Patriarchy represents a social system where men hold primary power and dominate roles in political leadership, moral authority, social privilege, and control of property. This structure influences cultural norms, gender roles, and the distribution of resources, often leading to systemic inequalities for women and marginalized groups. Explore the rest of the article to understand how patriarchy shapes societies and what challenges it poses to achieving gender equality.
Table of Comparison
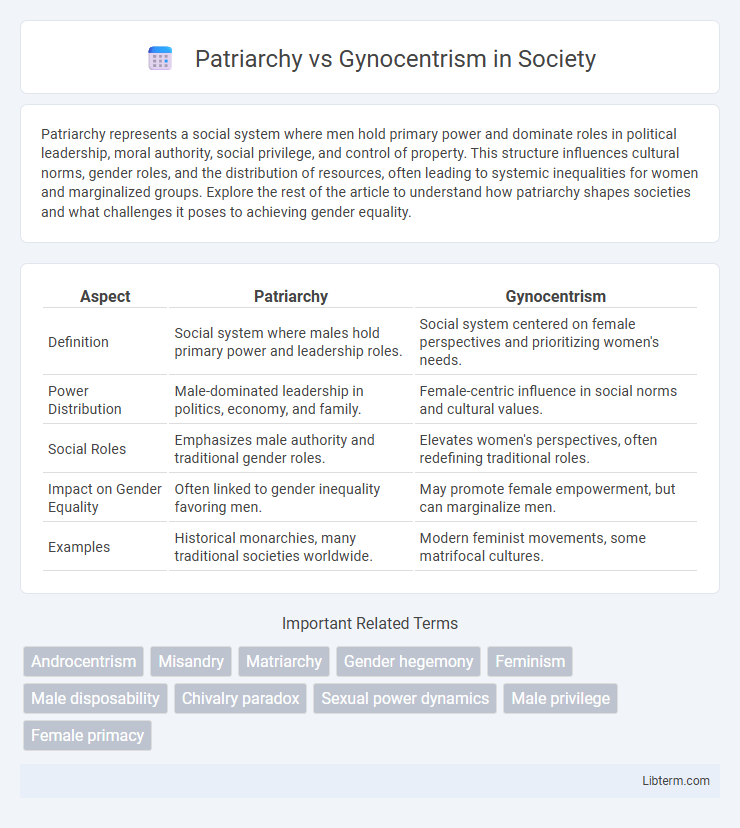
| Aspect | Patriarchy | Gynocentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social system where males hold primary power and leadership roles. | Social system centered on female perspectives and prioritizing women's needs. |
| Power Distribution | Male-dominated leadership in politics, economy, and family. | Female-centric influence in social norms and cultural values. |
| Social Roles | Emphasizes male authority and traditional gender roles. | Elevates women's perspectives, often redefining traditional roles. |
| Impact on Gender Equality | Often linked to gender inequality favoring men. | May promote female empowerment, but can marginalize men. |
| Examples | Historical monarchies, many traditional societies worldwide. | Modern feminist movements, some matrifocal cultures. |
Defining Patriarchy and Gynocentrism
Patriarchy is a social system in which men hold primary power and predominate in roles of political leadership, moral authority, social privilege, and control over property. Gynocentrism centers societal norms and values around women and female perspectives, often prioritizing women's needs and experiences in cultural and social dynamics. Understanding these concepts requires examining the power structures and cultural narratives that influence gender roles and social organization.
Historical Origins of Patriarchy
The historical origins of patriarchy trace back to ancient agrarian societies where male dominance emerged due to physical strength advantages and control over land and resources. Early legal codes and social structures institutionalized male authority, reinforcing gender hierarchies through inheritance, governance, and religious roles. This systemic male empowerment laid the foundation for patriarchal norms that persisted across civilizations, shaping the socio-political landscape for millennia.
Evolution of Gynocentrism in Society
Gynocentrism evolved from ancestral social structures emphasizing female roles in kinship, caregiving, and resource allocation, shaping societal norms and power dynamics. This evolution reflects a shift from traditional patriarchal dominance to cultures prioritizing female-centered values, influencing law, family organization, and social behavior. The ongoing interaction between patriarchy and gynocentrism highlights adaptive strategies in human social evolution and gender-based power distribution.
Core Principles: Patriarchy vs Gynocentrism
Patriarchy is a social system where men hold primary power and dominate roles of political leadership, moral authority, and control over property, emphasizing male authority and hierarchical gender roles. Gynocentrism centers on female perspectives and prioritizes women's needs and experiences, often valuing women's roles in society above men's. These core principles reflect contrasting frameworks of gender power dynamics, with patriarchy enforcing male dominance and gynocentrism highlighting female centrality in social structures.
Gender Roles and Social Expectations
Patriarchy enforces rigid gender roles by privileging male authority and valorizing traits like dominance and competitiveness, while often marginalizing feminine qualities and confining women to domestic responsibilities. Gynocentrism, conversely, centers women's experiences and values traits such as empathy and cooperation, potentially reshaping social expectations to prioritize caregiving and emotional labor. Both systems influence societal norms by defining power dynamics and prescribing distinct behavioral expectations for men and women.
Impact on Family and Relationships
Patriarchy structures prioritize male authority and decision-making, often leading to rigid gender roles and power imbalances that affect family dynamics and relationship satisfaction. Gynocentrism centers female experiences and perspectives, which can shift family priorities toward nurturing and emotional connectivity but may sometimes overlook equitable partner roles. Both systems influence communication patterns, conflict resolution, and the distribution of responsibilities, shaping the emotional wellbeing and stability of intimate relationships.
Representation in Culture and Media
Patriarchy dominates cultural and media representation by prioritizing male perspectives, often marginalizing female voices and reinforcing traditional gender roles. Gynocentrism in media challenges this by centering women's experiences, highlighting themes of empowerment and challenging stereotypes. The tension between these frameworks shapes narratives, character development, and audience perception, influencing societal norms and gender dynamics.
Contemporary Debates and Criticisms
Contemporary debates on patriarchy versus gynocentrism center on power dynamics and social structures shaping gender roles. Critics of patriarchy argue it upholds male dominance, perpetuating inequality and limiting women's opportunities, while gynocentrism is contested for prioritizing female perspectives potentially marginalizing men's experiences. Scholars emphasize the necessity of nuanced analysis recognizing diverse societal contexts to address intersecting issues of gender, power, and justice effectively.
Societal Consequences: Benefits and Challenges
Patriarchy often leads to structured social hierarchies that prioritize male authority, resulting in clearer leadership roles but potentially marginalizing women's voices and rights. Gynocentrism emphasizes female-centered perspectives, promoting gender equality and social welfare yet sometimes challenging traditional power dynamics and creating social friction. Both systems influence societal organization and resource allocation, shaping cultural norms, legal frameworks, and intergender relationships in complex ways.
Future Perspectives on Gender Dynamics
Future perspectives on gender dynamics indicate a complex interplay between patriarchy and gynocentrism, influenced by evolving social norms and technological advancements. Emerging gender theories and inclusive policies aim to balance power structures, promoting equity beyond traditional binary frameworks. Data from global gender studies suggest increasing acceptance of diverse identities will reshape societal roles, challenging entrenched patriarchal dominance while addressing criticism of gynocentric approaches.
Patriarchy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com