Obligatory tasks or actions are those required by law, rule, or duty, ensuring compliance and order in various aspects of life. Understanding these obligations helps you avoid penalties and maintain responsibilities effectively. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to identify and manage your obligatory duties efficiently.
Table of Comparison
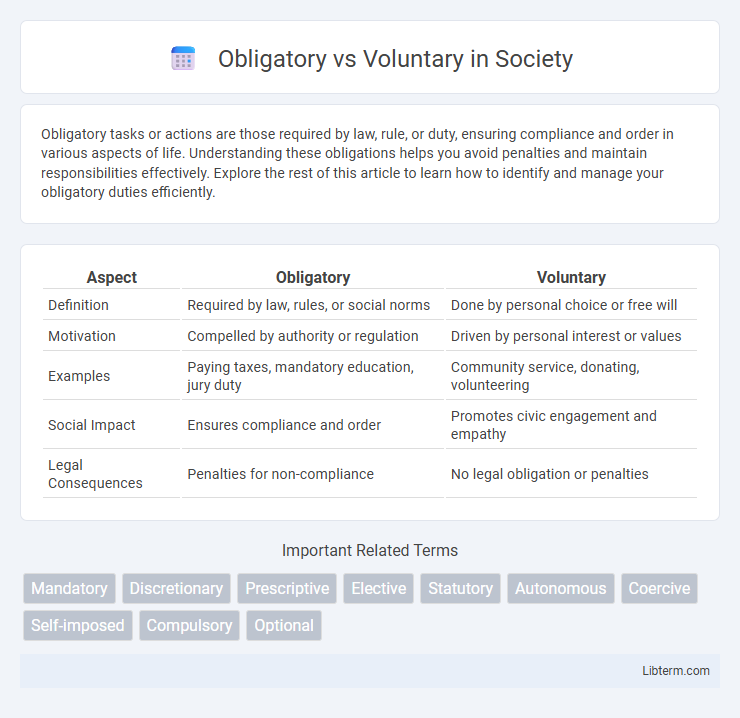
| Aspect | Obligatory | Voluntary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Required by law, rules, or social norms | Done by personal choice or free will |
| Motivation | Compelled by authority or regulation | Driven by personal interest or values |
| Examples | Paying taxes, mandatory education, jury duty | Community service, donating, volunteering |
| Social Impact | Ensures compliance and order | Promotes civic engagement and empathy |
| Legal Consequences | Penalties for non-compliance | No legal obligation or penalties |
Understanding Obligatory vs Voluntary Actions
Obligatory actions are duties or responsibilities mandated by laws, rules, or social norms, requiring compliance regardless of personal preference. Voluntary actions, in contrast, are performed by choice, reflecting personal willingness without external compulsion or mandatory enforcement. Understanding the distinction between obligatory and voluntary actions is essential for grasping concepts in ethics, law, and social behavior.
Key Definitions: Obligatory and Voluntary
Obligatory actions refer to duties or tasks that must be performed according to rules, laws, or moral requirements, ensuring compliance or adherence to set standards. Voluntary actions are those undertaken by choice, driven by personal willingness without any external compulsion or mandate. Understanding the distinction between obligatory and voluntary is essential for effective decision-making in legal, ethical, and organizational contexts.
Historical Perspectives on Obligation and Choice
Historical perspectives on obligation and choice reveal evolving societal norms where obligations were often tied to rigid social hierarchies and legal mandates, reflecting limited personal autonomy. In contrast, voluntary actions have gained emphasis in modern times, highlighting individual freedom and moral agency within democratic and human rights frameworks. Philosophers such as Immanuel Kant and John Stuart Mill have profoundly influenced this shift by exploring duty-based ethics and utilitarianism, framing obligation as both a social necessity and a personal choice.
Legal Context: Obligations vs Voluntary Compliance
Obligatory actions in a legal context refer to duties imposed by statutes, contracts, or regulations that require strict compliance, such as paying taxes or adhering to safety standards. Voluntary compliance occurs when individuals or entities choose to follow laws or guidelines without explicit enforcement, often motivated by ethical considerations or the desire to avoid penalties. The distinction between obligatory obligations and voluntary compliance significantly impacts legal accountability and the enforcement mechanisms employed by regulatory authorities.
Obligatory Actions in Workplaces and Organizations
Obligatory actions in workplaces and organizations refer to tasks and behaviors mandated by company policies, legal regulations, or professional standards, ensuring operational efficiency and compliance. These actions include punctual attendance, adherence to safety protocols, regular reporting, and confidentiality agreements, which maintain organizational integrity. Failure to perform obligatory duties often results in disciplinary measures, impacting both individual roles and overall organizational performance.
Voluntary Initiatives: Motivation and Impact
Voluntary initiatives are driven by organizational commitment to corporate social responsibility and sustainable practices, often motivated by enhancing brand reputation, stakeholder trust, and long-term risk management. These initiatives lead to measurable impacts such as improved environmental performance, community engagement, and innovation in sustainability practices without regulatory mandates. Their effectiveness relies on transparency, stakeholder collaboration, and integration into core business strategies to achieve meaningful social and environmental outcomes.
Psychological Factors Influencing Obligation and Voluntariness
Psychological factors influencing obligation and voluntariness include intrinsic motivation, perceived control, and social norms, which shape an individual's sense of duty versus free choice. Obligation often stems from external pressures and internalized expectations, creating a psychological need to comply despite personal preferences. Voluntariness arises when individuals experience autonomy and alignment with personal values, enhancing engagement and satisfaction in their actions.
Ethical Considerations: Duty vs Personal Choice
Obligatory actions are driven by ethical duties rooted in moral principles, requiring individuals to act in accordance with societal norms and professional responsibilities. Voluntary actions stem from personal choice, reflecting individual values and autonomy without external enforcement. Understanding the distinction between duty-based ethics and personal choice is crucial for navigating moral dilemmas and fostering ethical decision-making.
Consequences of Obligatory and Voluntary Behaviors
Obligatory behaviors often lead to predictable consequences such as compliance with established rules, social expectations, and legal requirements, which can ensure stability and accountability in various settings. Voluntary behaviors result in consequences influenced by personal choice, motivation, and intrinsic rewards, often fostering creativity, innovation, and personal growth. The contrast highlights how obligatory actions maintain order, while voluntary actions drive adaptability and individual fulfillment.
Striking the Balance: When Obligatory Meets Voluntary
Striking the balance between obligatory and voluntary actions enhances organizational efficiency by combining mandatory compliance with employee autonomy. Obligatory tasks ensure regulatory adherence and core responsibilities are met, while voluntary efforts foster innovation and engagement. Integrating both approaches creates a dynamic environment where structured accountability meets personal initiative, driving sustainable growth.
Obligatory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com