Welfare socialism emphasizes government intervention to provide social safety nets and reduce economic inequality through policies like universal healthcare, unemployment benefits, and public education. This approach aims to balance economic efficiency with social justice, ensuring that basic needs are met while promoting equal opportunities for all citizens. Explore the rest of the article to understand how welfare socialism impacts your community and economy.
Table of Comparison
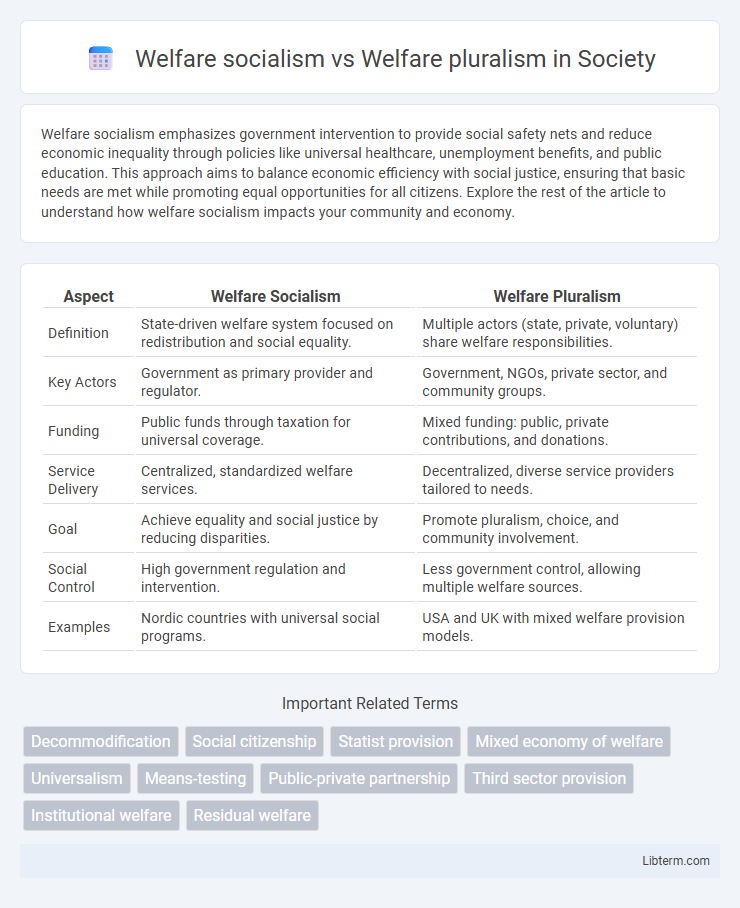
| Aspect | Welfare Socialism | Welfare Pluralism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-driven welfare system focused on redistribution and social equality. | Multiple actors (state, private, voluntary) share welfare responsibilities. |
| Key Actors | Government as primary provider and regulator. | Government, NGOs, private sector, and community groups. |
| Funding | Public funds through taxation for universal coverage. | Mixed funding: public, private contributions, and donations. |
| Service Delivery | Centralized, standardized welfare services. | Decentralized, diverse service providers tailored to needs. |
| Goal | Achieve equality and social justice by reducing disparities. | Promote pluralism, choice, and community involvement. |
| Social Control | High government regulation and intervention. | Less government control, allowing multiple welfare sources. |
| Examples | Nordic countries with universal social programs. | USA and UK with mixed welfare provision models. |
Defining Welfare Socialism and Welfare Pluralism
Welfare Socialism is defined by state-centric policies where government intervention ensures equitable distribution of resources and universal access to social services. Welfare Pluralism emphasizes multiple actors, including the state, private sector, and non-governmental organizations, sharing responsibility for welfare provision. This approach acknowledges a diversified and decentralized system aimed at meeting varied societal needs.
Historical Evolution of Welfare Models
Welfare socialism emerged in the early 20th century, characterized by state ownership and centralized control aimed at reducing social inequalities through extensive public welfare programs. Welfare pluralism evolved post-World War II, emphasizing a mix of state, private, and voluntary sector involvement to address social needs, reflecting a more decentralized approach. Key historical shifts include the post-war expansion of welfare states in Europe and the late 20th-century moves toward market-oriented reforms and diversification of welfare provision.
Core Principles of Welfare Socialism
Welfare socialism is grounded in the principle of state ownership and centralized redistribution of resources to ensure equality and social justice across all sectors. It emphasizes universal access to public services, collective responsibility, and the elimination of class-based disparities through government intervention. This model contrasts with welfare pluralism, which supports diverse providers and mixed funding to achieve social welfare goals.
Foundational Concepts in Welfare Pluralism
Welfare pluralism is grounded in the foundational concept that multiple actors, including state, market, voluntary, and informal sectors, collaboratively provide social welfare services to meet diverse societal needs. This contrasts with welfare socialism, where the state plays a central, dominant role in redistributing resources and ensuring welfare provision. Emphasizing decentralization, choice, and the coexistence of various providers, welfare pluralism promotes efficiency and responsiveness in social policy.
Government Role and Public Sector Influence
Welfare socialism features a strong government role, where the public sector directly manages and funds social services to ensure equitable distribution and reduce inequality. In contrast, welfare pluralism promotes a diversified approach, involving not only the state but also private organizations, voluntary associations, and market mechanisms in delivering welfare services. The public sector in welfare pluralism acts more as a regulator and facilitator, allowing multiple actors to contribute to social welfare provision while maintaining oversight.
The Function of Private and Voluntary Sectors
Welfare socialism emphasizes state control and provision of social services, limiting the role of private and voluntary sectors mainly to supporting functions under government regulation. Welfare pluralism prioritizes the significant contribution of private businesses, non-profit organizations, and voluntary groups in delivering diverse social services, promoting competition and choice in welfare provision. The private and voluntary sectors in welfare pluralism operate autonomously, filling gaps and complementing public services, while welfare socialism restricts their influence to ensure uniformity and state oversight.
Funding Mechanisms and Resource Allocation
Welfare socialism primarily relies on centralized funding mechanisms through progressive taxation and state-controlled resource allocation to ensure equitable distribution of social services. In contrast, welfare pluralism employs a diversified approach, combining public funding, private insurance, and voluntary contributions, allowing multiple actors to participate in resource allocation. This results in a more fragmented but flexible system where market forces and civil society influence the provision and financing of welfare services.
Social Equity and Access to Services
Welfare socialism prioritizes social equity by promoting universal access to services through state intervention and redistribution of resources to reduce inequalities. Welfare pluralism supports a mixed model where multiple sectors, including government, private entities, and non-profits, collaborate to provide diverse access to services, aiming to balance equity with efficiency. The contrasting approaches influence the degree of social equity, with welfare socialism emphasizing uniform access and welfare pluralism encouraging varied service provision tailored to different community needs.
Strengths and Criticisms of Each Approach
Welfare socialism emphasizes state control and extensive redistribution to achieve social equality, which strengthens social safety nets but may reduce individual incentives and economic efficiency. Welfare pluralism promotes a mix of public, private, and voluntary sectors, fostering innovation and tailored social services while risking fragmentation and unequal access. Critics of welfare socialism argue it can lead to bureaucratic inefficiencies, whereas welfare pluralism faces challenges in coordination and consistent policy implementation.
Future Trends in Welfare Policy Development
Welfare socialism emphasizes state-led universal welfare programs aimed at reducing inequality and ensuring comprehensive social protection, while welfare pluralism advocates for a mixed system incorporating state, market, and community actors to deliver services more efficiently. Future trends in welfare policy development indicate a shift towards integrated digital platforms enhancing accessibility and personalized support within pluralistic frameworks, alongside renewed debates on expanding universal basic income schemes popular in socialist welfare models. Policymakers increasingly focus on sustainability and adaptability of welfare systems to demographic changes and economic volatility, blending elements from both ideologies to address complex social needs.
Welfare socialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com