Individualism emphasizes the importance of personal freedom, self-reliance, and independence in shaping one's identity and life choices. It encourages you to prioritize your unique values and aspirations over collective norms or societal expectations. Explore the article to understand how embracing individualism can transform your perspective and empower your decision-making.
Table of Comparison
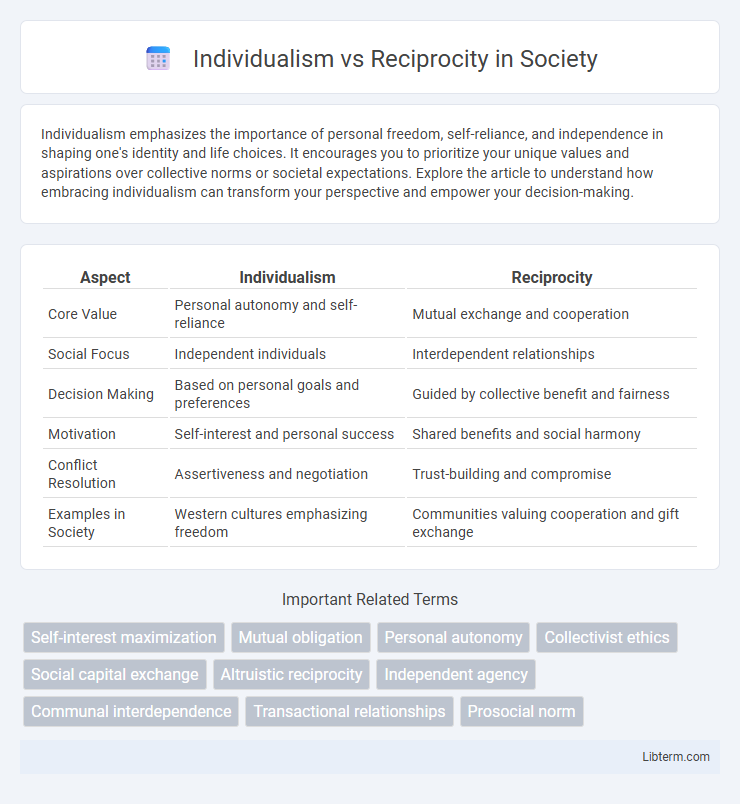
| Aspect | Individualism | Reciprocity |
|---|---|---|
| Core Value | Personal autonomy and self-reliance | Mutual exchange and cooperation |
| Social Focus | Independent individuals | Interdependent relationships |
| Decision Making | Based on personal goals and preferences | Guided by collective benefit and fairness |
| Motivation | Self-interest and personal success | Shared benefits and social harmony |
| Conflict Resolution | Assertiveness and negotiation | Trust-building and compromise |
| Examples in Society | Western cultures emphasizing freedom | Communities valuing cooperation and gift exchange |
Understanding Individualism: Core Principles
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the pursuit of individual goals as fundamental principles shaping behavior and decision-making. It values personal freedom, individual rights, and the importance of independent thought over collective conformity. Understanding individualism involves recognizing the priority given to personal achievements and responsibilities within social and cultural contexts.
The Essence of Reciprocity in Social Dynamics
Reciprocity in social dynamics embodies mutual exchange and trust, serving as a foundational mechanism for cooperation and social cohesion. Unlike individualism, which emphasizes personal autonomy and self-interest, reciprocity fosters interconnectedness by encouraging shared responsibilities and collective benefits. This reciprocal behavior enhances relational stability, enabling complex social networks and sustained community growth.
Historical Perspectives on Individualism and Reciprocity
Historical perspectives on individualism trace its roots to Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who emphasized personal liberty, autonomy, and the inherent rights of the individual. Reciprocity, deeply embedded in ancient and indigenous cultures, emphasizes mutual exchange and social obligations as foundational to community cohesion and moral conduct. Over time, Western societies have debated the balance between individualism's emphasis on personal freedom and reciprocity's focus on social responsibility, shaping modern political and ethical frameworks.
Cultural Impacts: East vs West
East Asian cultures emphasize reciprocity, fostering strong community ties and social harmony through mutual obligations and collective responsibilities. Western societies prioritize individualism, encouraging personal autonomy, self-expression, and independent decision-making. These cultural orientations influence social behaviors, communication styles, and conflict resolution approaches in their respective regions.
Psychological Foundations of Individual and Reciprocal Behavior
Psychological foundations of individualism emphasize autonomy, self-expression, and personal achievement, driven by intrinsic motivation and self-concept clarity. Reciprocity behaviors root in social exchange theory, highlighting mutual benefit, trust development, and norm internalization as key mechanisms fostering cooperation and social cohesion. Neuroscientific studies reveal distinct neural pathways, such as the prefrontal cortex's role in individual decision-making and the temporoparietal junction's involvement in reciprocal prosocial behavior.
Economic Systems: Competition vs Cooperation
Individualism in economic systems promotes competition, encouraging innovation and efficiency as businesses and individuals strive for personal gain and market dominance. Reciprocity emphasizes cooperation, fostering collaborative relationships and resource-sharing to achieve collective economic benefits and social stability. Balancing these approaches can optimize economic growth by integrating competitive incentives with cooperative frameworks.
Individual Rights vs Collective Responsibilities
Individualism emphasizes the protection of individual rights, prioritizing personal freedom, autonomy, and self-expression as foundational to a just society. Reciprocity highlights collective responsibilities, where mutual obligations and social cooperation promote community well-being and shared benefits. Balancing these perspectives ensures that personal liberties do not undermine societal cohesion, while collective duties respect individual freedoms.
Real-World Examples: Individualism and Reciprocity in Action
Individualism drives entrepreneurs like Elon Musk to innovate independently, prioritizing personal vision and success over collective gain. Reciprocity shapes community development programs in Scandinavian countries, where mutual support and trust foster social welfare and economic stability. Businesses that blend individualistic creativity with reciprocal collaboration, such as open-source tech communities, demonstrate combined benefits of personal initiative and cooperative exchange.
Navigating Conflicts: Balancing Self-Interest and Mutual Benefit
Navigating conflicts in individualism versus reciprocity requires balancing personal goals with the needs of others to achieve mutual benefit. Emphasizing open communication and empathy fosters understanding, reducing tensions between self-interest and collective welfare. Effective conflict resolution integrates assertiveness with cooperation, ensuring both individual rights and reciprocal relationships are maintained.
The Future: Integrating Individualism with Reciprocity
Integrating individualism with reciprocity in the future involves balancing personal autonomy with social cooperation to foster sustainable communities. Emphasizing mutual benefits while respecting individual rights can create adaptive systems that promote both innovation and collective well-being. Emerging technologies and social frameworks will play a crucial role in harmonizing these principles to address complex societal challenges.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com