Communitarianism emphasizes the importance of community values and social cohesion over individualism, asserting that the well-being of the community shapes personal identity and moral responsibilities. This political philosophy promotes the idea that individuals achieve fulfillment through active participation in communal life and shared norms. Explore this article to understand how communitarianism impacts your role within society and collective decision-making.
Table of Comparison
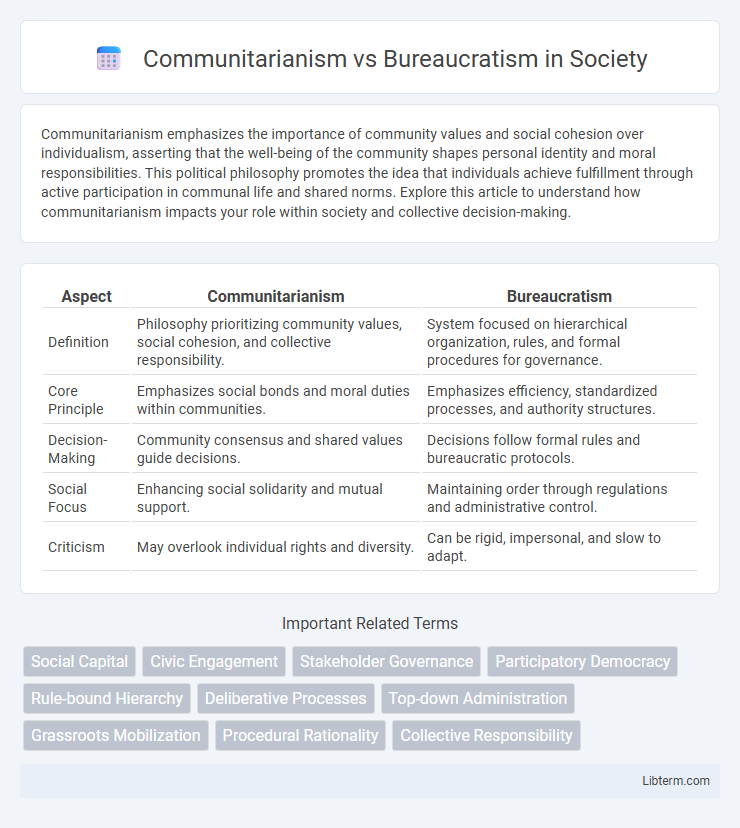
| Aspect | Communitarianism | Bureaucratism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophy prioritizing community values, social cohesion, and collective responsibility. | System focused on hierarchical organization, rules, and formal procedures for governance. |
| Core Principle | Emphasizes social bonds and moral duties within communities. | Emphasizes efficiency, standardized processes, and authority structures. |
| Decision-Making | Community consensus and shared values guide decisions. | Decisions follow formal rules and bureaucratic protocols. |
| Social Focus | Enhancing social solidarity and mutual support. | Maintaining order through regulations and administrative control. |
| Criticism | May overlook individual rights and diversity. | Can be rigid, impersonal, and slow to adapt. |
Defining Communitarianism: Core Principles
Communitarianism centers on the importance of community values, social cohesion, and collective responsibility, emphasizing the role of shared norms and mutual support in fostering individual well-being. It critiques bureaucratism for its reliance on rigid rules, hierarchical structures, and impersonal procedures that often undermine local traditions and social bonds. Core principles of communitarianism include fostering civic engagement, prioritizing communal goals over individualism, and promoting ethical obligations within social groups.
Understanding Bureaucratism: Key Characteristics
Bureaucratism is characterized by hierarchical organization, formal rules, and standardized procedures that emphasize efficiency and predictability within institutions. It prioritizes rigid adherence to established protocols over individual discretion, often leading to impersonal decision-making and reduced flexibility. This system contrasts with communitarian values by focusing on structure and control rather than community engagement and shared responsibility.
Historical Roots of Communitarianism and Bureaucratism
Communitarianism traces its historical roots to early philosophical traditions such as Aristotle's emphasis on the polis and communal virtue, as well as 20th-century thinkers like Charles Taylor and Amitai Etzioni who championed social cohesion and moral responsibility within communities. Bureaucratism, on the other hand, originated from the rational-legal authority principles articulated by Max Weber in the early 20th century, highlighting structured hierarchies, rule-based governance, and administrative efficiency as key elements. These foundational perspectives define communitarianism's focus on shared values and social bonds, contrasting sharply with bureaucratism's emphasis on formal procedures and organizational control.
Decision-Making: Community-Centric vs. Procedural Approaches
Communitarianism prioritizes decision-making that reflects community values, emphasizing collective well-being and social cohesion. Bureaucratism relies on standardized procedures and hierarchical rules to ensure consistency and accountability in decision processes. This contrast highlights the balance between flexible, value-driven choices and rigid, process-oriented governance structures.
Individual Rights in Communitarianism and Bureaucratism
Communitarianism emphasizes individual rights within the context of community responsibilities, advocating that personal freedoms are balanced by social duties to promote collective well-being. Bureaucratism prioritizes adherence to institutional rules and hierarchical authority, often limiting individual rights to ensure organizational efficiency and uniform decision-making. The tension between these approaches highlights differing views on the extent to which individual autonomy should be constrained by communal norms or bureaucratic regulations.
Social Cohesion and Collective Responsibility
Communitarianism emphasizes social cohesion through shared values and collective responsibility, fostering strong community bonds and mutual support among members. Bureaucratism, in contrast, prioritizes formal rules and hierarchical structures, which can undermine social cohesion by limiting personal accountability and reducing the sense of collective responsibility. Effective governance balances communitarian principles with bureaucratic efficiency to enhance community solidarity and ensure accountable decision-making.
Efficiency and Accountability in Governance Structures
Communitarianism emphasizes efficiency by fostering collaborative decision-making rooted in shared values and social cohesion, which enhances community-driven accountability through active citizen participation. Bureaucratism prioritizes standardized procedures and hierarchical oversight to ensure consistent accountability, often resulting in slower decision-making but clearer responsibility channels. Balancing communitarian engagement with bureaucratic structure can optimize governance by combining responsive community input with reliable institutional controls.
Impact on Public Policy and Administration
Communitarianism emphasizes the role of community values and collective responsibility in shaping public policy, promoting social cohesion and participatory governance that aligns policies with local needs. Bureaucratism, by contrast, prioritizes hierarchical structures, standardized procedures, and efficiency, often leading to rigid implementation of policies that may overlook community-specific nuances. The impact on public administration highlights communitarianism's adaptive approach fostering inclusiveness, while bureaucratism ensures consistency and accountability through formal institutional frameworks.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Communitarianism faces challenges in balancing collective welfare with individual rights, often criticized for suppressing personal freedoms in favor of community norms. Bureaucratism encounters difficulties with excessive red tape, inefficiency, and lack of responsiveness, leading to public dissatisfaction and rigidity in policy implementation. Both approaches struggle with achieving effective governance while maintaining accountability and fostering social cohesion.
Future Prospects: Balancing Community and Bureaucracy
Future prospects in Communitarianism vs Bureaucratism hinge on achieving a balance where community values influence bureaucratic decision-making, ensuring policies reflect collective interests without sacrificing efficiency. Advances in digital governance and participatory platforms can empower communities to engage directly with bureaucratic processes, fostering transparency and responsiveness. Sustainable governance models will increasingly integrate communal insights with institutional frameworks to address complex social challenges effectively.
Communitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com