Critical consciousness involves recognizing and challenging social inequalities by developing an awareness of systemic injustices and power structures. It empowers individuals to question dominant narratives and engage in transformative actions that promote equity and social justice. Explore the article to discover how cultivating your critical consciousness can lead to meaningful change.
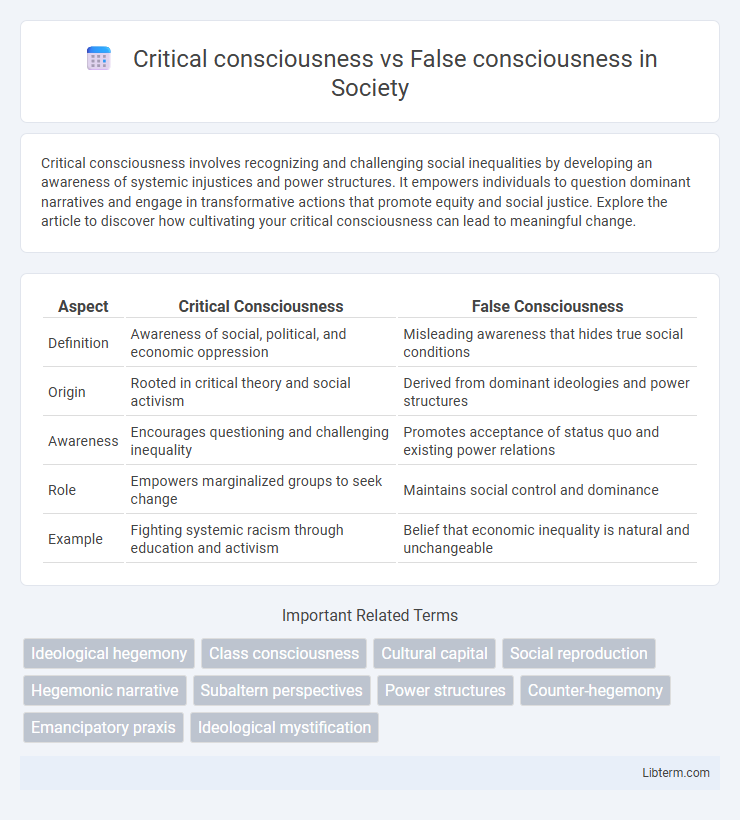
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Critical Consciousness | False Consciousness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Awareness of social, political, and economic oppression | Misleading awareness that hides true social conditions |
| Origin | Rooted in critical theory and social activism | Derived from dominant ideologies and power structures |
| Awareness | Encourages questioning and challenging inequality | Promotes acceptance of status quo and existing power relations |
| Role | Empowers marginalized groups to seek change | Maintains social control and dominance |
| Example | Fighting systemic racism through education and activism | Belief that economic inequality is natural and unchangeable |
Understanding Critical Consciousness
Critical consciousness involves the deep awareness of social, political, and economic oppressions, enabling individuals to recognize and challenge systemic inequalities. It contrasts with false consciousness, which obscures social realities by fostering acceptance of dominant ideologies that perpetuate marginalization. Developing critical consciousness promotes empowerment and fosters transformative action toward social justice and equity.
Defining False Consciousness
False consciousness refers to a distorted awareness where individuals or groups fail to recognize the true nature of their social or economic oppression, often internalizing dominant ideologies that perpetuate their subjugation. This concept highlights how people may misinterpret their social position, aligning with interests that work against their real welfare due to misleading beliefs shaped by ruling classes. Understanding false consciousness is crucial for analyzing power dynamics, as it contrasts with critical consciousness, which involves developing an accurate awareness of oppression and striving for social change.
Historical Origins of Both Concepts
Critical consciousness emerged from liberation theology and Paulo Freire's pedagogy in the 1970s, emphasizing awareness of social injustices and empowerment for transformative action. False consciousness, rooted in Marxist theory introduced by Karl Marx and later elaborated by Friedrich Engels, describes the misperception of social reality that prevents the proletariat from recognizing class exploitation. The historical origins of these concepts reflect contrasting understandings of societal awareness and the potential for revolutionary change.
Core Differences Between Critical and False Consciousness
Critical consciousness involves awareness of social, political, and economic contradictions, enabling individuals to recognize and challenge oppressive systems, whereas false consciousness refers to a distorted understanding that aligns with dominant ideology, obscuring true exploitation. The core difference lies in critical consciousness fostering empowerment and transformative action, while false consciousness perpetuates acceptance of inequality and hinders social change. Critical consciousness is grounded in reflexivity and critical analysis, contrasting with false consciousness's reliance on misinformation and ideological manipulation.
Role of Education in Shaping Consciousness
Education plays a pivotal role in shaping critical consciousness by encouraging individuals to recognize and challenge social inequalities and systemic oppression. Through critical pedagogy, learners develop the ability to analyze power structures and question dominant ideologies, contrasting with false consciousness where education perpetuates acceptance of the status quo and ideological manipulation. Empowering students with critical thinking skills and reflexivity fosters awareness and transformative action, essential for social change.
Impact on Social and Political Awareness
Critical consciousness empowers individuals to recognize and challenge systemic inequalities through heightened social and political awareness, fostering active participation in transformative movements. False consciousness obscures awareness by promoting distorted perceptions of reality, leading to acceptance of oppressive structures and limiting engagement in social change. The contrast significantly influences collective ability to address injustice and advocate for equitable policies.
Manifestations in Modern Society
Critical consciousness manifests in modern society through increased awareness of systemic inequalities, fostering proactive social movements and advocating for transformative justice. In contrast, false consciousness appears in widespread acceptance of dominant ideologies that obscure class struggles, perpetuating economic disparities and social complacency. Media narratives and consumer culture often reinforce false consciousness by distracting individuals from recognizing exploitative power structures.
Barriers to Achieving Critical Consciousness
Barriers to achieving critical consciousness include ideological manipulation, social conditioning, and lack of access to transformative education, which perpetuate false consciousness by obscuring systemic inequalities. Structural factors such as media control, cultural hegemony, and economic dependence reinforce dominant narratives that prevent individuals from recognizing oppressive forces. Overcoming these obstacles requires fostering critical pedagogy, inclusive dialogue, and empowerment strategies that challenge internalized oppression and promote social awareness.
Strategies to Overcome False Consciousness
Strategies to overcome false consciousness include promoting critical consciousness through education that encourages questioning social norms and power structures, fostering awareness of systemic inequalities. Empowerment initiatives such as community organizing and participatory decision-making help individuals recognize their collective interests against dominant ideology. Engaging in dialogues that challenge internalized oppression supports the development of a critical perspective, enabling resistance to manipulation and false beliefs.
The Importance of Consciousness in Social Change
Critical consciousness empowers individuals to recognize systemic inequalities and actively challenge oppressive structures, making it essential for meaningful social change. False consciousness obscures social realities by perpetuating dominant ideologies, hindering awareness and collective action. Consciousness shaped by accurate social understanding is crucial for mobilizing communities and fostering transformative movements.
Critical consciousness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com