The private sector drives economic growth by fostering innovation, creating jobs, and enhancing competition across various industries. Businesses in this sector operate independently from government control, delivering goods and services that meet consumer demands efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to discover how the private sector impacts your daily life and the broader economy.
Table of Comparison
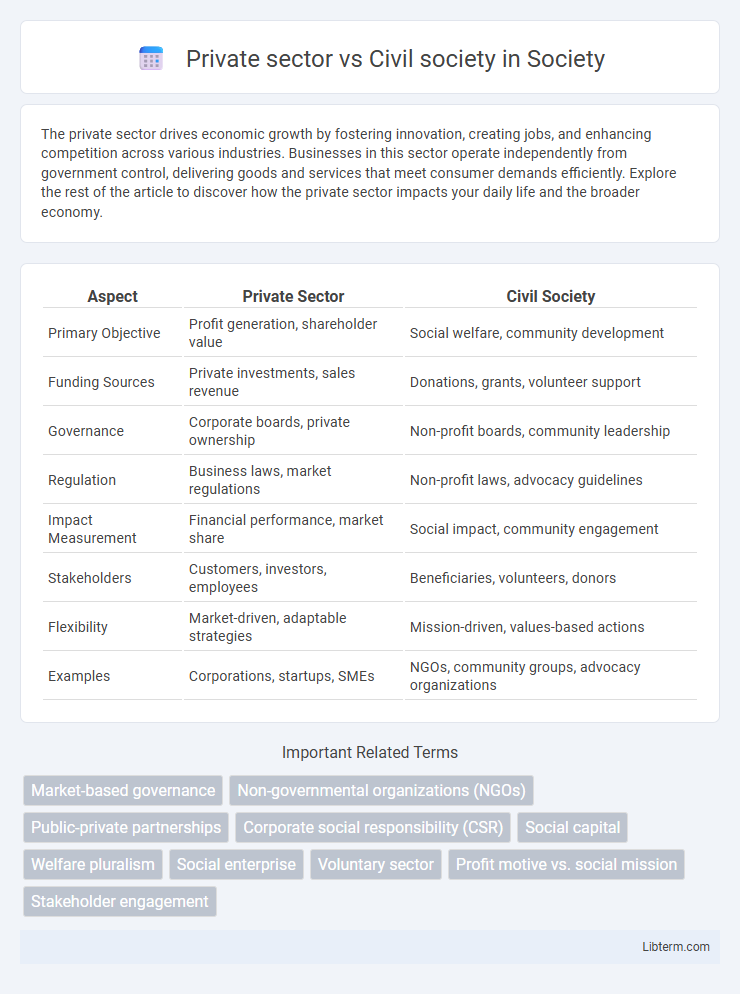
| Aspect | Private Sector | Civil Society |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Objective | Profit generation, shareholder value | Social welfare, community development |
| Funding Sources | Private investments, sales revenue | Donations, grants, volunteer support |
| Governance | Corporate boards, private ownership | Non-profit boards, community leadership |
| Regulation | Business laws, market regulations | Non-profit laws, advocacy guidelines |
| Impact Measurement | Financial performance, market share | Social impact, community engagement |
| Stakeholders | Customers, investors, employees | Beneficiaries, volunteers, donors |
| Flexibility | Market-driven, adaptable strategies | Mission-driven, values-based actions |
| Examples | Corporations, startups, SMEs | NGOs, community groups, advocacy organizations |
Overview of Private Sector and Civil Society
The private sector encompasses businesses and corporations driven by profit, including small enterprises, multinational companies, and startups that contribute significantly to economic growth and employment. Civil society consists of non-governmental organizations, advocacy groups, community organizations, and social movements focused on promoting social causes, human rights, and public interests independent of governmental and commercial influences. These two sectors operate distinctly but often intersect in areas such as corporate social responsibility, social innovation, and public policy advocacy.
Core Objectives and Missions
The private sector primarily focuses on profit maximization, market expansion, and shareholder value, driving economic growth through goods and services production. Civil society centers on social advocacy, community development, and promoting public interests, aiming to address societal challenges and foster social justice. Both sectors play complementary roles, with the private sector emphasizing financial performance and the civil society prioritizing collective well-being and policy influence.
Organizational Structures: Key Differences
Private sector organizations are typically structured around hierarchical models focused on profitability and efficiency, featuring clear lines of authority and decision-making processes to drive business goals. Civil society organizations often adopt more flexible, participatory structures emphasizing collaboration and grassroots involvement, reflecting their mission-driven focus on social impact rather than profit. These structural differences influence operational strategies, resource allocation, and stakeholder engagement within each sector.
Funding Sources and Financial Models
Private sector funding primarily relies on profit-driven models, including investments, sales revenue, and shareholder capital, enabling scalability and market competitiveness. Civil society organizations depend largely on donations, grants from governments and philanthropic foundations, and crowdfunding, reflecting mission-driven financial sustainability. While private entities pursue financial returns, civil society prioritizes social impact, influencing diverse financial structures and reporting standards.
Roles in Economic Development
The private sector drives economic development by fostering entrepreneurship, generating employment, and enabling capital investment that stimulates market growth and innovation. Civil society organizations complement this by promoting social equity, advocating for inclusive policies, and supporting community development programs that ensure sustainable and equitable economic progress. Together, these sectors create a balanced ecosystem that advances economic development while addressing social needs.
Social Impact and Community Engagement
The private sector drives social impact primarily through corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and sustainable business practices that integrate profit with purpose. Civil society organizations focus on community engagement by mobilizing volunteers, advocating for policy change, and addressing social issues at grassroots levels. Both sectors collaboratively enhance social outcomes by leveraging resources, expertise, and local knowledge to foster inclusive development.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration between the private sector and civil society drives innovation and sustainable development by leveraging corporate resources and community expertise. Strategic partnerships enhance social impact through shared goals, combining private sector efficiency with civil society's grassroots reach. These alliances foster trust, transparency, and scalable solutions addressing complex societal challenges.
Regulatory Frameworks and Governance
Private sector entities operate within regulatory frameworks designed to promote market efficiency, competition, and compliance with financial and labor laws, often overseen by government agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Civil society organizations function under governance structures that emphasize transparency, accountability, and advocacy, guided by nonprofit regulations and policies established by bodies like the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for tax-exempt status and the United Nations' principles on civil society participation. The interplay between private sector regulation and civil society governance shapes policy implementation, public accountability, and sustainable development outcomes by balancing economic growth with social responsibility.
Challenges and Opportunities
The private sector faces challenges such as market volatility and regulatory pressures while offering opportunities for innovation and economic growth. Civil society encounters obstacles including limited funding and political constraints but plays a crucial role in social advocacy and community empowerment. Collaboration between both sectors can enhance resource sharing and drive sustainable development outcomes.
Future Trends in Private Sector and Civil Society Interaction
Emerging trends in private sector and civil society interactions highlight increased collaboration through technology-driven platforms, enabling real-time data sharing and joint problem-solving initiatives. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is evolving into integrated sustainability strategies, where private companies engage civil society to co-create value and enhance social impact measurement. The rise of social enterprises and impact investment further blurs traditional boundaries, fostering partnerships that address global challenges such as climate change and social inequality more effectively.
Private sector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com