Globalism drives interconnected economies, cultures, and political systems, fostering international cooperation and trade. It presents challenges such as economic inequality and cultural homogenization that require careful management. Explore the full article to understand how globalism shapes your world and future.
Table of Comparison
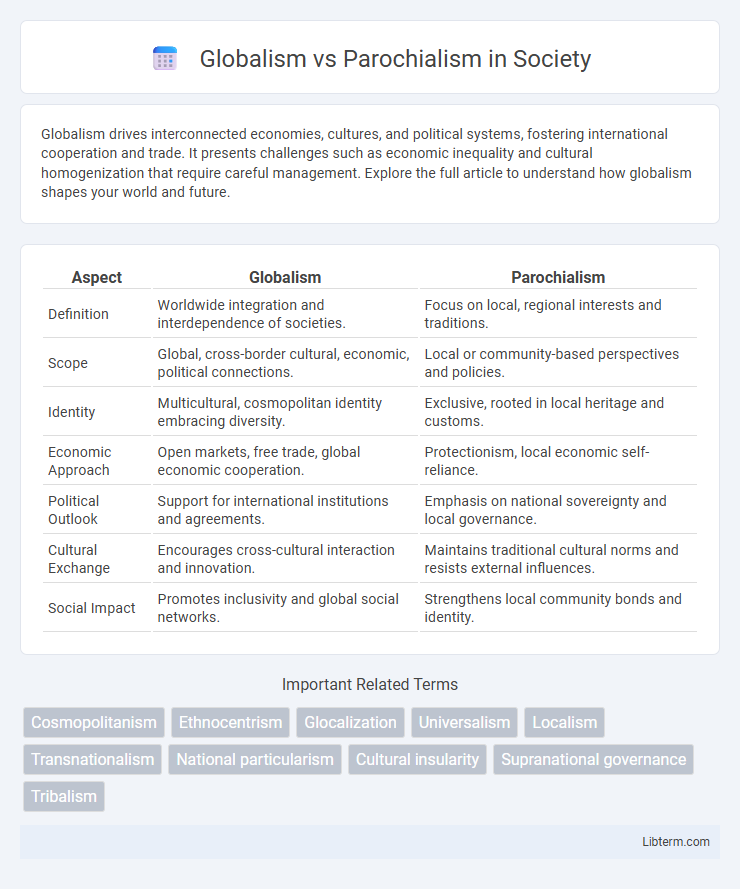
| Aspect | Globalism | Parochialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Worldwide integration and interdependence of societies. | Focus on local, regional interests and traditions. |
| Scope | Global, cross-border cultural, economic, political connections. | Local or community-based perspectives and policies. |
| Identity | Multicultural, cosmopolitan identity embracing diversity. | Exclusive, rooted in local heritage and customs. |
| Economic Approach | Open markets, free trade, global economic cooperation. | Protectionism, local economic self-reliance. |
| Political Outlook | Support for international institutions and agreements. | Emphasis on national sovereignty and local governance. |
| Cultural Exchange | Encourages cross-cultural interaction and innovation. | Maintains traditional cultural norms and resists external influences. |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusivity and global social networks. | Strengthens local community bonds and identity. |
Defining Globalism and Parochialism
Harmonic analysis examines steady-state response of electrical circuits to sinusoidal inputs by decomposing signals into fundamental frequencies and their harmonics, revealing circuit behavior under periodic excitation. It provides insights into voltage, current phasors, power factor, and distortion levels critical for designing filters, amplifiers, and power systems. Unlike transient analysis, which studies time-domain responses to sudden changes, harmonic analysis focuses on frequency-domain characteristics essential for optimizing system performance and mitigating harmonic distortion.
Historical Roots of Global and Local Perspectives
Globalism finds its historical roots in ancient trade routes like the Silk Road and the Age of Exploration, which connected diverse cultures and economies, fostering early forms of international cooperation and exchange. Parochialism, deeply embedded in local traditions and community-centric governance, emerged as societies prioritized immediate social bonds and self-sufficiency over distant alliances. The tension between these perspectives highlights the enduring balance between embracing expansive global networks and preserving localized identities shaped by historical experience.
Key Differences Between Globalism and Parochialism
Globalism emphasizes interconnectedness, promoting international cooperation, economic integration, and cultural exchange across borders. Parochialism, in contrast, prioritizes local traditions, values, and interests, often resisting external influences to preserve unique community identities. The key differences lie in globalism's emphasis on broad, inclusive perspectives versus parochialism's focus on narrow, localized viewpoints.
The Impact of Globalism on Economies and Cultures
Globalism fosters interconnected economies, driving trade expansion, innovation, and access to diverse markets, which boosts GDP growth worldwide. Cultural exchanges under globalism promote multiculturalism, leading to the blending of traditions, languages, and practices while sometimes challenging local identities. Economic integration often results in increased foreign direct investment and job creation, yet it can also exacerbate income inequality and threaten indigenous cultural heritage.
Parochialism: Benefits and Drawbacks for Communities
Parochialism fosters strong community bonds and preserves local culture by emphasizing shared traditions and close interpersonal relationships. This localized focus often results in greater social cohesion and mutual support among community members, enhancing resilience in times of crisis. However, parochialism can also limit exposure to diverse ideas and innovations, potentially hindering economic growth and adaptability in a globalized world.
Globalism and Parochialism in Politics
Globalism in politics promotes international cooperation, emphasizing global governance, multilateral agreements, and the integration of economies to address transnational issues like climate change and security. Parochialism in politics prioritizes local or national interests, often advocating for sovereignty, cultural preservation, and protectionist policies to safeguard domestic industries and social values. The tension between globalism and parochialism shapes policy decisions on immigration, trade, and international alliances, influencing the balance between global interconnectedness and national autonomy.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Global and Local Views
Technology drives the tension between globalism and parochialism by enabling instant communication and access to diverse cultures, fostering global interconnectedness and awareness. Digital platforms amplify both universal values and localized perspectives, allowing communities to preserve distinct identities while participating in global dialogues. Advanced algorithms and AI shape information consumption, influencing whether users gravitate toward global integration or localism in their worldview.
Education: Fostering Global Citizens or Local Loyalties
Education systems play a pivotal role in shaping global citizens by integrating multicultural curricula, promoting language diversity, and encouraging cross-cultural exchanges that broaden students' worldviews. Conversely, parochial educational approaches prioritize local histories, traditions, and values, strengthening community ties and fostering a strong sense of identity and loyalty. Balancing global perspectives with local rootedness in education cultivates individuals who are both globally aware and deeply connected to their cultural heritage.
Challenges in Balancing Globalism and Parochialism
Balancing globalism and parochialism presents challenges such as reconciling international economic integration with local cultural preservation and addressing the uneven distribution of globalization's benefits that often exacerbate regional inequalities. Policies must navigate the tension between promoting open trade and protecting domestic industries while ensuring social cohesion amid diverse global influences. Effective governance requires adaptive frameworks that respect local identities while fostering inclusive participation in the global economy.
Future Trends: Toward Integration or Fragmentation
Future trends in globalism versus parochialism reveal a complex interplay between increasing economic interdependence and rising nationalist sentiments. Advances in technology, such as artificial intelligence and digital communication, continue to promote global integration by facilitating cross-border collaboration and cultural exchange. However, geopolitical tensions and protectionist policies may accelerate fragmentation, leading to more localized governance and cultural preservation efforts.
Globalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com