Sustainable development focuses on meeting present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. It integrates economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection to create long-lasting benefits for communities worldwide. Discover how your actions can contribute to a more sustainable future by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
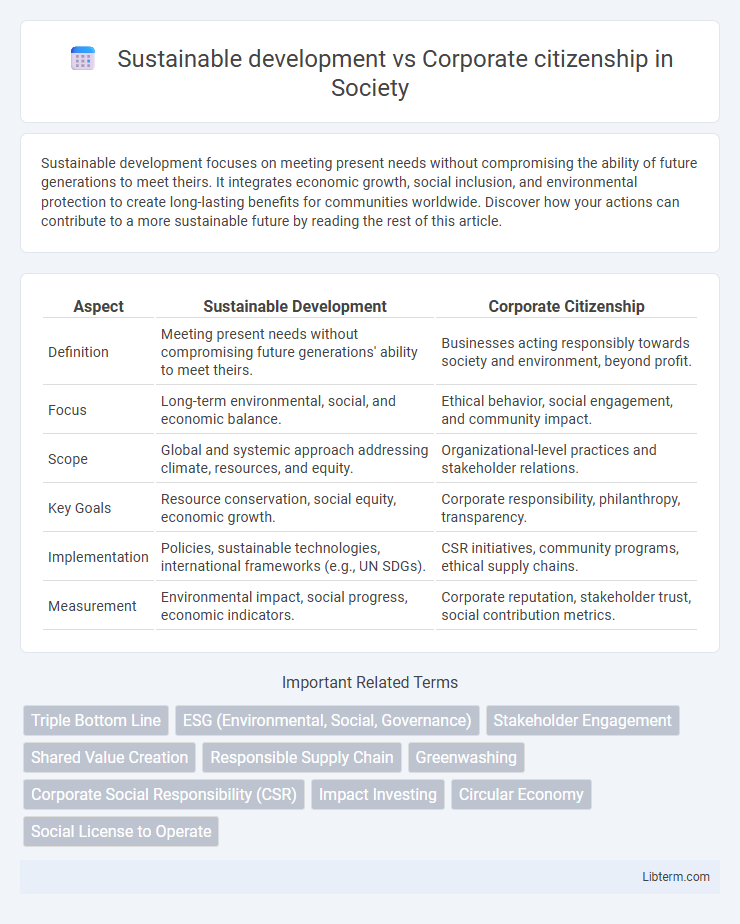
| Aspect | Sustainable Development | Corporate Citizenship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Meeting present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet theirs. | Businesses acting responsibly towards society and environment, beyond profit. |
| Focus | Long-term environmental, social, and economic balance. | Ethical behavior, social engagement, and community impact. |
| Scope | Global and systemic approach addressing climate, resources, and equity. | Organizational-level practices and stakeholder relations. |
| Key Goals | Resource conservation, social equity, economic growth. | Corporate responsibility, philanthropy, transparency. |
| Implementation | Policies, sustainable technologies, international frameworks (e.g., UN SDGs). | CSR initiatives, community programs, ethical supply chains. |
| Measurement | Environmental impact, social progress, economic indicators. | Corporate reputation, stakeholder trust, social contribution metrics. |
Defining Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is defined as meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, emphasizing environmental protection, social equity, and economic growth. Corporate citizenship refers to a company's responsibilities toward society, often encompassing sustainable development principles but focusing more on ethical behavior and community engagement. While sustainable development is a broad concept applied globally, corporate citizenship specifically addresses how businesses integrate sustainability and social responsibility into their operations.
The Concept of Corporate Citizenship
The concept of corporate citizenship emphasizes a company's responsibility to operate ethically, contribute positively to society, and engage in community development beyond profit-making. It integrates social, environmental, and economic considerations into corporate strategies, promoting transparency, stakeholder engagement, and accountability. Unlike sustainable development, which focuses broadly on balancing ecological, social, and economic needs for future generations, corporate citizenship specifically highlights the proactive role businesses play in societal well-being and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Key Differences Between Sustainable Development and Corporate Citizenship
Sustainable development focuses on long-term environmental, social, and economic goals to meet present needs without compromising future generations, emphasizing resource management and ecological balance. Corporate citizenship centers on a company's ethical responsibilities and active engagement in community welfare, promoting social accountability and stakeholder trust. The key difference lies in sustainable development's broad systemic approach versus corporate citizenship's specific organizational commitment to social and ethical practices.
Corporate Social Responsibility: A Bridge Between the Two
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) acts as a crucial bridge connecting sustainable development goals with corporate citizenship by embedding ethical practices within business operations. By aligning CSR initiatives with environmental stewardship, social equity, and economic viability, companies enhance their role as responsible corporate citizens. This integration fosters long-term value creation, community engagement, and sustainable innovation, driving measurable impacts on global sustainability targets.
The Role of Stakeholders in Sustainable Development
Stakeholders in sustainable development include employees, investors, customers, suppliers, regulators, and local communities whose engagement and collaboration drive long-term environmental, social, and economic goals. Corporate citizenship emphasizes the responsibility of businesses to actively contribute to societal well-being through ethical practices and community involvement, aligning with stakeholder interests. Effective stakeholder management integrates diverse perspectives, enabling companies to implement sustainable initiatives that support equitable growth and resource conservation.
Measuring Impact: Metrics for Sustainability and Citizenship
Measuring impact in sustainable development involves metrics such as carbon footprint reduction, resource efficiency, and social equity indicators to assess environmental and societal progress. Corporate citizenship impact is evaluated using frameworks like ESG scores, community engagement indices, and ethical governance benchmarks that reflect a company's contributions to social responsibility. Both approaches employ quantitative and qualitative data to drive transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement in sustainability and corporate social performance.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementation
Sustainable development faces challenges such as balancing economic growth with environmental preservation and addressing social inequalities, while corporate citizenship struggles with aligning business goals with ethical responsibilities and stakeholder expectations. Opportunities in sustainable development include innovation in green technologies and inclusive policies promoting long-term well-being, whereas corporate citizenship benefits from enhanced brand reputation and increased employee engagement through transparent, accountable practices. Both frameworks require robust measurement tools and strategic integration to overcome resistance and leverage their full potential in driving systemic change.
Case Studies: Companies Leading in Both Areas
Unilever exemplifies leadership in sustainable development through its Sustainable Living Plan, targeting waste reduction, water conservation, and renewable energy use, while also advancing corporate citizenship by actively supporting community health and education programs globally. Patagonia integrates sustainability into its business by using recycled materials and committing to environmental activism, simultaneously fostering corporate citizenship with fair labor practices and transparent supply chains. IKEA's People & Planet Positive strategy addresses climate action and sustainable sourcing while promoting employee welfare and engaging in philanthropic initiatives, demonstrating commitment to both sustainable development and corporate citizenship.
Integrating Sustainable Development into Corporate Strategy
Integrating sustainable development into corporate strategy involves embedding environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into core business operations, driving long-term value creation and risk management. Corporate citizenship emphasizes a company's responsibility toward societal well-being, promoting ethical practices, community engagement, and stakeholder collaboration. Effective integration of sustainable development enhances corporate citizenship by aligning sustainability goals with business objectives, fostering innovation, and strengthening brand reputation in global markets.
The Future of Corporate Responsibility in a Sustainable World
Sustainable development drives companies to integrate environmental, social, and economic goals into their core strategies, ensuring long-term value creation and resource preservation. Corporate citizenship emphasizes ethical practices, community engagement, and transparency, fostering trust and social license to operate in evolving markets. The future of corporate responsibility lies in combining these approaches to achieve resilient business models that promote global sustainability and stakeholder well-being.
Sustainable development Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com