Social movements play a crucial role in shaping societal change by mobilizing collective action to address issues such as civil rights, environmental protection, and social justice. These movements often rely on grassroots organizing, advocacy, and public awareness campaigns to influence policies and cultural norms. Discover how understanding the dynamics of social movements can empower your participation and inspire you to engage with transformative causes. Read the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
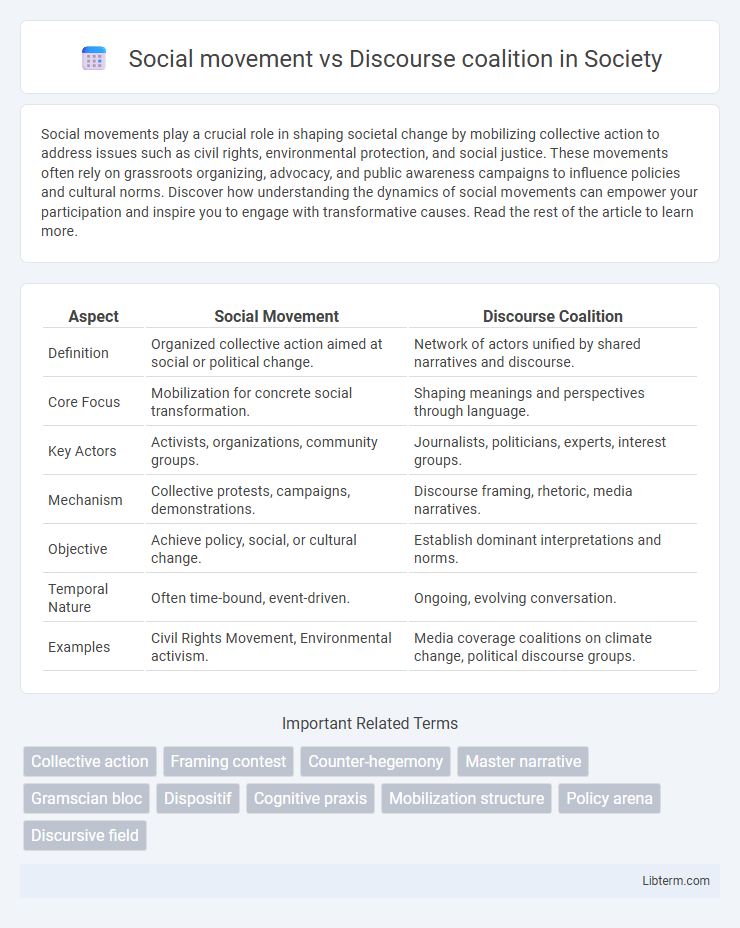
| Aspect | Social Movement | Discourse Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized collective action aimed at social or political change. | Network of actors unified by shared narratives and discourse. |
| Core Focus | Mobilization for concrete social transformation. | Shaping meanings and perspectives through language. |
| Key Actors | Activists, organizations, community groups. | Journalists, politicians, experts, interest groups. |
| Mechanism | Collective protests, campaigns, demonstrations. | Discourse framing, rhetoric, media narratives. |
| Objective | Achieve policy, social, or cultural change. | Establish dominant interpretations and norms. |
| Temporal Nature | Often time-bound, event-driven. | Ongoing, evolving conversation. |
| Examples | Civil Rights Movement, Environmental activism. | Media coverage coalitions on climate change, political discourse groups. |
Defining Social Movements
Social movements are organized collective efforts aimed at promoting or resisting change in society, driven by shared values and sustained activism over time. They mobilize resources, frame issues, and engage various stakeholders to influence public opinion and policy. Unlike discourse coalitions, which primarily consist of actors united by shared narratives and language around an issue, social movements encompass broader organizational structures and direct action strategies.
Understanding Discourse Coalitions
Discourse coalitions consist of diverse actors who share common storylines and vocabularies, aligning their narratives to influence public opinion and policy debates. Unlike social movements that mobilize collective action and protest, discourse coalitions operate by shaping meaning and framing issues within political and media environments. Understanding discourse coalitions involves analyzing how language, symbols, and shared beliefs create alliances that sustain policy preferences and social norms over time.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Social movements originated in the 18th and 19th centuries as collective actions aiming for social or political change, rooted in labor, suffrage, and civil rights struggles. Discourse coalitions emerged in the late 20th century through discourse analysis, emphasizing alliances formed through shared narratives and language rather than collective action alone. The evolution of social movements involved mass mobilization and institutional challenges, while discourse coalitions highlight the power of communicative processes in shaping policy and public understanding.
Key Differences Between Social Movements and Discourse Coalitions
Social movements mobilize collective action and sustained efforts to achieve social or political change, often organized around shared goals and values, whereas discourse coalitions consist of diverse actors united through shared narratives or rhetoric rather than direct activism. Social movements emphasize overt engagement and public demonstrations, while discourse coalitions primarily influence through framing ideas and shaping public debates. The key difference lies in the tangible collective action of social movements versus the discursive alignment and endorsement found in discourse coalitions.
Goals and Objectives of Each Group
Social movements aim to achieve broad societal change by mobilizing collective action around shared grievances, often pursuing transformative goals such as social justice, equality, or policy reforms. Discourse coalitions focus on shaping public narratives and influencing discourse through shared storylines and rhetoric to align perspectives and legitimize specific viewpoints. While social movements prioritize concrete structural changes, discourse coalitions work to construct and maintain ideological frameworks that support or oppose these changes.
Structures and Organizational Patterns
Social movements are characterized by formal hierarchies, established leadership, and organized membership networks that facilitate coordinated actions and resource mobilization. In contrast, discourse coalitions consist of loosely connected actors unified by shared narratives and discursive frames without centralized authority or rigid organizational structures. The structural flexibility of discourse coalitions allows for fluid participation and adaptability, whereas social movements typically rely on structured organizational patterns to sustain collective identities and strategic campaigns.
Influencing Social Change: Strategies and Tactics
Social movements mobilize collective action through grassroots organizing, protests, and advocacy campaigns to drive social change, emphasizing mass participation and public visibility. Discourse coalitions influence social change by shaping public narratives, framing issues in media and policy debates, and aligning diverse actors around shared meanings and language. Strategic use of storytelling, symbolic actions, and coalition-building enables both approaches to reframe societal norms and affect policy reform.
Case Studies: Examples in Practice
Social movements, such as the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s, mobilize collective action and public protests to drive social change, often gaining widespread media attention and political influence. Discourse coalitions, exemplified by climate change debates, consist of networks of actors sharing common narratives and frames that shape public discourse without necessarily engaging in direct activism. Case studies reveal that social movements often catalyze policy shifts through visible mobilization, while discourse coalitions influence long-term ideological alignment by controlling the language and meanings in public arenas.
Interactions and Overlaps Between Social Movements and Discourse Coalitions
Social movements and discourse coalitions intersect through shared narratives and collective framing strategies that shape public opinion and policy agendas. Social movements utilize discourse coalitions to amplify their messages by aligning diverse actors who propagate similar beliefs, creating a network effect that strengthens mobilization and legitimacy. These interactions foster dynamic overlaps where discursive practices influence movement tactics, while social movements enrich discourse coalitions with grassroots energy and experiential knowledge.
Implications for Policy and Society
Social movements mobilize collective action to challenge existing power structures and influence policy reforms, often leading to significant societal changes by raising public awareness and altering political agendas. Discourse coalitions shape policy development by framing problems and solutions within dominant narratives, impacting legislative outcomes through strategic communication and alliance-building among diverse actors. Understanding the interplay between social movements and discourse coalitions is crucial for analyzing how ideas transform into concrete policies and how societal norms evolve over time.
Social movement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com