Uncertainty avoidance reflects how cultures handle the unknown and ambiguity, influencing rules, routines, and risk tolerance in society and business. High uncertainty avoidance societies prefer structured environments and clear guidelines, while low uncertainty avoidance cultures embrace flexibility and innovation. Explore the full article to understand how this dimension impacts your personal and professional interactions.
Table of Comparison
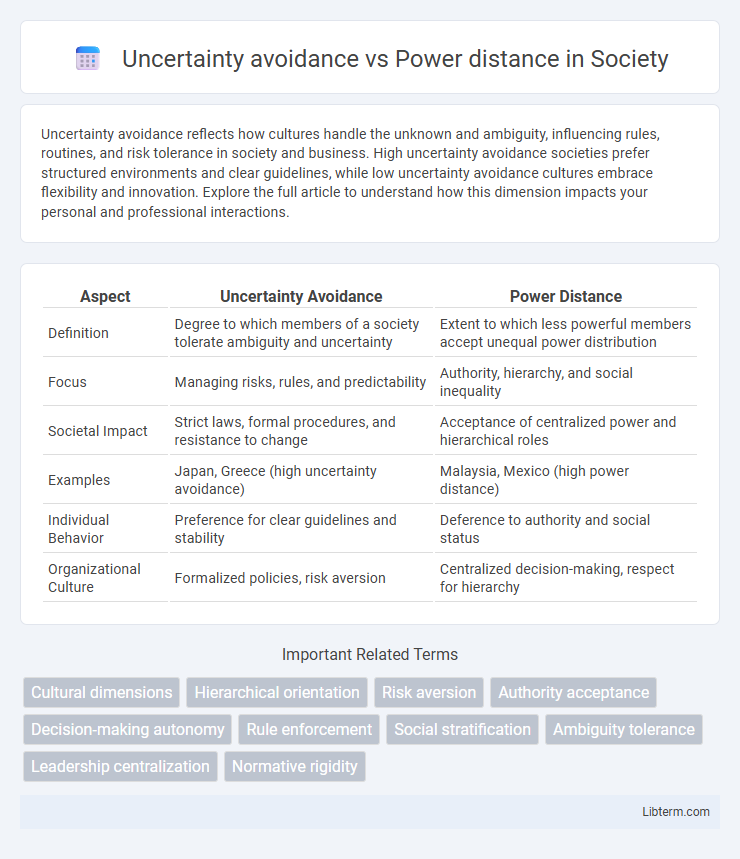
| Aspect | Uncertainty Avoidance | Power Distance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Degree to which members of a society tolerate ambiguity and uncertainty | Extent to which less powerful members accept unequal power distribution |
| Focus | Managing risks, rules, and predictability | Authority, hierarchy, and social inequality |
| Societal Impact | Strict laws, formal procedures, and resistance to change | Acceptance of centralized power and hierarchical roles |
| Examples | Japan, Greece (high uncertainty avoidance) | Malaysia, Mexico (high power distance) |
| Individual Behavior | Preference for clear guidelines and stability | Deference to authority and social status |
| Organizational Culture | Formalized policies, risk aversion | Centralized decision-making, respect for hierarchy |
Introduction to Uncertainty Avoidance and Power Distance
Uncertainty avoidance measures the extent to which individuals in a culture feel threatened by ambiguous situations and seek clarity through established rules and structures. Power distance reflects how a society handles inequalities among people, determining the acceptance of hierarchical order and centralized authority. Both dimensions significantly influence organizational behavior, communication styles, and decision-making processes in different cultural contexts.
Defining Uncertainty Avoidance: Key Concepts
Uncertainty avoidance measures a society's tolerance for ambiguity and unstructured situations, reflecting how members respond to unknown risks through rules, norms, and security measures. High uncertainty avoidance cultures emphasize strict codes of behavior, formalized procedures, and a desire for predictability to mitigate anxiety over unpredictable future events. This dimension contrasts with power distance, which assesses acceptance of hierarchical inequalities rather than modes of coping with uncertainty.
Understanding Power Distance: Core Principles
Power distance measures the extent to which less powerful members of organizations and institutions accept and expect unequal power distribution, highlighting hierarchical structures and authority dynamics. Core principles of power distance include the degree of autonomy granted to subordinates, communication openness, and the centralization of decision-making, which influence organizational culture and leadership styles. Cultures with high power distance often exhibit formal hierarchies and clear status distinctions, while those with low power distance promote egalitarian relations and participative management.
Cultural Dimensions: Hofstede’s Framework
Uncertainty Avoidance measures a society's tolerance for ambiguity and structured rules, influencing how cultures handle risk and change, while Power Distance assesses the acceptance of hierarchical inequalities and authority distribution within a society. Hofstede's framework highlights that cultures with high uncertainty avoidance prefer clear guidelines and stability, whereas high power distance cultures emphasize respect for centralized power and formal rank. Understanding these dimensions aids multinational organizations in navigating cultural preferences for decision-making, communication, and leadership styles.
Impact of Uncertainty Avoidance on Organizations
High uncertainty avoidance in organizations leads to strict rules, formal procedures, and risk-averse decision-making to minimize ambiguity and unpredictable outcomes. Employees in such cultures prefer clear guidelines and structured environments, which can slow innovation but increase stability and consistency. Power distance interacts with uncertainty avoidance by influencing the acceptance of hierarchical control; organizations with high power distance tend to reinforce authority to reduce uncertainty and maintain order.
Influence of Power Distance in Leadership Styles
High power distance cultures feature hierarchical leadership styles where authority is centralized, and subordinates expect clear directives from leaders. Leaders in low power distance societies often adopt participative or democratic approaches, encouraging collaboration and shared decision-making. The influence of power distance profoundly shapes organizational communication patterns, employee autonomy, and leadership effectiveness across different cultural contexts.
Comparing Uncertainty Avoidance and Power Distance
Uncertainty Avoidance measures a society's tolerance for ambiguity and risk, influencing how rules and structure are prioritized to minimize uncertainty. Power Distance reflects the acceptance of hierarchical order and unequal power distribution in organizations and society. Comparing these dimensions reveals that high Uncertainty Avoidance cultures emphasize predictability and procedures, while high Power Distance cultures accept centralized authority and unequal power as natural.
Implications for Cross-Cultural Communication
High uncertainty avoidance cultures prefer structured communication and clear rules, minimizing ambiguity in interactions, whereas low uncertainty avoidance cultures are more comfortable with flexibility and informal exchanges. Power distance affects hierarchical communication patterns, with high power distance cultures expecting deference to authority and formal protocol, contrasting with low power distance cultures favoring egalitarian dialogue and open feedback. Understanding these dimensions helps tailor communication strategies to reduce misunderstandings and enhance collaboration in multicultural environments.
Business Strategies and Cultural Differences
Uncertainty avoidance impacts business strategies by influencing risk tolerance, with high uncertainty avoidance cultures favoring structured planning and clear rules, while low uncertainty avoidance cultures adapt flexibly to change. Power distance affects organizational hierarchy and decision-making, where high power distance cultures expect centralized authority and top-down communication, contrasted with low power distance cultures that promote egalitarianism and participative management. Understanding these cultural dimensions helps multinational companies tailor leadership styles and operational approaches to enhance efficiency and cross-cultural collaboration.
Conclusion: Navigating Uncertainty Avoidance and Power Distance
Navigating uncertainty avoidance and power distance requires understanding how cultural attitudes towards risk and hierarchy impact decision-making and communication. High uncertainty avoidance cultures prefer structured environments and clear rules, while high power distance cultures emphasize respect for authority and centralized control. Balancing these dimensions encourages adaptive leadership styles that foster trust, innovation, and effective collaboration across diverse organizational settings.
Uncertainty avoidance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com