A childless family often enjoys unique opportunities for personal growth, career advancement, and financial freedom that can be less accessible to families with children. These households may invest more in their relationships, hobbies, and community involvement, creating a fulfilling and balanced lifestyle. Discover how understanding the dynamics of childless families can enrich your perspective and lifestyle choices by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
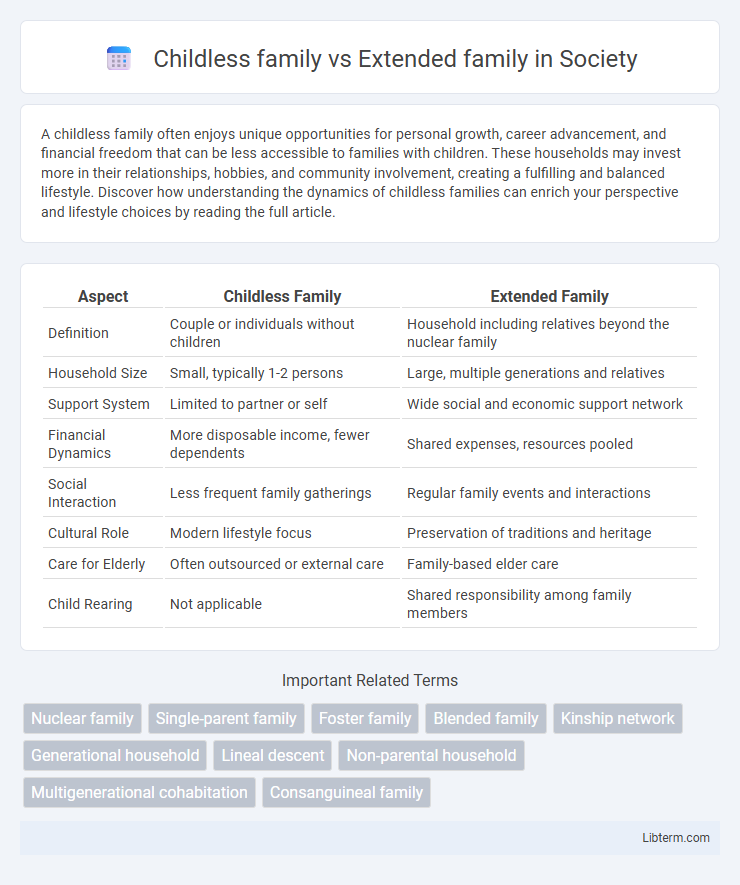
| Aspect | Childless Family | Extended Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Couple or individuals without children | Household including relatives beyond the nuclear family |
| Household Size | Small, typically 1-2 persons | Large, multiple generations and relatives |
| Support System | Limited to partner or self | Wide social and economic support network |
| Financial Dynamics | More disposable income, fewer dependents | Shared expenses, resources pooled |
| Social Interaction | Less frequent family gatherings | Regular family events and interactions |
| Cultural Role | Modern lifestyle focus | Preservation of traditions and heritage |
| Care for Elderly | Often outsourced or external care | Family-based elder care |
| Child Rearing | Not applicable | Shared responsibility among family members |
Definition of Childless Family
A childless family is defined as a household composed of two adults who do not have children, either by choice or due to circumstances. Unlike extended families, which include multiple generations or relatives living together or maintaining close ties, childless families center solely on the partnership between adults. This family structure is increasingly common in modern societies where personal lifestyle and career priorities influence family planning decisions.
Definition of Extended Family
An extended family includes multiple generations living together or maintaining close relationships, such as grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins alongside the nuclear family. This family structure contrasts with a childless family, which consists of a couple without children, focusing on the absence of offspring rather than the presence of multiple relatives. Extended families typically provide broader social support, resource sharing, and cultural continuity across generations.
Societal Perceptions and Cultural Norms
Childless families often face societal perceptions shaped by cultural norms that value procreation and traditional family structures, resulting in stigmatization or misunderstanding in many communities. Extended families reinforce collective identity and social support, aligning with cultural expectations in societies that prioritize kinship networks and multigenerational households. These differing perceptions influence social roles, community engagement, and acceptance within various cultural contexts.
Emotional Dynamics and Support Systems
Childless families often develop intense emotional bonds and rely heavily on partnerships for mutual support, fostering close-knit, intimate dynamics. Extended families provide broader support systems with multiple caregivers and sources of emotional assistance, but may experience complex interpersonal tensions due to diverse personalities and generational differences. Emotional dynamics in childless families center on dyadic connection and independence, while extended families emphasize collective responsibility and interdependence.
Economic Advantages and Challenges
Childless families often experience greater financial flexibility due to fewer dependents, allowing for increased savings and discretionary spending, whereas extended families may benefit from shared living expenses and pooled resources, reducing individual economic burdens. The economic challenges for childless families include potential long-term care costs without familial support, while extended families face complexities in balancing income disparities and resource allocation among multiple members. Both family types navigate distinct financial dynamics that influence their economic stability and opportunities.
Impact on Family Traditions and Heritage
Childless families often experience challenges in preserving family traditions and heritage due to the absence of direct descendants to pass customs and values onto future generations. Extended families, encompassing multiple generations and relatives, typically serve as vital conduits for maintaining cultural practices and familial legacies through shared experiences and collective memory. The presence of grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins in extended families strengthens intergenerational transmission of heritage, ensuring traditions are actively observed and celebrated.
Parenting and Role Distribution
Parenting in childless families often centers on nurturing adult relationships and personal growth, with role distribution focusing on career advancement and shared household responsibilities. In extended families, child-rearing typically involves multiple generations, allowing for a broader support system and diverse influences on the child's development. Role distribution in extended families is more fluid, often adapting to the needs of children, elders, and collective family goals.
Social Life and Community Engagement
Childless families often have more flexibility and time to engage in social activities and community events, fostering diverse networks beyond traditional family obligations. Extended families typically maintain stronger, multigenerational ties that provide built-in support systems and frequent communal interactions within the family unit. Social life in extended families revolves around shared responsibilities and cultural practices, enhancing community cohesion and collective participation.
Adaptability to Modern Lifestyles
Childless families often have greater flexibility to adapt to modern lifestyles due to fewer caregiving responsibilities and financial commitments, allowing for increased mobility and career focus. Extended families provide a built-in support network that can help balance work-life demands, offering shared childcare and household duties. Both family structures demonstrate unique adaptability by leveraging their inherent dynamics to meet contemporary social and economic challenges.
Future Trends in Family Structures
Future trends in family structures indicate a rise in childless families, driven by shifting societal values, economic considerations, and increased career focus among adults. Extended families are evolving but remain significant in multicultural societies where multigenerational living supports caregiving and economic stability. Demographic changes and urbanization trends influence how both family forms adapt, with extended families often providing social safety nets as childless households seek alternative support networks.
Childless family Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com