Pluralism promotes a society where diverse perspectives, cultures, and beliefs coexist harmoniously, enriching social and political life. It encourages mutual respect and collaboration among different groups to strengthen democratic values and drive innovation. Explore this article to understand how pluralism can shape your community and foster inclusive growth.
Table of Comparison
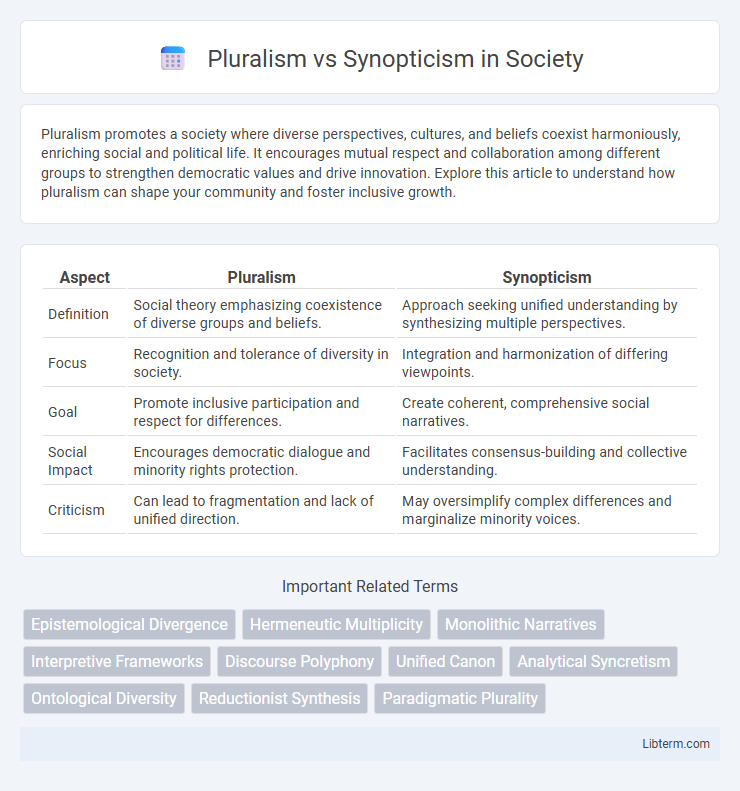
| Aspect | Pluralism | Synopticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social theory emphasizing coexistence of diverse groups and beliefs. | Approach seeking unified understanding by synthesizing multiple perspectives. |
| Focus | Recognition and tolerance of diversity in society. | Integration and harmonization of differing viewpoints. |
| Goal | Promote inclusive participation and respect for differences. | Create coherent, comprehensive social narratives. |
| Social Impact | Encourages democratic dialogue and minority rights protection. | Facilitates consensus-building and collective understanding. |
| Criticism | Can lead to fragmentation and lack of unified direction. | May oversimplify complex differences and marginalize minority voices. |
Defining Pluralism: Embracing Diversity
Pluralism in philosophy and social theory emphasizes the acceptance and celebration of diverse perspectives, beliefs, and cultural values, arguing that no single viewpoint holds absolute truth. This approach contrasts with synopticism, which seeks to unify multiple perspectives into a single coherent framework. Embracing pluralism promotes inclusivity, fostering dialogue and understanding across different ideologies, and recognizing complexity in social, ethical, and epistemological contexts.
Synopticism Explained: Seeking Unified Perspectives
Synopticism emphasizes the integration of diverse viewpoints to form a cohesive and comprehensive understanding, often synthesizing information from multiple disciplines or sources. This approach seeks common ground and overarching themes to create unified perspectives that transcend individual differences. By prioritizing holistic analysis, synopticism aims to resolve contradictions and foster clearer, more inclusive insights into complex issues.
Historical Roots: Origins of Pluralism and Synopticism
The origins of pluralism trace back to ancient Greek philosophy, emphasizing multiple perspectives and coexistence of diverse viewpoints, influencing political and cultural discourses throughout history. Synopticism, rooted in religious studies, primarily emerges from the New Testament's Synoptic Gospels--Matthew, Mark, and Luke--highlighting their interconnectedness and shared narrative. Understanding these historical roots reveals pluralism's foundation in philosophical inclusivity and synopticism's basis in textual comparison within early Christian traditions.
Key Philosophical Differences
Pluralism emphasizes the coexistence of multiple, equally valid perspectives, rejecting the notion of a single, unified truth, while Synopticism seeks to integrate diverse viewpoints into a comprehensive, cohesive understanding. Pluralism values epistemic diversity and relativism, promoting tolerance and inclusivity in knowledge systems. Synopticism prioritizes synthesis and coherence, aiming to reconcile contradictions and create a holistic worldview that transcends individual perspectives.
Pluralism in Modern Society
Pluralism in modern society fosters a dynamic coexistence of diverse cultural, religious, and ideological perspectives, encouraging mutual respect and dialogue among different groups. It supports democratic governance by valuing minority rights and promoting inclusive decision-making processes, thereby enhancing social cohesion and reducing conflict. Pluralism drives innovation and adaptability by integrating multiple viewpoints, which enrich public discourse and contribute to sustainable societal development.
Synopticism in Academia and Thought
Synopticism in academia emphasizes the integration of diverse disciplines to create holistic perspectives, fostering comprehensive understanding by synthesizing knowledge across fields. This approach contrasts with pluralism's acceptance of multiple independent views by prioritizing convergence and coherence in theoretical frameworks. Synoptic methodologies enhance interdisciplinary research and promote unified theories that address complex societal and philosophical issues.
Advantages of Pluralistic Approaches
Pluralistic approaches in philosophy and social sciences allow for the integration of diverse perspectives, fostering richer understanding and innovation by accommodating multiple viewpoints. This flexibility enhances problem-solving by recognizing the complexity of human experiences and avoiding reductionist conclusions. Empirical studies show that pluralism encourages dialogue and inclusivity, leading to more resilient and adaptive decision-making processes in multicultural contexts.
Critiques and Limitations of Synopticism
Synopticism faces critiques for oversimplifying the distinct theological perspectives and historical contexts of the Gospels, often ignoring the unique messages and audiences of Matthew, Mark, and Luke. Scholars argue that this approach can lead to selective harmonization, which may distort the original intent and literary nuances of each Gospel narrative. The limitation of Synopticism lies in its tendency to prioritize similarities at the expense of acknowledging the rich diversity and complexity within the Synoptic Gospels.
Interplay: Can Pluralism and Synopticism Coexist?
Pluralism and synopticism can coexist through a dynamic interplay where pluralism's embrace of multiple perspectives enriches synopticism's holistic viewing of interconnected systems. This coexistence fosters a nuanced understanding by integrating diverse viewpoints without losing the coherence offered by synoptic synthesis. The balance highlights how complex realities benefit from both respecting individual differences and seeking overarching patterns.
Future Implications and Ongoing Debates
The future implications of pluralism emphasize diverse perspectives driving innovation and resilience in societal structures, challenging monolithic narratives often upheld by synopticism. Ongoing debates revolve around balancing inclusivity with coherence, as pluralism's acceptance of multiple viewpoints can complicate unified decision-making compared to synoptic approaches that prioritize overarching synthesis. Emerging discussions highlight how technological advancements, like AI and big data, influence this dynamic by either fostering pluralistic dialogue or enabling synoptic aggregation of knowledge.
Pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com