Social marginalization isolates individuals or groups from mainstream society, limiting their access to resources, opportunities, and social networks. This exclusion often leads to diminished well-being, economic hardship, and a lack of voice in community or political processes. Discover how social marginalization impacts communities and what can be done to foster inclusion in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
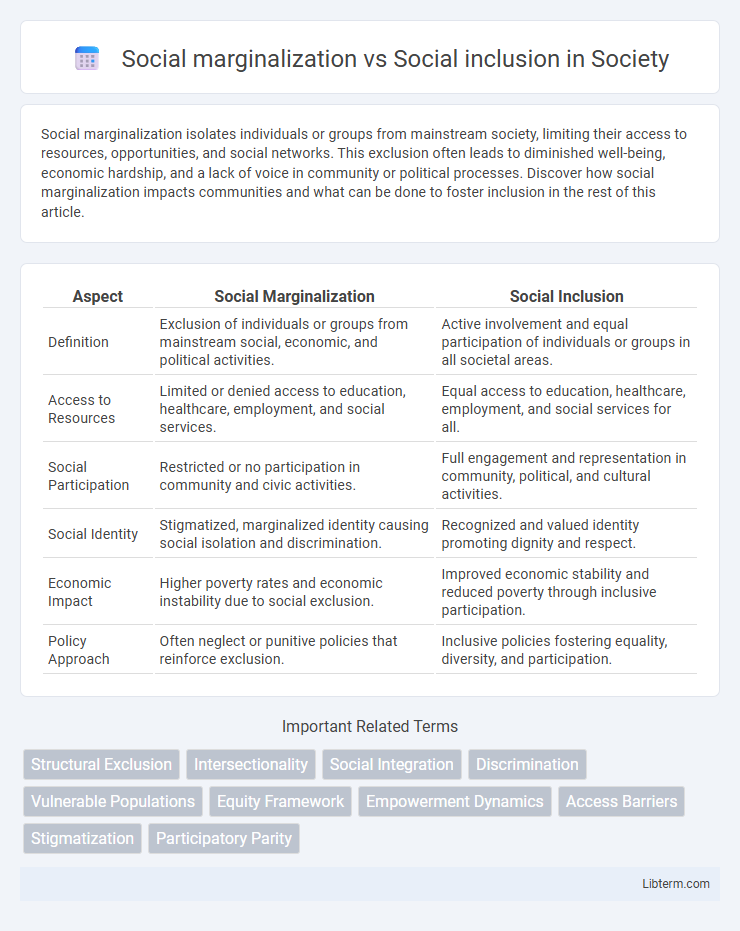
| Aspect | Social Marginalization | Social Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exclusion of individuals or groups from mainstream social, economic, and political activities. | Active involvement and equal participation of individuals or groups in all societal areas. |
| Access to Resources | Limited or denied access to education, healthcare, employment, and social services. | Equal access to education, healthcare, employment, and social services for all. |
| Social Participation | Restricted or no participation in community and civic activities. | Full engagement and representation in community, political, and cultural activities. |
| Social Identity | Stigmatized, marginalized identity causing social isolation and discrimination. | Recognized and valued identity promoting dignity and respect. |
| Economic Impact | Higher poverty rates and economic instability due to social exclusion. | Improved economic stability and reduced poverty through inclusive participation. |
| Policy Approach | Often neglect or punitive policies that reinforce exclusion. | Inclusive policies fostering equality, diversity, and participation. |
Understanding Social Marginalization
Social marginalization refers to the process by which individuals or groups are systematically excluded from full participation in social, economic, and political life, often due to factors like poverty, race, ethnicity, gender, or disability. This exclusion results in limited access to resources, opportunities, and rights, perpetuating inequality and social injustice. Understanding social marginalization requires examining structural barriers and power dynamics that contribute to the isolation and disenfranchisement of marginalized communities.
Defining Social Inclusion
Social inclusion refers to the process of improving the terms of participation in society, especially for disadvantaged groups, by enhancing opportunities, access to resources, and rights. It emphasizes equal access to education, employment, healthcare, and social services, thereby reducing barriers created by social marginalization. Effective social inclusion policies promote diversity, equity, and empowerment to foster a cohesive and participatory community.
Causes of Social Marginalization
Social marginalization arises from factors such as poverty, discrimination, limited access to education, and systemic inequalities that exclude individuals or groups from mainstream society. Causes include racial and ethnic biases, lack of social networks, and economic disparities that impede participation in social, political, and economic institutions. Addressing these root causes is essential to promoting social inclusion and equal opportunities for marginalized populations.
Impacts of Social Exclusion on Communities
Social exclusion diminishes community cohesion by limiting access to resources, employment, and social networks, which exacerbates poverty and inequality. Marginalized groups often experience reduced participation in decision-making processes, weakening social trust and increasing tensions. These impacts hinder economic growth and perpetuate cycles of disadvantage within affected communities.
Benefits of Social Inclusion
Social inclusion fosters community engagement by providing equal access to resources, education, and employment opportunities, which reduces poverty and social disparities. It enhances mental health and well-being by promoting a sense of belonging and reducing feelings of isolation among marginalized groups. Inclusive societies experience greater social cohesion and economic growth due to diverse perspectives and active participation from all members.
Barriers to Achieving Social Inclusion
Social marginalization creates systemic barriers such as discrimination, limited access to education, and economic inequality, which hinder individuals from fully participating in society. Social inclusion efforts aim to dismantle these obstacles by promoting equal opportunities, fostering community engagement, and ensuring accessible social services. Addressing barriers like stigma, lack of affordable housing, and inadequate healthcare is crucial for achieving comprehensive social inclusion.
Strategies for Reducing Social Marginalization
Strategies for reducing social marginalization include implementing inclusive education programs that provide equal access to learning opportunities for marginalized communities, promoting economic empowerment through job training and microfinance initiatives, and fostering community engagement by creating safe spaces for dialogue and participation. Policymakers can enhance social inclusion by enforcing anti-discrimination laws and facilitating social services that address mental health, housing, and healthcare disparities. Strengthening partnerships between government agencies, non-profits, and local leaders ensures sustainable support structures that bridge gaps in social capital and promote equity.
Case Studies: Marginalization vs Inclusion
Case studies on social marginalization versus social inclusion reveal significant disparities in access to resources, education, and community participation among marginalized groups such as ethnic minorities, refugees, and persons with disabilities. Research from urban areas in the United States and Europe highlights programs promoting social inclusion through targeted education, employment opportunities, and participatory governance that effectively reduce social exclusion. Evidence from these case studies demonstrates that inclusive policies result in improved socio-economic outcomes and enhanced social cohesion compared to communities experiencing persistent marginalization.
Policy Interventions for Social Inclusion
Policy interventions for social inclusion prioritize equitable access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities to counteract social marginalization. Targeted programs such as affirmative action, social protection schemes, and community development initiatives empower marginalized groups by reducing systemic barriers and promoting participation in economic and social life. Effective policies also incorporate data-driven approaches and stakeholder engagement to ensure inclusivity and sustainability in diverse social contexts.
Building a More Inclusive Society
Social inclusion fosters equitable access to resources, opportunities, and rights, directly counteracting the effects of social marginalization experienced by vulnerable groups. Building a more inclusive society requires implementing policies that promote diversity, reduce discrimination, and support community engagement across socioeconomic, racial, and cultural lines. Empowering marginalized populations through education, healthcare, and economic participation strengthens social cohesion and sustainable development.
Social marginalization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com