Suburban areas offer a unique blend of residential comfort and proximity to urban amenities, making them ideal for families and professionals seeking balance. These neighborhoods often feature spacious homes, green spaces, and community-oriented facilities that enhance quality of life. Explore the rest of the article to discover how suburban living can transform your lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
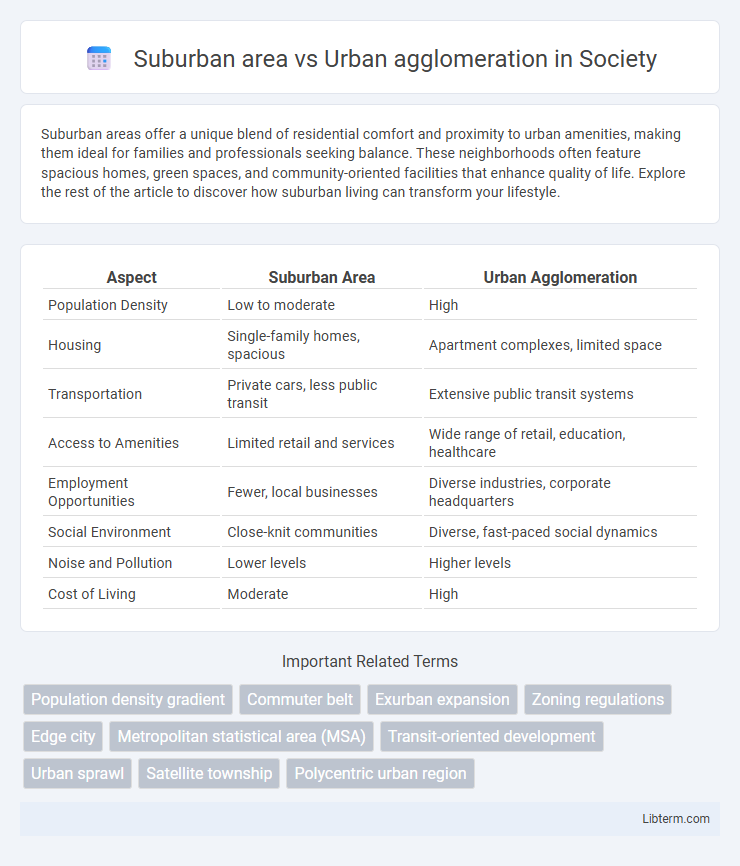
| Aspect | Suburban Area | Urban Agglomeration |
|---|---|---|
| Population Density | Low to moderate | High |
| Housing | Single-family homes, spacious | Apartment complexes, limited space |
| Transportation | Private cars, less public transit | Extensive public transit systems |
| Access to Amenities | Limited retail and services | Wide range of retail, education, healthcare |
| Employment Opportunities | Fewer, local businesses | Diverse industries, corporate headquarters |
| Social Environment | Close-knit communities | Diverse, fast-paced social dynamics |
| Noise and Pollution | Lower levels | Higher levels |
| Cost of Living | Moderate | High |
Definition of Suburban Areas and Urban Agglomerations
Suburban areas are residential zones located on the outskirts of a central city, characterized by lower population density, single-family homes, and a reliance on automobiles for commuting. Urban agglomerations encompass a central city and its surrounding suburbs and towns, forming a contiguous metropolitan region with high population density and extensive economic and social integration. Definitions emphasize that suburban areas serve primarily as residential or commuter zones, while urban agglomerations function as complex spatial entities combining multiple administrative units into a single urbanized region.
Population Density: Suburbs vs Urban Centers
Suburban areas typically exhibit lower population density compared to urban agglomerations, with suburban densities often ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 people per square mile, whereas urban centers can exceed 10,000 people per square mile. The spatial distribution in suburbs favors single-family homes and green spaces, contributing to a more dispersed population pattern. Urban agglomerations concentrate residents in multi-story residential buildings and mixed-use developments, intensifying the population density and supporting more extensive public transportation networks.
Housing Types and Architectural Styles
Suburban areas typically feature single-family homes, townhouses, and low-rise apartments characterized by more traditional or contemporary architectural styles with an emphasis on space and privacy. Urban agglomerations tend to have high-density housing such as skyscrapers, condominiums, and mixed-use buildings showcasing modern, brutalist, and occasionally historic architectural styles reflecting cultural diversity and functional design. The contrast highlights how suburban living prioritizes spacious, detached residences while urban agglomerations focus on maximizing space through vertical development and architectural innovation.
Transportation and Connectivity
Suburban areas typically experience lower traffic congestion and rely heavily on personal vehicles, with limited public transportation options compared to urban agglomerations. Urban agglomerations feature extensive, multimodal transportation networks including subways, buses, and commuter trains that enhance connectivity and reduce commute times. Enhanced infrastructure in urban agglomerations supports higher population density and economic activity, fostering better accessibility and integration within metropolitan regions.
Employment Opportunities and Economic Activities
Suburban areas typically offer employment opportunities concentrated in retail, education, and light manufacturing sectors, catering primarily to local populations with a focus on commuter-based jobs. Urban agglomerations, by contrast, serve as economic hubs with diverse employment opportunities spanning finance, technology, healthcare, and creative industries, supported by extensive infrastructure and a high degree of labor market specialization. The economic activities in urban agglomerations drive regional growth and innovation, while suburban zones often provide complementary functions such as residential support and localized services.
Access to Public Services and Amenities
Suburban areas typically offer more spacious living with easier access to parks, schools, and local healthcare facilities, but may have limited public transportation options compared to urban agglomerations. Urban agglomerations provide dense networks of public services, including extensive mass transit systems, hospitals, cultural institutions, and retail centers, catering to a diverse population. The concentration of amenities in urban agglomerations enhances accessibility but often comes with higher congestion and competition for resources compared to suburban settings.
Quality of Life and Living Costs
Suburban areas generally offer higher quality of life with more green spaces, lower pollution levels, and less noise compared to urban agglomerations, which tend to be densely populated and experience heavy traffic congestion. Living costs in suburban areas are typically lower, especially in terms of housing prices and property taxes, whereas urban agglomerations have higher costs due to demand for limited space and amenities. Accessibility to services and employment is greater in urban agglomerations, but this often comes with trade-offs in terms of stress and commute times.
Environmental Impact and Green Spaces
Suburban areas typically feature more extensive green spaces and lower population densities, which can reduce urban heat island effects and promote biodiversity compared to densely packed urban agglomerations. Urban agglomerations often face significant environmental challenges such as higher air pollution levels, limited green spaces, and increased carbon emissions due to concentrated traffic and industrial activities. Effective urban planning that integrates green infrastructure within agglomerations is essential to mitigate environmental impacts and improve residents' quality of life.
Social Dynamics and Community Life
Suburban areas often exhibit close-knit community life characterized by lower population density, family-oriented social dynamics, and a strong emphasis on local schools and neighborhood activities. In contrast, urban agglomerations experience diverse social interactions due to higher density, multicultural populations, and vibrant public spaces that foster dynamic community engagement. Social cohesion in suburban areas tends to rely on shared values and long-term residency, while urban agglomerations thrive on diversity and constant social flux.
Trends in Urbanization and Suburbanization
Trends in urbanization reveal rapid growth of urban agglomerations, where densely populated cities expand through mergers of adjacent towns, creating extensive metropolitan regions. Suburbanization trends show increasing migration from urban centers to suburban areas, driven by demand for affordable housing, reduced congestion, and improved quality of life. Urban agglomerations exhibit economic concentration and infrastructure development, while suburban areas emphasize residential expansion and commuter connectivity.
Suburban area Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com