Social structure defines the organized pattern of relationships and institutions that shape society, influencing individual roles and interactions. Understanding these frameworks helps you navigate cultural norms and power dynamics effectively. Explore the rest of the article to delve deeper into how social structures impact daily life and societal development.
Table of Comparison
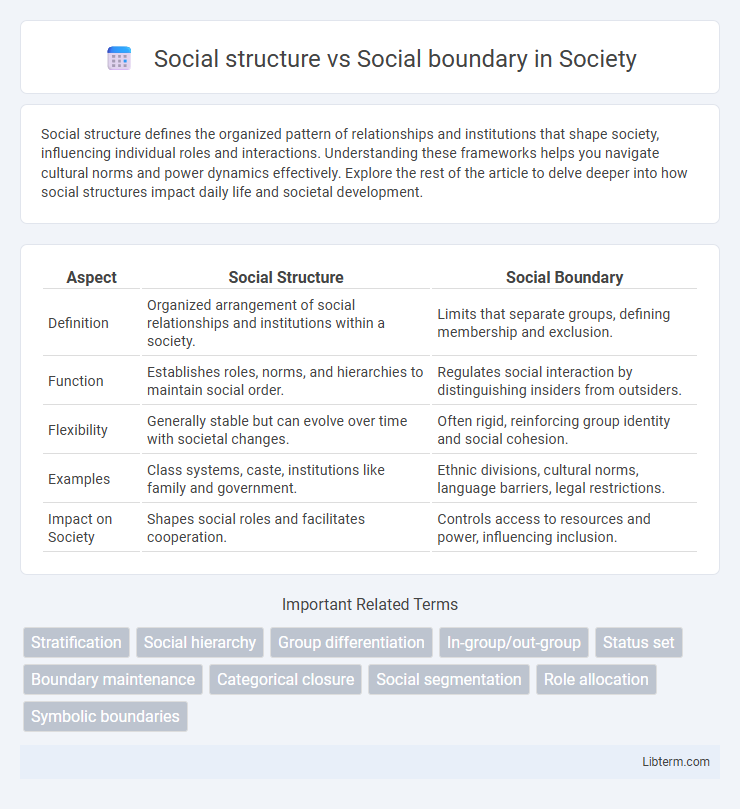
| Aspect | Social Structure | Social Boundary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized arrangement of social relationships and institutions within a society. | Limits that separate groups, defining membership and exclusion. |
| Function | Establishes roles, norms, and hierarchies to maintain social order. | Regulates social interaction by distinguishing insiders from outsiders. |
| Flexibility | Generally stable but can evolve over time with societal changes. | Often rigid, reinforcing group identity and social cohesion. |
| Examples | Class systems, caste, institutions like family and government. | Ethnic divisions, cultural norms, language barriers, legal restrictions. |
| Impact on Society | Shapes social roles and facilitates cooperation. | Controls access to resources and power, influencing inclusion. |
Understanding Social Structure: Foundations and Frameworks
Social structure refers to the organized pattern of social relationships and institutions that form the foundation of society, shaping individual behavior and social interaction. It includes key components such as social roles, norms, and hierarchies that provide stability and predictability within a community. Social boundaries, by contrast, define the distinctions and limits between groups, influencing social cohesion and identity within the broader structural framework.
Defining Social Boundaries: Meaning and Manifestations
Social boundaries define the limits that distinguish groups within a social structure by establishing who belongs and who does not based on criteria such as ethnicity, class, or occupation. These boundaries manifest through social norms, symbols, and practices that enforce inclusion or exclusion, shaping interactions and group identity. Understanding social boundaries is essential for analyzing how power, status, and inequality are maintained within complex social structures.
Key Differences Between Social Structure and Social Boundary
Social structure refers to the organized pattern of social relationships and social institutions that together compose society, providing a framework for behavior and interaction. Social boundary, in contrast, signifies the invisible or explicit lines that separate groups within society, often based on factors like class, ethnicity, or gender, restricting interaction between distinct groups. The key difference lies in social structure organizing society broadly through roles and institutions, while social boundaries specifically define and limit divisions between social groups.
The Role of Social Structure in Shaping Societies
Social structure, consisting of organized patterns of relationships and institutions, fundamentally shapes societies by defining roles, norms, and hierarchies that guide individual behavior and social interaction. These structures create predictable frameworks for social life, influencing access to resources, power distribution, and social mobility, thereby maintaining order and cohesion within communities. Social boundaries emerge from these structures, delineating group membership and identity, while reinforcing social stratification and cultural distinctions.
How Social Boundaries Influence Group Identity
Social boundaries shape group identity by defining clear distinctions between "insiders" and "outsiders," reinforcing a sense of belonging and shared values among members. These boundaries, whether based on ethnicity, religion, or socioeconomic status, influence social cohesion and collective behavior within groups. By creating limits on interaction and membership, social boundaries help maintain group solidarity and cultural continuity.
Interactions Between Social Structure and Social Boundary
Social structures define the organized patterns of relationships and roles within a society, while social boundaries establish the limits that separate different groups based on factors like class, ethnicity, or religion. Interactions between social structure and social boundary shape access to resources, influence social mobility, and impact group cohesion by reinforcing inclusion or exclusion mechanisms. These dynamics create a framework where power distribution and social norms are continually negotiated and maintained.
Social Stratification: Linking Structure and Boundaries
Social stratification organizes society into hierarchical layers based on factors like class, status, and power, creating structural divisions that influence social interactions. These layers establish social boundaries that restrict or enable access to resources, opportunities, and privileges within and between groups. Understanding the interplay between social structure and boundaries reveals how inequality is maintained and challenges to social mobility occur in complex social systems.
Impacts of Social Boundaries on Inclusion and Exclusion
Social boundaries define the limits of group membership, directly influencing patterns of inclusion and exclusion within social structures by determining who is accepted or marginalized in communities. These boundaries, shaped by factors such as ethnicity, class, and gender, impact access to resources, social mobility, and participation in institutional networks. The enforcement or permeability of social boundaries often leads to systemic inequalities, reinforcing social hierarchies and affecting social cohesion and integration.
Transformations in Social Structures and Shifting Boundaries
Transformations in social structures reflect changes in hierarchical roles, institutions, and group dynamics that alter power distribution and social mobility patterns. Shifting social boundaries redefine inclusion and exclusion criteria, impacting identity formation and community cohesion through evolving norms and cultural expectations. These processes are interlinked, as structural changes often drive boundary renegotiations, reshaping societal organization and individual interactions.
Implications for Modern Society: Navigating Structure and Boundaries
Social structure defines the organized patterns of relationships and institutions shaping societal roles, while social boundaries mark the divisions between different groups based on identity, status, or cultural norms. The interplay between social structure and boundaries impacts access to resources, social mobility, and inclusion in modern society, often reinforcing inequalities or enabling social cohesion. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing policies that promote equity and bridge divides in increasingly diverse and interconnected populations.
Social structure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com