Exclusion refers to the deliberate or systemic process of preventing individuals or groups from participating in social, economic, or political activities. It often leads to inequality, marginalization, and limited access to essential resources and opportunities. Discover how exclusion impacts communities and ways you can help promote inclusion by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
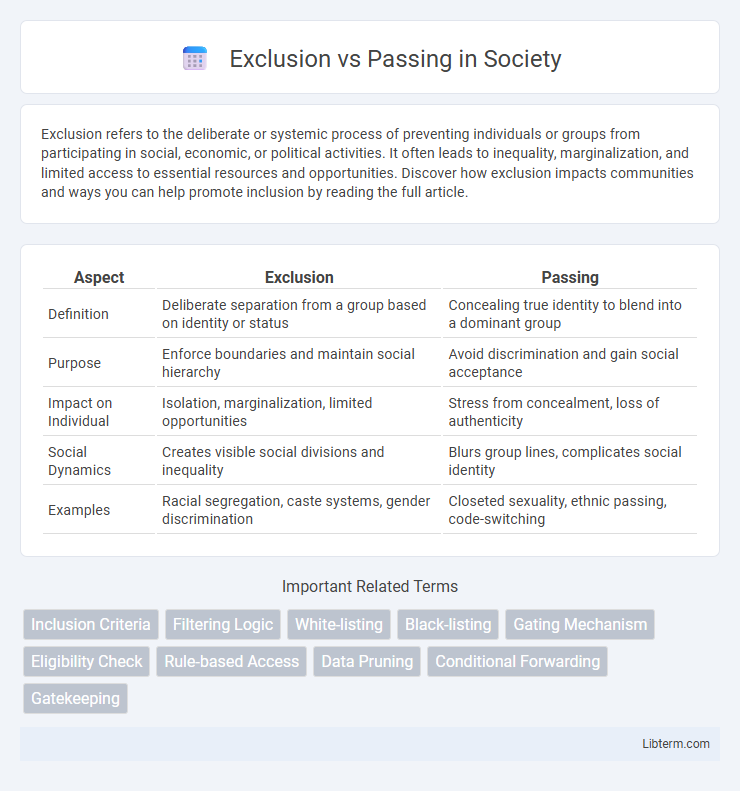
| Aspect | Exclusion | Passing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate separation from a group based on identity or status | Concealing true identity to blend into a dominant group |
| Purpose | Enforce boundaries and maintain social hierarchy | Avoid discrimination and gain social acceptance |
| Impact on Individual | Isolation, marginalization, limited opportunities | Stress from concealment, loss of authenticity |
| Social Dynamics | Creates visible social divisions and inequality | Blurs group lines, complicates social identity |
| Examples | Racial segregation, caste systems, gender discrimination | Closeted sexuality, ethnic passing, code-switching |
Introduction to Exclusion and Passing
Exclusion refers to the deliberate omission or restriction of certain data, groups, or variables from analysis or participation, often to enhance the accuracy or relevance of results. Passing involves allowing specific data or elements to proceed through a filter or criterion to be included in further processing or decision-making. Understanding the distinction between exclusion and passing is crucial for effective data management and unbiased interpretation in research and analytical contexts.
Defining Exclusion: Meaning and Implications
Defining exclusion involves recognizing the deliberate omission or rejection of individuals or groups from access to resources, opportunities, or social participation, often resulting in marginalization. Exclusion implies barriers that prevent equitable involvement in economic, political, or cultural domains, reinforcing inequality and limiting social mobility. Understanding exclusion's implications reveals its role in perpetuating disparities and hindering inclusive development across societies.
Understanding Passing: Concept and Context
Passing refers to the ability of an individual to be perceived as a member of a different social group, often to avoid discrimination or gain social acceptance. This concept is significant in contexts like race, gender, and class, where passing can affect identity and social dynamics. Understanding passing involves examining how societal norms and pressures shape personal experiences and the implications of navigating multiple identities.
Key Differences Between Exclusion and Passing
Exclusion involves denying individuals access or participation based on specific criteria, often leading to social or systemic isolation, while passing refers to the act of an individual presenting themselves as part of a different group to avoid discrimination or gain acceptance. Key differences lie in Exclusion being an external imposed barrier, whereas Passing is an internal strategy employed by individuals. Exclusion impacts group dynamics and access to resources, whereas Passing affects personal identity expression and social interactions.
Psychological Impact of Exclusion vs Passing
Exclusion triggers feelings of social rejection, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and decreased self-esteem, profoundly impacting mental health. Passing, or presenting oneself as part of a dominant group, often causes internal conflict, identity confusion, and emotional distress due to concealment of true self. Both exclusion and passing affect psychological well-being, but while exclusion directly harms through social isolation, passing creates chronic psychological strain from sustained identity suppression.
Social Dynamics: Exclusion vs Passing
Social dynamics of exclusion involve actively rejecting or isolating individuals from groups based on perceived differences, which often leads to social marginalization and identity challenges. Passing, in contrast, refers to individuals concealing or downplaying aspects of their identity to blend into a dominant group, thereby avoiding exclusion but risking internal conflict and loss of authenticity. Both exclusion and passing significantly impact social interactions, self-perception, and group cohesion within diverse communities.
Cultural Perspectives on Exclusion and Passing
Cultural perspectives on exclusion and passing reveal how marginalized groups navigate social boundaries by either embracing or concealing aspects of their identity to gain acceptance. Exclusion often stems from rigid societal norms that systematically marginalize certain ethnic, racial, or cultural identities, while passing involves strategically presenting oneself as part of a dominant group to avoid discrimination. This dynamic underscores complex social power structures and highlights the psychological and cultural costs associated with identity negotiation in multicultural societies.
Real-World Examples: Exclusion and Passing
Exclusion involves deliberately keeping individuals or groups out of certain social, economic, or political opportunities, as seen in historical examples like racial segregation in apartheid South Africa or caste-based discrimination in India. Passing refers to marginalized individuals presenting themselves as part of a dominant or privileged group to gain acceptance or avoid discrimination, exemplified by light-skinned African Americans passing as white during Jim Crow-era United States. These phenomena highlight complex societal dynamics where exclusion reinforces inequality, while passing complicates identity and belonging in real-world contexts.
Navigating Exclusion and Passing in Modern Society
Navigating exclusion and passing in modern society involves understanding the complex dynamics of identity concealment and social acceptance. Exclusion often stems from systemic biases and social prejudices, impacting marginalized groups' access to opportunities and resources. Passing, as a strategy, enables individuals to avoid discrimination but can lead to psychological stress and identity conflicts, highlighting the need for inclusive policies and supportive environments.
Strategies for Addressing Exclusion and Passing
Strategies for addressing exclusion and passing involve fostering inclusive environments through awareness campaigns and anti-discrimination policies that validate diverse identities. Implementing comprehensive education programs promotes understanding of marginalized experiences, reducing stigma and encouraging authentic self-expression. Support networks and mental health resources serve as crucial tools for individuals navigating exclusion or the pressures of passing, enhancing resilience and community connection.
Exclusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com