Compulsory measures ensure compliance and establish clear expectations in various contexts, from education to legal regulations. Understanding how these mandatory requirements impact your responsibilities can help you navigate systems more effectively. Explore the full article to learn how compulsory rules affect you and why they matter.
Table of Comparison
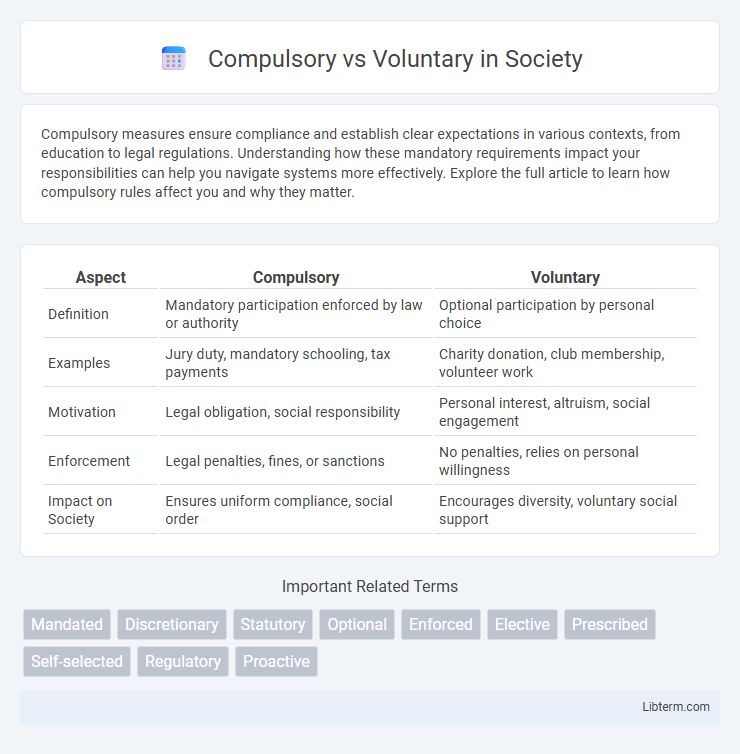
| Aspect | Compulsory | Voluntary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mandatory participation enforced by law or authority | Optional participation by personal choice |
| Examples | Jury duty, mandatory schooling, tax payments | Charity donation, club membership, volunteer work |
| Motivation | Legal obligation, social responsibility | Personal interest, altruism, social engagement |
| Enforcement | Legal penalties, fines, or sanctions | No penalties, relies on personal willingness |
| Impact on Society | Ensures uniform compliance, social order | Encourages diversity, voluntary social support |
Introduction to Compulsory vs Voluntary
Compulsory actions or measures are mandated by laws, regulations, or authoritative rules, ensuring compliance across individuals or organizations. Voluntary actions are initiated by choice, driven by personal, ethical, or organizational motivations without legal enforcement. Understanding the distinction between compulsory and voluntary frameworks is crucial for effective policy implementation and behavioral analysis.
Key Definitions: Compulsory and Voluntary
Compulsory refers to actions or requirements mandated by law, rule, or authority, compelling individuals or entities to comply without choice. Voluntary describes actions or participation made by free will, where individuals or entities choose to engage without external obligation. Understanding these definitions is critical in legal, social, and organizational contexts where the distinction impacts rights, responsibilities, and consequences.
Historical Overview of Compulsory and Voluntary Systems
Compulsory and voluntary systems have evolved through distinct historical trajectories, with compulsory systems often emerging from legal mandates during industrialization to protect workers and citizens, exemplified by the Social Security Act of 1935 in the United States. Voluntary systems trace their roots to early mutual aid societies and charitable organizations in the 19th century, which emphasized community support and individual choice without government enforcement. Over time, compulsory systems expanded to include healthcare, education, and insurance, while voluntary systems adapted to niche markets and personalized services, reflecting differing societal priorities and governance models.
Legal Frameworks and Policy Differences
Compulsory legal frameworks mandate specific actions or compliance, such as tax laws requiring payment, while voluntary frameworks encourage participation without legal penalties, often seen in corporate social responsibility initiatives. Policy differences are evident in enforcement mechanisms; compulsory policies rely on sanctions and judicial authority, whereas voluntary policies depend on incentives, public recognition, and stakeholder engagement. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for designing effective regulatory approaches that balance government control with individual or organizational autonomy.
Social and Ethical Implications
Compulsory measures enforce participation, often raising ethical concerns about autonomy and individual rights, particularly in social contexts where consent is a central value. Voluntary actions emphasize personal choice and moral responsibility but may result in uneven participation, potentially exacerbating social inequalities. Balancing these approaches requires careful consideration of fairness, societal welfare, and respect for individual freedoms in policy design.
Benefits of Compulsory Approaches
Compulsory approaches ensure universal participation, leading to comprehensive coverage and reducing gaps in protection or compliance within a population. They facilitate consistent enforcement of regulations, which enhances public safety and accountability by mandating adherence to standards. These approaches also promote equity by guaranteeing that all individuals contribute and benefit, minimizing risks that arise from voluntary opt-outs.
Advantages of Voluntary Participation
Voluntary participation enables individuals to engage based on genuine interest and motivation, which often leads to higher commitment and better performance. This approach fosters creativity and innovation as participants contribute willingly without external pressure. Organizations benefit from improved morale and stronger community bonds when involvement is driven by choice rather than obligation.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Compulsory approaches often face criticism for limiting individual autonomy and causing resistance due to perceived coercion, which can reduce motivation and engagement. Voluntary approaches may struggle with inconsistent participation and lack of accountability, resulting in uneven implementation and diminished overall effectiveness. Both methods encounter challenges in balancing enforcement with personal freedom, impacting the sustainability and acceptance of the initiative.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Compulsory participation in programs like vaccinations often yields higher compliance rates, as demonstrated by California's mandatory school immunization laws reducing measles outbreaks. Voluntary initiatives, such as blood donation drives, rely on individual motivation but can achieve significant success through targeted campaigns, as evidenced by the Red Cross increasing donor turnout via social media outreach. Case studies comparing seatbelt use highlight how compulsory laws lead to greater adoption and reduced fatalities compared to voluntary use recommendations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing between compulsory and voluntary approaches depends on the specific context and desired outcomes of a policy or program. Compulsory measures ensure compliance and uniformity, often necessary for public safety or legal requirements, while voluntary participation encourages personal motivation and flexibility, leading to higher engagement and satisfaction. Balancing these factors by assessing stakeholder needs, potential risks, and resource availability helps in selecting the most effective approach for long-term success.
Compulsory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com