with early civilizations like Mesopotamia establishing centralized governance to manage resources and social order. Feudal systems in medieval Europe highlight decentralized power where local lords governed communities, reflecting a complex interaction between government authority and societal hierarchies. The Enlightenment era introduced concepts of social contract theory, emphasizing government legitimacy through the consent of the governed, shaping modern democratic principles and citizen-state relations.
The Role of Government in Shaping Society
The government plays a crucial role in shaping society by establishing laws, policies, and frameworks that regulate social behavior and promote public welfare. Through institutions such as the legal system, education sector, and healthcare infrastructure, governments influence social norms, economic opportunities, and citizens' quality of life. Effective governance balances individual freedoms with collective security to create a stable and equitable society.
Society’s Influence on Government Policy
Society significantly shapes government policy through public opinion, advocacy, and voting behaviors that reflect collective values and priorities. Grassroots movements and social organizations mobilize citizens, applying pressure on policymakers to address social issues such as healthcare, education, and environmental protection. Democratic institutions facilitate this interaction by translating societal demands into legislative agendas and regulatory frameworks.
Power Dynamics: Who Truly Leads?
Government wields formal authority through laws, policies, and institutions designed to regulate society, yet society exerts influence via collective norms, cultural values, and grassroots movements shaping governance. Power dynamics reveal a symbiotic tension where governments respond to social demands, while societal groups leverage mobilization to sway political decisions. True leadership emerges from the interplay between institutional control and social agency, highlighting a continuous negotiation of power between state structures and the citizenry.
Rights, Responsibilities, and Social Contracts
Governments establish legal frameworks that define individual rights and collective responsibilities, ensuring order and protecting freedoms within society. Social contracts represent the implicit agreements where individuals consent to governmental authority in exchange for security and social welfare. Balancing these elements fosters civic engagement, promotes justice, and maintains societal cohesion.
Conflict and Cooperation: Case Studies
Government and society often experience tension and collaboration, exemplified by the 1960s Civil Rights Movement in the United States, where grassroots activism challenged institutional segregation leading to landmark legislation like the Civil Rights Act of 1964. In contrast, the cooperative management of public health during the COVID-19 pandemic illustrates how government directives and societal compliance can align to mitigate crises. These case studies highlight the dynamic interplay where conflict drives social reform while cooperation enables effective governance.
Modern Challenges: Democracy, Authoritarianism, and Social Movements
Modern challenges in government and society revolve around balancing democratic principles with rising authoritarian tendencies, often influenced by digital surveillance and misinformation. Social movements leverage technology and grassroots mobilization to demand transparency, accountability, and reform in political systems worldwide. Navigating these dynamics requires addressing polarization, protecting civil liberties, and fostering inclusive governance to sustain democratic resilience.
The Future of Government-Society Interaction
Advancements in digital technology and AI are reshaping government-society interaction, enabling real-time public engagement and data-driven policy-making. Emerging smart governance models emphasize transparency, accountability, and citizen-centric services, fostering increased trust and collaboration. Predictive analytics and decentralized platforms will enhance decision-making processes, making governments more responsive to societal needs in the future.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance
Striking a balance between government authority and societal needs is crucial for sustainable development and social harmony. Effective governance requires responsive policies that reflect the diverse interests of society while ensuring law, order, and economic stability. Empowering civic participation alongside transparent administration fosters trust and cooperative progress in democratic systems.
Government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com