Social movements are organized efforts by groups of people aiming to promote or resist change in society through collective action and advocacy. They play a crucial role in shaping public policies, raising awareness, and driving cultural transformations across communities worldwide. Explore this article to understand how social movements impact Your world and inspire lasting change.
Table of Comparison
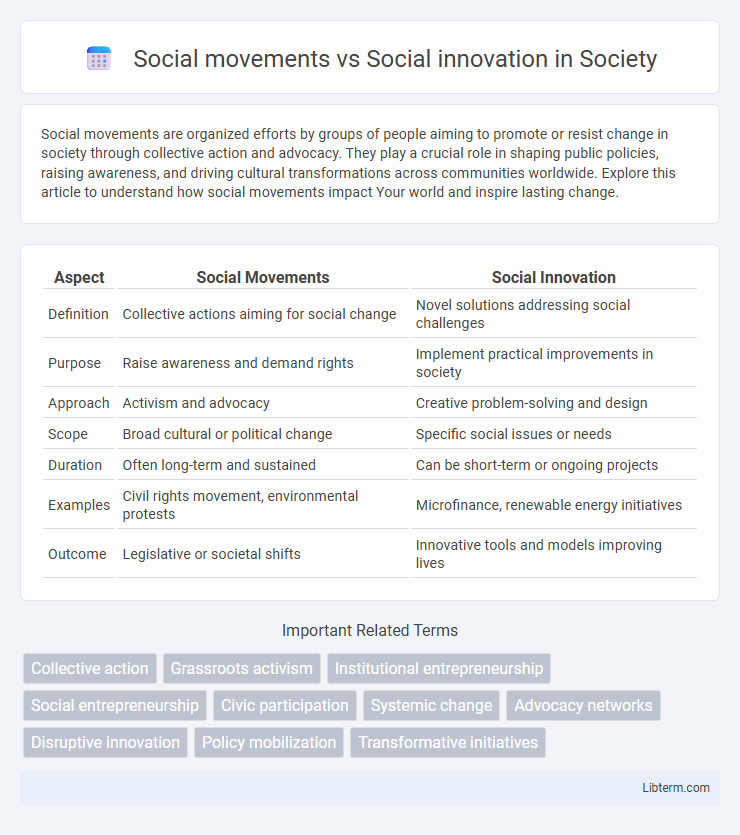
| Aspect | Social Movements | Social Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective actions aiming for social change | Novel solutions addressing social challenges |
| Purpose | Raise awareness and demand rights | Implement practical improvements in society |
| Approach | Activism and advocacy | Creative problem-solving and design |
| Scope | Broad cultural or political change | Specific social issues or needs |
| Duration | Often long-term and sustained | Can be short-term or ongoing projects |
| Examples | Civil rights movement, environmental protests | Microfinance, renewable energy initiatives |
| Outcome | Legislative or societal shifts | Innovative tools and models improving lives |
Understanding Social Movements: Definition and Characteristics
Social movements are organized collective efforts aiming to promote or resist social change, characterized by sustained campaigns, shared goals, and a sense of collective identity among participants. They typically emerge in response to perceived social injustices and employ tactics such as protests, advocacy, and public demonstrations to influence public opinion and policy. Understanding social movements involves analyzing their grassroots origins, organizational structure, and ability to mobilize resources and supporters over time.
What is Social Innovation? Key Concepts Explored
Social innovation refers to the development and implementation of novel solutions to social problems that are more effective, efficient, or sustainable than existing approaches. Key concepts include collaboration among diverse stakeholders, systemic change, and scalability to address issues such as poverty, education, and healthcare. Unlike social movements, which primarily focus on advocacy and collective action, social innovation emphasizes practical solutions with measurable social impact.
Historical Evolution: Social Movements and Social Innovation
Social movements have historically arisen as collective efforts to challenge social injustices, with key examples including the civil rights movement of the 1960s and the suffragette movement in the early 20th century. Social innovation evolved alongside these movements, emphasizing novel solutions to social problems, such as microfinance pioneered by Muhammad Yunus in the 1970s. The interplay between social movements and social innovation reflects a dynamic process where activism drives awareness and demand for innovative approaches to achieve systemic change.
Goals and Motivations: Comparative Analysis
Social movements primarily aim to achieve systemic social or political change by mobilizing collective action against perceived injustices, driven by motivations rooted in advocacy, equity, and social justice. In contrast, social innovation focuses on developing and implementing novel solutions to social problems, motivated by creativity, sustainability, and practical impact. Both approaches address societal challenges, but social movements emphasize advocacy and transformation, while social innovation prioritizes problem-solving and scalable solutions.
Methods and Strategies: How Change Happens
Social movements primarily utilize collective action, grassroots mobilization, and public demonstrations to pressure institutions and shift societal norms. Social innovation relies on developing novel solutions, such as new technologies, business models, or policy approaches, aimed at addressing systemic problems sustainably. Methods of social movements often emphasize awareness and activism, while social innovation focuses on iterative experimentation and scalable impact.
The Role of Technology in Driving Social Change
Technology accelerates social change by enabling social movements to rapidly mobilize support, disseminate information, and coordinate actions on a global scale. Social innovation leverages digital tools and platforms to design sustainable solutions addressing societal challenges, such as blockchain for transparent governance and AI for inclusive healthcare. The integration of emerging technologies transforms traditional activism and problem-solving, fostering more efficient and scalable impact in social change initiatives.
Impact Measurement: Evaluating Success in Social Efforts
Social movements measure impact through shifts in public awareness, policy changes, and sustained community engagement, reflecting large-scale societal transformation. Social innovation evaluates success by tangible outcomes such as improved social services, increased access to resources, and scalable solutions addressing specific social issues. Both approaches benefit from mixed-method impact measurement combining quantitative data and qualitative narratives to capture short-term effects and long-term systemic change.
Collaboration and Opposition: Stakeholders in Action
Social movements embody collective action driven by shared goals and grassroots collaboration among activists, communities, and NGOs, often challenging established systems and norms. Social innovation emerges through partnerships involving diverse stakeholders, including businesses, governments, and civil society, working together to develop and implement novel solutions to social problems. Collaboration in social innovation fosters synergy and resource sharing, while opposition in social movements can mobilize resistance and generate critical awareness, both influencing societal change through distinct but intersecting dynamics.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Movements and Innovations
Social movements like the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s catalyzed sweeping societal changes by mobilizing collective action and advocating for systemic reform, demonstrating the power of grassroots advocacy. In contrast, social innovations such as the introduction of microfinance pioneered by Grameen Bank transformed economic opportunities by providing financial services to underserved populations, illustrating practical solutions to social problems. Case studies reveal that while movements prioritize policy and cultural shifts, innovations focus on tangible tools and models, both driving progress in complementary ways.
Future Trends: The Intersection of Social Movements and Innovation
Future trends highlight the increasing convergence of social movements and social innovation, where grassroots activism drives technological and organizational breakthroughs aimed at addressing societal challenges. Digital platforms and data analytics empower communities to co-create solutions, accelerating impact and scalability in areas like climate action, equality, and public health. The fusion of ethical innovation with collective action fosters resilient ecosystems that anticipate and adapt to evolving social needs.
Social movements Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com