Masculinity encompasses traits and behaviors traditionally associated with men, including strength, assertiveness, and emotional resilience. Understanding the evolving definitions and cultural perceptions of masculinity is crucial for fostering healthier gender dynamics. Explore the rest of this article to discover how modern masculinity shapes identity and relationships.
Table of Comparison
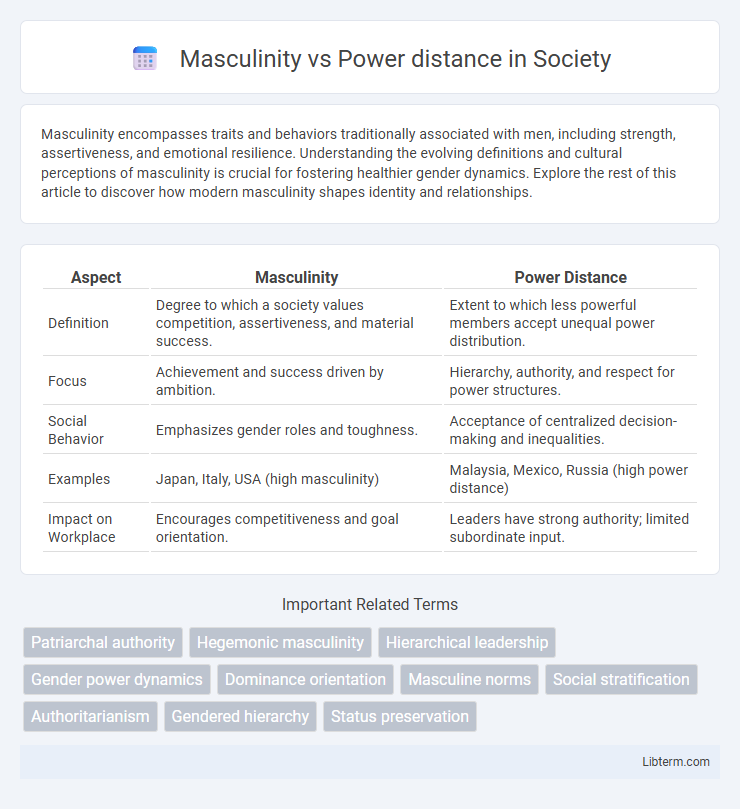
| Aspect | Masculinity | Power Distance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Degree to which a society values competition, assertiveness, and material success. | Extent to which less powerful members accept unequal power distribution. |
| Focus | Achievement and success driven by ambition. | Hierarchy, authority, and respect for power structures. |
| Social Behavior | Emphasizes gender roles and toughness. | Acceptance of centralized decision-making and inequalities. |
| Examples | Japan, Italy, USA (high masculinity) | Malaysia, Mexico, Russia (high power distance) |
| Impact on Workplace | Encourages competitiveness and goal orientation. | Leaders have strong authority; limited subordinate input. |
Understanding Masculinity in Cultural Contexts
Masculinity in cultural contexts reflects a society's emphasis on competitiveness, achievement, and assertiveness, correlating with Hofstede's cultural dimension of power distance where hierarchical structures influence gender roles and expectations. Cultures with high masculinity often promote traditional male dominance and distinct gender roles, which intersect with power distance by reinforcing authority and status differences within social and organizational settings. Understanding the interplay between masculinity and power distance is crucial for navigating cultural norms, communication styles, and leadership approaches in global interactions.
Defining Power Distance: Origins and Impact
Power distance, a cultural dimension developed by Geert Hofstede, measures the extent to which less powerful members of organizations accept unequal power distribution. It originates from societal norms and historical hierarchies, influencing workplace dynamics and decision-making processes. High power distance cultures typically exhibit centralized authority and clear hierarchical structures, affecting communication and leadership styles.
Masculinity and Power Distance: Key Differences
Masculinity in cultural dimensions emphasizes achievement, competitiveness, and assertiveness, while power distance measures acceptance of unequal power distribution in societies. High masculinity cultures prioritize success and ambition, whereas high power distance cultures accept hierarchical order and centralized authority. Understanding how masculinity interacts with power distance reveals variations in workplace dynamics, leadership styles, and decision-making processes across different countries.
How Masculine Values Shape Organizational Hierarchies
Masculine values emphasize assertiveness, competition, and achievement, which often lead to hierarchical organizational structures where authority and status are clearly defined and power is concentrated at the top. In cultures with high masculinity, leadership roles are typically associated with strength and decisiveness, reinforcing distinct power distances between managers and subordinates. This dynamic fosters environments where performance and success metrics drive decision-making processes and reward systems within the hierarchy.
The Role of Power Distance in Workplace Dynamics
High power distance cultures often exhibit hierarchical workplace structures where authority is rarely challenged, resulting in clear distinctions between managers and subordinates. This dynamic can influence communication patterns, with employees less likely to express dissent or innovate openly, impacting organizational agility. Understanding power distance helps managers tailor leadership styles to foster engagement and optimize team performance in diverse cultural contexts.
Interaction Between Masculinity and Power Distance
The interaction between masculinity and power distance shapes organizational culture and leadership styles, where high masculinity combined with high power distance often fosters competitive, hierarchical environments prioritizing assertiveness and control. In contrast, cultures with low masculinity and low power distance encourage collaborative decision-making and emphasize equality and relational harmony. Understanding this dynamic is essential for multinational companies to tailor management approaches that align with local cultural dimensions, enhancing employee motivation and organizational effectiveness.
Case Studies: Masculinity vs Power Distance in Global Cultures
Case studies on Masculinity vs Power Distance reveal distinct cultural dynamics influencing organizational behavior and leadership styles globally. For instance, Japan exhibits high Masculinity with moderate Power Distance, fostering competitive yet hierarchical workplaces, whereas Scandinavian countries show low Masculinity and low Power Distance, promoting egalitarian and collaborative environments. Analyzing these contrasts aids multinational corporations in tailoring management strategies to enhance cultural compatibility and operational efficiency.
Leadership Styles: Influences of Masculinity and Power Distance
Masculinity and power distance significantly shape leadership styles by influencing decision-making and authority dynamics within organizations. High masculinity cultures prioritize assertiveness and competitiveness, promoting transformational and transactional leadership approaches. Cultures with high power distance emphasize hierarchical structures and centralized authority, fostering authoritarian and paternalistic leadership styles that maintain clear power differentials.
Reducing Conflict: Balancing Masculinity and Power Distance
Reducing conflict in organizations requires balancing masculinity, which values competitiveness and achievement, with power distance, the acceptance of hierarchical authority. High masculinity cultures emphasize assertiveness, potentially escalating disputes, while high power distance may suppress open communication, hindering conflict resolution. Effective conflict management involves fostering open dialogue and promoting equity to temper aggressive tendencies and reduce dominance-related tensions.
Future Trends: Evolving Views on Masculinity and Authority
Future trends in masculinity and power distance reveal a shift towards more inclusive and flexible leadership models that challenge traditional gender norms and hierarchical structures. Emerging research highlights a growing acceptance of emotional intelligence, collaboration, and vulnerability as key traits in effective authority figures across cultures with varying power distance levels. Organizations are increasingly adopting policies that promote gender equality and flatten power hierarchies, reflecting evolving societal values that redefine masculinity and authority in contemporary workplaces.
Masculinity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com