Participation is essential for fostering collaboration and achieving shared goals in any community or organization. Engaging actively allows you to contribute your unique ideas and skills, enhancing collective success. Discover more about how meaningful participation can transform your experiences in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
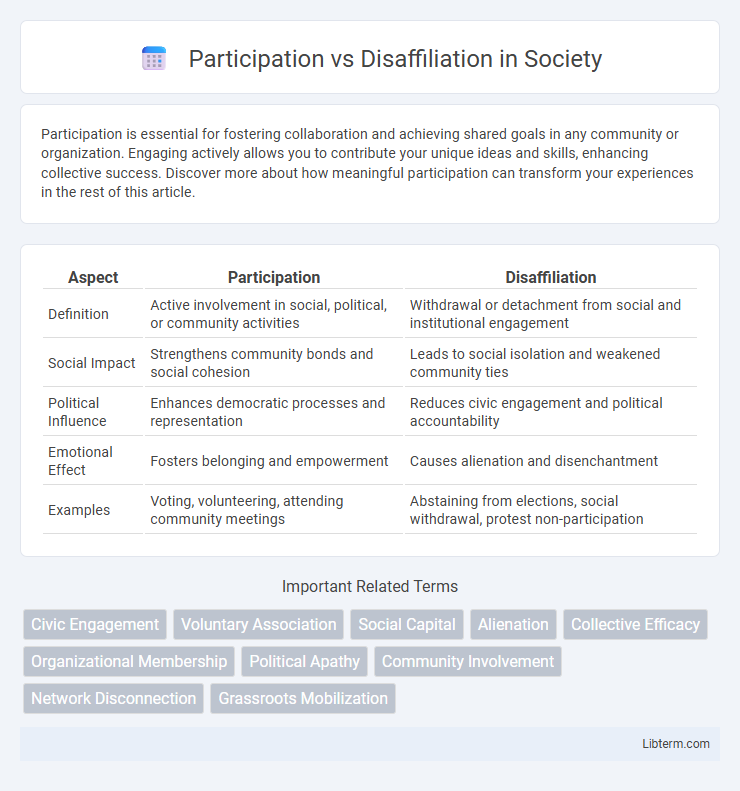
| Aspect | Participation | Disaffiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active involvement in social, political, or community activities | Withdrawal or detachment from social and institutional engagement |
| Social Impact | Strengthens community bonds and social cohesion | Leads to social isolation and weakened community ties |
| Political Influence | Enhances democratic processes and representation | Reduces civic engagement and political accountability |
| Emotional Effect | Fosters belonging and empowerment | Causes alienation and disenchantment |
| Examples | Voting, volunteering, attending community meetings | Abstaining from elections, social withdrawal, protest non-participation |
Understanding Participation and Disaffiliation
Participation involves active engagement and commitment within a group or community, fostering social cohesion and mutual support. Disaffiliation refers to the process of withdrawing or detaching from such groups, often leading to social isolation or identity shifts. Understanding participation and disaffiliation provides insights into personal identity dynamics and societal integration.
Historical Context and Trends
Participation in political systems has historically fluctuated, with voter turnout and civic engagement peaking during periods of major social or political change, such as the civil rights movement in the 1960s. Disaffiliation trends often rise in contexts of political distrust or disenfranchisement, exemplified by declining party memberships and increased independent voters since the late 20th century. Long-term analysis reveals cycles of engagement and disengagement influenced by economic conditions, media evolution, and systemic reforms.
Motivations Behind Participation
Participation in social or political movements is often driven by motivations such as belonging, identity affirmation, and the pursuit of collective goals. Individuals seek meaningful engagement to express shared values, achieve social recognition, or influence policy changes that align with their interests. Understanding these motivational factors is crucial for analyzing patterns of active involvement versus withdrawal or disaffiliation.
Reasons for Disaffiliation
Disaffiliation often occurs due to perceived misalignment between individual values and organizational goals, leading to decreased motivation and commitment. Structural factors such as lack of representation, ineffective communication, and exclusionary practices contribute significantly to members' decisions to disengage. Emotional factors like dissatisfaction, distrust, and feeling undervalued further accelerate the withdrawal from active participation.
Social and Cultural Impacts
Participation fosters social cohesion by encouraging community engagement and cultural exchange, strengthening collective identities and shared values. Disaffiliation often leads to social fragmentation, weakening networks of support and eroding cultural traditions and communal practices. These dynamics influence societal stability, identity formation, and the transmission of cultural heritage across generations.
Effects on Community Dynamics
Participation fosters inclusive community dynamics by enhancing social cohesion, trust, and collective efficacy among members, which leads to increased collaboration and shared resources. Disaffiliation, conversely, often results in social fragmentation, weakened communal ties, and reduced civic engagement, creating challenges in maintaining community resilience. Studies show that higher participation rates correlate with lower crime levels and improved local governance outcomes, whereas disaffiliation can exacerbate social isolation and economic disparities.
Psychological Factors Influencing Decisions
Psychological factors influencing participation versus disaffiliation often include identity affirmation, social belonging, and cognitive dissonance resolution. Individuals who perceive alignment between personal values and group norms tend to participate actively, while those experiencing identity threats or unmet psychological needs may disaffiliate. Emotional attachment, perceived autonomy, and self-efficacy also critically shape decisions to stay engaged or disengage from social groups or communities.
Case Studies: Participation vs Disaffiliation
Case studies on participation versus disaffiliation reveal contrasting dynamics in social movements and organizational behavior. In contexts where participation thrives, individuals report higher engagement, empowerment, and collective identity, as seen in community-led environmental initiatives that successfully mobilize local resources and foster sustained involvement. Conversely, disaffiliation cases, such as employee disengagement in corporate restructurings, highlight increased turnover, reduced productivity, and weakened organizational commitment, emphasizing the critical role of inclusive strategies in maintaining active participation.
Strategies to Encourage Engagement
Strategies to encourage engagement hinge on fostering a sense of community through inclusive communication and personalized outreach, which counteracts disaffiliation by strengthening relational ties. Implementing participatory decision-making processes allows individuals to feel valued and invested, directly enhancing participation rates. Leveraging digital platforms to create accessible, interactive environments further promotes sustained involvement and prevents disengagement.
Future Outlook: Reversing Disaffiliation
Reversing disaffiliation requires targeted community engagement strategies that foster a sense of belonging and shared purpose among marginalized groups. Employing data-driven initiatives, such as inclusive policy reforms and digital platforms for civic participation, can significantly increase individual and collective involvement. Future outlooks emphasize leveraging technology and social innovation to rebuild trust and encourage sustained participation in social, political, and cultural institutions.
Participation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com