Automation streamlines repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing human error across various industries. By implementing automated systems, businesses can optimize workflows, boost productivity, and lower operational costs. Discover how automation can transform your processes by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
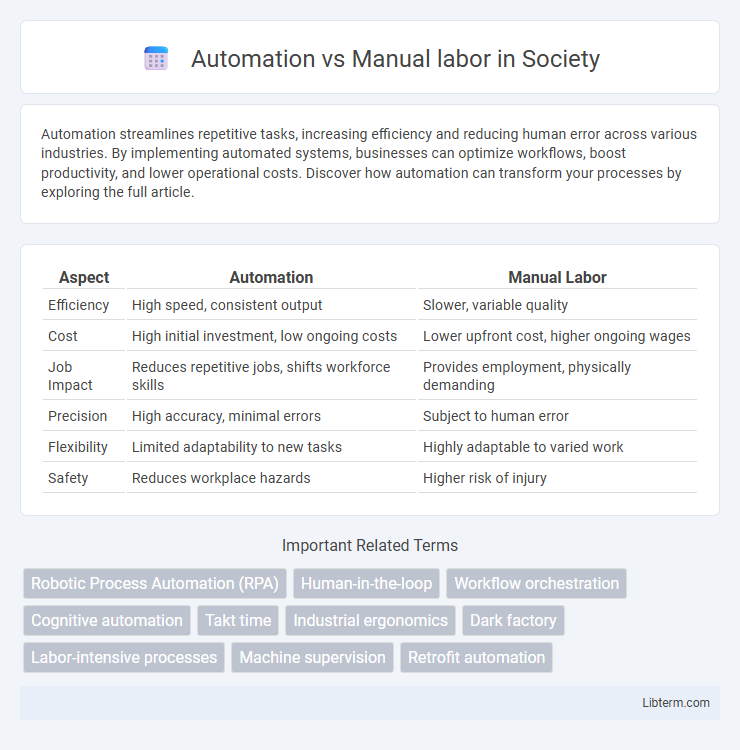
| Aspect | Automation | Manual Labor |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High speed, consistent output | Slower, variable quality |
| Cost | High initial investment, low ongoing costs | Lower upfront cost, higher ongoing wages |
| Job Impact | Reduces repetitive jobs, shifts workforce skills | Provides employment, physically demanding |
| Precision | High accuracy, minimal errors | Subject to human error |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability to new tasks | Highly adaptable to varied work |
| Safety | Reduces workplace hazards | Higher risk of injury |
Introduction to Automation and Manual Labor
Automation leverages advanced technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to perform tasks traditionally done by humans, significantly increasing productivity and consistency. Manual labor relies on human physical effort and skill, often involving repetitive or physically demanding tasks that require adaptability and problem-solving. The shift from manual labor to automation drives efficiency and cost reduction but also presents challenges related to workforce displacement and skill adaptation.
Key Differences Between Automation and Manual Labor
Automation involves the use of machines and technology to perform tasks traditionally done by human workers, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Manual labor relies on human physical effort and skill, often resulting in greater flexibility but slower production rates. Key differences include speed, accuracy, scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the reduction of repetitive strain injuries associated with automation.
Historical Perspective: Evolution of Work Practices
The evolution of work practices has shifted significantly from manual labor to automation, driven by technological advancements like the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century, which introduced mechanized manufacturing processes. Early manual labor relied heavily on human skill and physical effort, whereas contemporary automation incorporates robotics, artificial intelligence, and computerized systems to enhance productivity and precision. This historical transition reflects an ongoing trend toward reducing labor costs, increasing efficiency, and transforming workforce dynamics across industries worldwide.
Advantages of Automation in Modern Industries
Automation in modern industries significantly boosts productivity by enabling continuous, high-speed operations with minimal human error. It reduces labor costs and enhances precision in repetitive tasks such as assembly line manufacturing and quality control. Advanced technologies like robotics and AI-driven systems increase safety by performing hazardous duties, thereby lowering workplace injuries and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Strengths and Limitations of Manual Labor
Manual labor excels in tasks requiring adaptability, intricate hand-eye coordination, and nuanced judgment that machines might struggle to replicate. It provides employment opportunities and supports economic sectors reliant on skilled craftsmanship but often faces limitations in efficiency, scalability, and consistency when compared to automated processes. Despite technological advances, manual labor remains indispensable in scenarios demanding customization, tactile feedback, and problem-solving in unstructured environments.
Economic Impact: Jobs, Productivity, and Cost
Automation significantly boosts productivity by enabling faster production rates and consistent quality, reducing operational costs for businesses. While automation can lead to job displacement in manual labor sectors, it also creates new opportunities in tech development, maintenance, and oversight roles. Economically, the shift toward automation often results in higher overall output and competitiveness but requires policies to manage workforce transitions and skill development.
Human Factors: Job Satisfaction and Skill Development
Automation improves job satisfaction by reducing repetitive, physically demanding tasks, allowing workers to focus on more engaging, creative responsibilities that foster skill development and cognitive growth. However, manual labor offers a sense of accomplishment and mastery over tangible tasks, contributing to intrinsic motivation and hands-on expertise that automation may diminish. Balancing automation with opportunities for human skill enhancement is crucial to maintaining workforce morale and long-term professional growth.
Technological Innovations Driving Automation
Technological innovations such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and machine learning have accelerated the shift from manual labor to automation, significantly enhancing efficiency and precision in manufacturing, logistics, and service industries. Advanced sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices enable real-time data collection and process optimization, reducing human error and operational costs. Automation powered by these cutting-edge technologies drives scalability and allows businesses to reallocate human resources towards more complex and creative tasks.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Automation presents challenges such as workforce displacement, skill gaps, and increased dependency on complex technologies, while manual labor raises concerns about worker safety, physical strain, and inconsistent productivity. Ethical considerations include ensuring fair labor practices, addressing socioeconomic inequalities caused by automation, and maintaining transparency in decision-making processes influenced by automated systems. Balancing efficiency with social responsibility requires policies that support retraining programs, protect vulnerable workers, and promote inclusive technological adoption.
The Future Landscape: Balancing Automation and Human Work
The future landscape of work demands a strategic balance between automation and manual labor to enhance productivity and preserve human creativity. Automation technologies such as AI, robotics, and machine learning optimize repetitive tasks, while human workers provide critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and adaptability. Integrating both approaches ensures sustainable economic growth, job creation in emerging sectors, and long-term workforce resilience.
Automation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com