Social cohesion fosters a sense of belonging and trust within communities, enhancing cooperation and collective well-being. Strong social bonds contribute to economic stability, reduced crime rates, and improved mental health outcomes. Discover how strengthening social cohesion can transform Your community by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
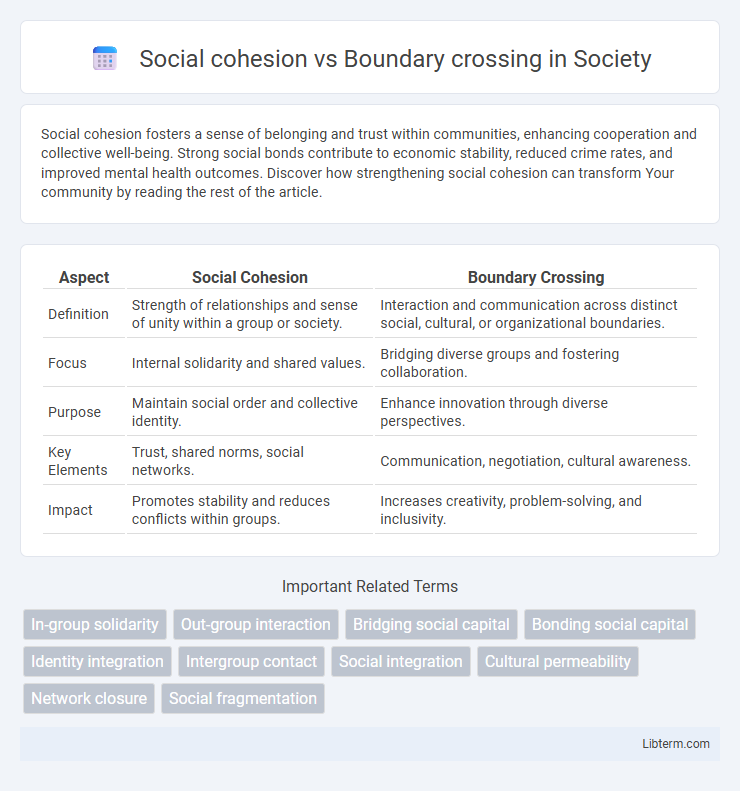
| Aspect | Social Cohesion | Boundary Crossing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strength of relationships and sense of unity within a group or society. | Interaction and communication across distinct social, cultural, or organizational boundaries. |
| Focus | Internal solidarity and shared values. | Bridging diverse groups and fostering collaboration. |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and collective identity. | Enhance innovation through diverse perspectives. |
| Key Elements | Trust, shared norms, social networks. | Communication, negotiation, cultural awareness. |
| Impact | Promotes stability and reduces conflicts within groups. | Increases creativity, problem-solving, and inclusivity. |
Understanding Social Cohesion: Definition and Importance
Social cohesion refers to the strength of relationships and the sense of solidarity among members of a community or society, fostering trust, cooperation, and shared values that contribute to social stability and collective well-being. Boundary crossing involves interactions that transcend social, cultural, or organizational divides, promoting inclusiveness and diverse perspectives but potentially challenging existing social cohesion. Understanding social cohesion is crucial for addressing social integration, reducing conflict, and enhancing community resilience by balancing unity with openness to boundary crossing.
What is Boundary Crossing in Social Contexts?
Boundary crossing in social contexts refers to the process where individuals or groups navigate and engage across different cultural, social, or organizational divides, facilitating understanding and collaboration. This concept contrasts with social cohesion, which emphasizes unity and shared identity within a group, while boundary crossing involves interaction that bridges diverse perspectives and practices. Effective boundary crossing promotes innovation, reduces conflict, and enhances integration in multicultural or interdisciplinary environments.
Historical Perspectives on Social Cohesion and Boundary Crossing
Historical perspectives reveal that social cohesion often emerged from shared values, collective identities, and common goals within homogeneous groups, reinforcing unity and stability. In contrast, boundary crossing involves interactions across diverse social, cultural, or ethnic lines, which historically challenged existing norms and promoted integration or conflict depending on context. Understanding these dynamics highlights how societies balance maintaining internal solidarity while adapting to external influences through cross-boundary engagements.
Key Drivers of Social Cohesion in Communities
Key drivers of social cohesion in communities include shared values, mutual trust, and inclusive participation that promote a sense of belonging and collective identity. Boundary crossing fosters social cohesion by encouraging interaction across diverse groups, reducing prejudices, and facilitating knowledge exchange. Effective communication, equitable resource distribution, and strong social networks are essential to strengthening these connections and sustaining cohesive communities.
Factors Facilitating Effective Boundary Crossing
Effective boundary crossing is facilitated by trust-building, open communication, and shared goals among diverse groups, enabling collaboration across social and organizational divides. Interpersonal empathy and cultural competence further enhance mutual understanding, allowing individuals to navigate and integrate differing perspectives. Organizational support, including inclusive policies and leadership commitment, strengthens ties and reduces resistance, fostering social cohesion through seamless boundary interactions.
Social Cohesion vs Boundary Crossing: Core Differences
Social cohesion emphasizes the unity and shared identity within a group, fostering trust, cooperation, and collective well-being. Boundary crossing involves navigating and bridging differences between distinct social groups, promoting interaction and mutual understanding across diverse communities. Core differences lie in social cohesion prioritizing internal solidarity, while boundary crossing focuses on external engagement and integration across social divides.
The Interdependence Between Cohesion and Boundary Crossing
Social cohesion strengthens group identity by fostering trust, shared norms, and mutual support, which facilitates smoother boundary crossing between diverse communities. Boundary crossing enhances social cohesion by promoting understanding, collaboration, and integration across different social, cultural, or organizational groups. The interdependence between cohesion and boundary crossing creates a dynamic cycle where increased interaction across boundaries reinforces collective identity and social stability.
Challenges in Balancing Social Cohesion and Boundary Crossing
Balancing social cohesion and boundary crossing presents challenges such as maintaining group identity while fostering inclusivity across diverse communities. Social cohesion demands shared values and trust, whereas boundary crossing requires openness to different perspectives and cultural practices, often leading to tensions in group norms. Managing these dynamics requires strategies that promote mutual understanding without eroding social solidarity.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Failures
Case studies on social cohesion reveal success stories where inclusive policies and community engagement fostered mutual trust and reduced social fragmentation. Boundary crossing initiatives succeeded by promoting intercultural dialogue and collaborative networks, enhancing social capital across diverse groups. Failures often stemmed from neglecting power imbalances or insufficiently addressing underlying prejudices, leading to weakened social ties and increased conflict.
Policy Implications and Strategies for Integration
Social cohesion policies emphasize fostering shared values and trust within communities to reduce social fragmentation, while boundary crossing strategies promote interactions across diverse groups to dismantle segregation and encourage mutual understanding. Effective integration requires combining inclusive policy frameworks that support equal access to resources, social participation, and anti-discrimination measures with programs that facilitate intercultural dialogue and collaborative activities across different social, ethnic, or cultural boundaries. Policymakers should prioritize multi-level governance approaches that synchronize efforts in education, housing, and employment sectors to enhance both social cohesion and boundary crossing, thereby fostering sustainable, inclusive societies.
Social cohesion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com