Collective consciousness refers to the shared beliefs, ideas, and moral attitudes that operate as a unifying force within a society. This concept shapes social norms, influences behavior, and fosters a sense of belonging among individuals. Explore the rest of the article to understand how collective consciousness impacts your community and everyday life.
Table of Comparison
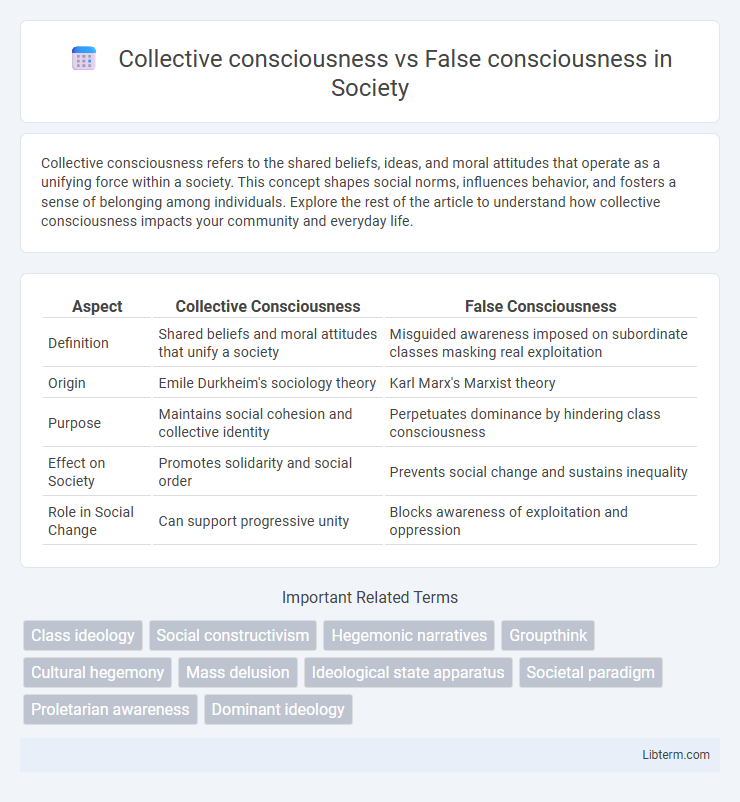
| Aspect | Collective Consciousness | False Consciousness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared beliefs and moral attitudes that unify a society | Misguided awareness imposed on subordinate classes masking real exploitation |
| Origin | Emile Durkheim's sociology theory | Karl Marx's Marxist theory |
| Purpose | Maintains social cohesion and collective identity | Perpetuates dominance by hindering class consciousness |
| Effect on Society | Promotes solidarity and social order | Prevents social change and sustains inequality |
| Role in Social Change | Can support progressive unity | Blocks awareness of exploitation and oppression |
Understanding Collective Consciousness
Collective consciousness refers to the shared beliefs, values, and attitudes that unify a group, shaping social cohesion and identity. It operates as a framework for collective understanding, influencing societal norms and behaviors through common knowledge and cultural symbols. Distinct from false consciousness, which involves misinterpretation or manipulation of social realities, collective consciousness fosters authentic social solidarity and collective awareness.
Defining False Consciousness
False consciousness refers to a flawed understanding or distorted awareness that hinders individuals or groups from recognizing their true social class position, often perpetuating the interests of dominant or ruling classes. It contrasts with collective consciousness, which represents a shared awareness and solidarity among members of a society or class, fostering collective action and social change. The concept is pivotal in Marxist theory, emphasizing how ideology and culture can obscure exploitation and maintain systemic inequalities.
Historical Origins of Both Concepts
The concept of collective consciousness originated with Emile Durkheim, who in the early 20th century described it as the set of shared beliefs and moral attitudes that unify a society. False consciousness, on the other hand, emerged from Karl Marx's theories in the mid-19th century, referring to the distorted understanding of social relations imposed by dominant classes to maintain their power. Both concepts illustrate different dimensions of how societal awareness and ideology influence group behavior and social structures.
Key Theorists and their Perspectives
Emile Durkheim pioneered the concept of collective consciousness, emphasizing shared beliefs and values that unify society and maintain social order. Karl Marx introduced false consciousness, highlighting how dominant ideologies mask class exploitation, preventing the proletariat from recognizing their true interests. Louis Althusser expanded on Marx's theory, arguing that ideological state apparatuses perpetuate false consciousness through cultural institutions.
Collective Consciousness in Modern Society
Collective consciousness in modern society manifests as shared beliefs, values, and norms that unify diverse groups through digital communication platforms and global media networks. This collective awareness drives social movements, shapes cultural identity, and fosters a sense of belonging that transcends individual experiences. Unlike false consciousness, which distorts reality to maintain power structures, collective consciousness promotes genuine social cohesion and progressive change.
Mechanisms of False Consciousness
False consciousness operates through mechanisms such as ideological manipulation, where dominant groups impose beliefs that obscure true social relations and perpetuate exploitation. It involves the internalization of misleading ideologies that lead individuals to accept their subordinate status as natural or unchangeable. This psychological process inhibits collective consciousness by preventing recognition of shared class interests and obstructing social solidarity.
Collective Action vs Social Manipulation
Collective consciousness represents the shared beliefs and moral attitudes that unify a group, enabling effective collective action to address social issues and drive systemic change. False consciousness, often perpetuated through social manipulation, obscures the true interests of subordinate groups, preventing mobilization and maintaining existing power structures. Understanding the distinction between genuine collective awareness and manipulated perceptions is crucial for fostering authentic social movements and resisting ideological control.
Impacts on Social Movements
Collective consciousness unites individuals around shared beliefs and values, strengthening social movements by fostering solidarity and coordinated action. False consciousness obscures awareness of exploitation and systemic inequalities, weakening movements through misdirected goals and internal divisions. Understanding these concepts helps activists diagnose challenges and strategize for more effective social change.
Overcoming False Consciousness
Overcoming false consciousness requires critical awareness of social and economic realities to challenge misleading beliefs imposed by dominant ideologies. Collective consciousness forms when groups develop shared understanding and solidarity, enabling resistance against false narratives that perpetuate oppression. Conscious education and grassroots movements play pivotal roles in transforming false consciousness into authentic collective awareness.
Toward an Enlightened Collective Awareness
Collective consciousness represents a shared awareness and understanding that emerges from genuine social interactions and common values, fostering unity and progressive action within communities. False consciousness, in contrast, involves distorted perceptions imposed by dominant ideologies that obscure true social relations and inhibit collective empowerment. Moving toward an enlightened collective awareness requires critical reflection, increased education, and open dialogue to dismantle these ideological barriers and cultivate authentic social solidarity.
Collective consciousness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com