Autonomous action empowers individuals or systems to make decisions and execute tasks independently, enhancing efficiency and adaptability in dynamic environments. This capability is crucial in fields like robotics, artificial intelligence, and organizational management, where responsiveness and self-regulation drive success. Discover how autonomous action can transform your operations and enable smarter decision-making by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
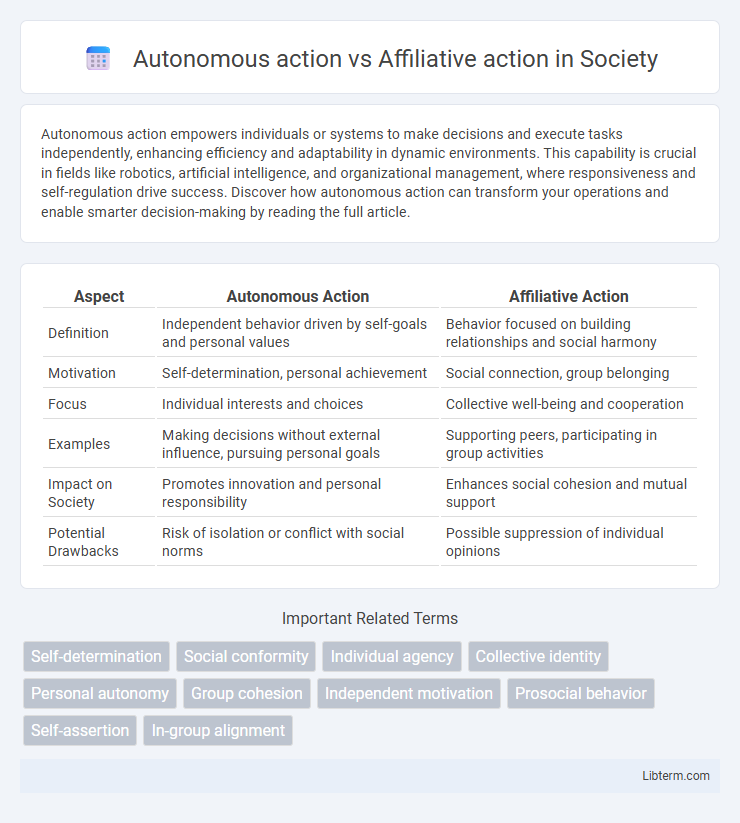
| Aspect | Autonomous Action | Affiliative Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Independent behavior driven by self-goals and personal values | Behavior focused on building relationships and social harmony |
| Motivation | Self-determination, personal achievement | Social connection, group belonging |
| Focus | Individual interests and choices | Collective well-being and cooperation |
| Examples | Making decisions without external influence, pursuing personal goals | Supporting peers, participating in group activities |
| Impact on Society | Promotes innovation and personal responsibility | Enhances social cohesion and mutual support |
| Potential Drawbacks | Risk of isolation or conflict with social norms | Possible suppression of individual opinions |
Understanding Autonomous Action
Autonomous action emphasizes individual decision-making based on personal values, beliefs, and goals, highlighting self-governance and independence. Understanding autonomous action involves recognizing the importance of self-direction and intrinsic motivation in shaping behavior without external influence or social conformity. This concept is crucial in psychological theories related to self-determination and personal agency, underscoring the role of autonomy in human development and ethical reasoning.
Defining Affiliative Action
Affiliative action involves behaviors aimed at building and maintaining positive social relationships, often emphasizing cooperation, empathy, and group harmony. It contrasts with autonomous action, which centers on independent decision-making and self-direction. Key characteristics of affiliative action include fostering trust, collaboration, and mutual support within social or organizational contexts.
Core Differences Between Autonomous and Affiliative Actions
Autonomous actions emphasize individual decision-making and self-direction, prioritizing personal goals and independence, while affiliative actions focus on building relationships and group harmony, valuing cooperation and social bonds. The core difference lies in the motivation behind the behavior: autonomy-driven behavior seeks self-expression and control, whereas affiliative behavior aims to maintain social connections and acceptance. Understanding these distinctions aids in analyzing human interactions and predicting behavioral outcomes in social and organizational contexts.
Psychological Foundations of Autonomy
Autonomous action reflects an individual's intrinsic motivation and self-determination, rooted in the psychological foundation of autonomy as the need to experience volition and agency. Affiliative action, by contrast, is driven by the desire for social connection and belonging, emphasizing relatedness within Self-Determination Theory. Psychological research highlights that autonomy support enhances well-being by fostering internal locus of control, whereas affiliative actions satisfy fundamental social needs crucial for mental health.
Social Dynamics in Affiliative Actions
Affiliative actions in social dynamics emphasize building and maintaining positive relationships through empathy, cooperation, and mutual support, fostering group cohesion and trust. These actions promote open communication, reduce conflict, and enhance collective problem-solving by prioritizing the needs and feelings of others. The effectiveness of affiliative behavior is crucial in teamwork, leadership, and community settings for creating harmonious and productive social environments.
Impact on Decision-Making
Autonomous action enhances decision-making by promoting individual creativity, accountability, and rapid problem-solving, leading to innovative and independent choices. Affiliative action influences decisions through collaboration, consensus-building, and relationship management, resulting in more harmonious and socially aligned outcomes. Balancing both approaches optimizes decision quality by integrating personal initiative with collective input.
Benefits and Challenges of Autonomy
Autonomous action fosters individual creativity and decision-making, enhancing personal accountability and motivation in professional settings. Benefits include increased innovation, flexibility, and faster problem-solving, while challenges involve potential isolation, inconsistent team alignment, and the risk of misjudgment without collaborative input. Balancing autonomy with clear communication and defined goals helps mitigate these challenges, promoting both personal growth and organizational coherence.
Importance of Affiliation in Group Settings
Affiliative action plays a crucial role in group settings by fostering trust, cooperation, and social cohesion among members, which enhances overall group performance. Unlike autonomous action, which emphasizes individual decision-making and independence, affiliative behavior promotes empathy, mutual support, and conflict resolution that sustain long-term collaboration. Studies show teams with strong affiliative bonds experience higher morale, reduced stress, and improved problem-solving capabilities, making affiliation essential for effective teamwork.
Balancing Autonomy and Affiliation
Balancing autonomy and affiliation involves integrating independent decision-making with meaningful social connections to enhance overall well-being and productivity. Autonomous action emphasizes self-governance and individual goals, while affiliative action prioritizes collaboration and relationship-building for group harmony. Effective balance requires adaptive strategies that respect personal freedom while fostering trust and cooperation within teams or social networks.
Practical Applications in Real-World Scenarios
Autonomous action emphasizes independent decision-making and initiative, crucial in fields such as entrepreneurship and emergency response where rapid, self-directed choices drive success. Affiliative action fosters collaboration and relationship-building, proving essential in team-based environments like healthcare and corporate management to enhance cohesion and collective problem-solving. Balancing autonomous and affiliative strategies optimizes productivity and adaptability in dynamic workplaces and complex social settings.
Autonomous action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com