Cultural pluralism celebrates the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, encouraging mutual respect and understanding. It promotes the idea that different cultural identities can thrive together while contributing to the social fabric. Explore the rest of the article to discover how cultural pluralism shapes your community and enriches social interactions.
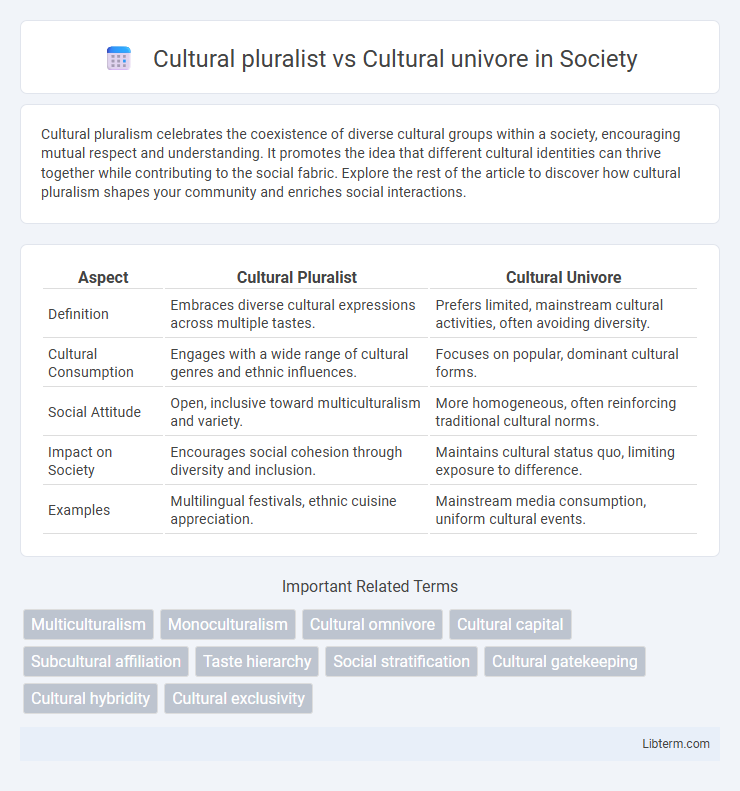
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Pluralist | Cultural Univore |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Embraces diverse cultural expressions across multiple tastes. | Prefers limited, mainstream cultural activities, often avoiding diversity. |
| Cultural Consumption | Engages with a wide range of cultural genres and ethnic influences. | Focuses on popular, dominant cultural forms. |
| Social Attitude | Open, inclusive toward multiculturalism and variety. | More homogeneous, often reinforcing traditional cultural norms. |
| Impact on Society | Encourages social cohesion through diversity and inclusion. | Maintains cultural status quo, limiting exposure to difference. |
| Examples | Multilingual festivals, ethnic cuisine appreciation. | Mainstream media consumption, uniform cultural events. |
Understanding Cultural Pluralism
Cultural pluralism emphasizes the coexistence and mutual respect of diverse cultural groups within a society, promoting inclusivity and acceptance of multiple identities. In contrast, cultural univores tend to engage predominantly with mainstream or dominant cultural expressions, often limiting exposure to diverse cultural experiences. Understanding cultural pluralism involves recognizing the value of cultural diversity as a dynamic and enriching force that enhances social cohesion and fosters intercultural dialogue.
Defining the Cultural Univore
The cultural univore consumes a diverse range of cultural products across multiple genres and mediums, reflecting a broad and eclectic taste. Unlike cultural pluralists who embrace cultural diversity through varied cultural participation, univores specifically demonstrate their cultural engagement by consuming widely accepted mainstream and non-mainstream forms. Their behavior indicates a deep immersion in culture without restricting preferences to highbrow or lowbrow categories, often associated with greater social capital and cultural competence.
Key Differences Between Pluralists and Univores
Cultural pluralists engage with diverse cultural experiences and actively seek out a wide range of artistic expressions across multiple genres and traditions, fostering inclusivity and cultural exchange. Univores prefer a narrow selection of cultural content, often gravitating towards mainstream or familiar genres, resulting in limited cultural exposure and less diversity in their consumption patterns. The key difference lies in pluralists' openness to cultural variety and adaptability versus univores' tendency toward cultural homogeneity and consistent preference for similar cultural products.
Historical Origins of Both Concepts
The concept of cultural pluralism originated in early 20th-century sociology and political theory, emphasizing the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, prominently influenced by the works of Horace Kallen and the pluralist traditions in the United States. In contrast, the cultural univore concept emerged from consumer behavior research in the late 20th century, highlighting individuals who consume a wide range of cultural products without a strong preference, a term popularized through studies by scholars like D. W. Peterson and M. Simkus. Both frameworks reflect societal responses to cultural diversity, with pluralism focusing on group identity preservation and univorism on individual eclecticism in cultural consumption.
Cultural Consumption Patterns
Cultural pluralists exhibit diverse cultural consumption patterns by engaging with a broad range of genres, arts, and traditions, reflecting inclusivity and openness to multiple cultural influences. In contrast, cultural univores tend to have narrower consumption habits, favoring limited, mainstream cultural forms that align with a dominant cultural narrative or identity. These differing patterns influence how individuals relate to cultural capital, social identity, and community belonging.
Social Implications of Pluralism vs Univorism
Cultural pluralism supports diverse cultural identities within a society, fostering social cohesion and mutual respect by encouraging inclusion and intercultural dialogue. Univorism, favoring homogeneous cultural consumption, often leads to social fragmentation and reinforces echo chambers that limit exposure to diverse perspectives. The social implications of pluralism promote equitable participation and reduce prejudice, while univore tendencies can exacerbate polarization and hinder societal integration.
Media and Entertainment Preferences
Cultural pluralists engage with diverse media and entertainment genres, reflecting openness to multiple cultural narratives and global content. Cultural univores prefer limited, mainstream media offerings, often favoring dominant cultural productions and genres aligned with their social identity. These preferences shape consumption patterns and influence cultural representation in entertainment industries.
Impact on Identity Formation
Cultural pluralists embrace diverse cultural influences, fostering multifaceted identity formation by integrating multiple heritages and perspectives, which enhances social cohesion and personal adaptability. Cultural univores consume a limited range of cultural inputs, resulting in more homogenized identities that may lack exposure to differing viewpoints, potentially restricting personal growth and cross-cultural understanding. The contrast in cultural consumption patterns directly impacts how individuals construct their self-concept, social affiliations, and worldview in multicultural societies.
Cultural Openness and Exclusivity
Cultural pluralists demonstrate high cultural openness by actively engaging with and appreciating diverse cultural expressions, promoting inclusivity and mutual respect across different communities. In contrast, cultural univores exhibit cultural exclusivity by limiting their consumption to a narrow range of culturally dominant or mainstream activities, often reinforcing social boundaries and reducing intercultural exchange. This distinction highlights how cultural openness fosters diversity and social cohesion, whereas exclusivity can perpetuate cultural homogeneity and social segregation.
The Future of Cultural Engagement
Cultural pluralists actively seek diverse cultural experiences, embracing a wide range of traditions, languages, and artistic expressions, which fosters inclusivity and deeper intercultural understanding. Cultural univores, by contrast, consume cultural products from a limited spectrum, often favoring mainstream or homogeneous content, which may inhibit exposure to new perspectives and reduce cultural empathy. The future of cultural engagement favors pluralism as global connectivity and digital platforms enable unprecedented access to diverse cultures, encouraging more inclusive participation and richer intercultural dialogue.
Cultural pluralist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com