Inclusivism promotes the acceptance and respect of diverse perspectives, fostering unity without erasing individual differences. It encourages open-mindedness and understanding by acknowledging that multiple viewpoints can coexist meaningfully. Explore the rest of the article to discover how inclusivism can positively impact your interactions and worldview.
Table of Comparison
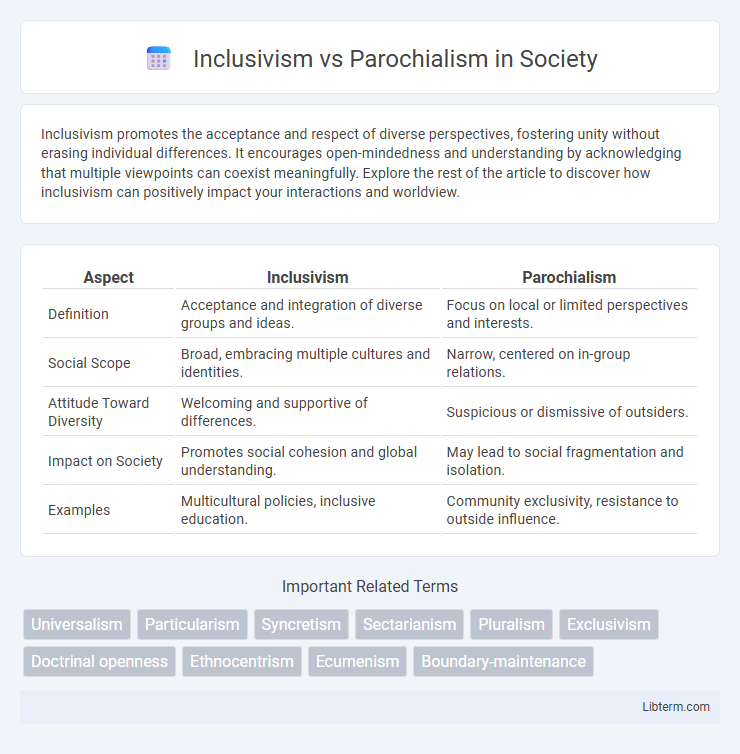
| Aspect | Inclusivism | Parochialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acceptance and integration of diverse groups and ideas. | Focus on local or limited perspectives and interests. |
| Social Scope | Broad, embracing multiple cultures and identities. | Narrow, centered on in-group relations. |
| Attitude Toward Diversity | Welcoming and supportive of differences. | Suspicious or dismissive of outsiders. |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social cohesion and global understanding. | May lead to social fragmentation and isolation. |
| Examples | Multicultural policies, inclusive education. | Community exclusivity, resistance to outside influence. |
Understanding Inclusivism: Definition and Core Concepts
Inclusivism is a philosophical and theological perspective that acknowledges the validity of multiple belief systems while maintaining the superiority of a particular worldview. Core concepts of inclusivism emphasize openness, acceptance, and integration of diverse ideas, promoting harmony without demanding complete uniformity. This approach contrasts with parochialism by encouraging broader understanding and respect beyond narrow, localized viewpoints.
Parochialism Explained: Meaning and Characteristics
Parochialism refers to a limited or narrow outlook, especially focused on a local area or small community, often resisting external influence or broader perspectives. Characterized by prioritizing local traditions, interests, and values over global or diverse viewpoints, parochialism can hinder openness and adaptability in social, cultural, or organizational contexts. This mindset typically results in resistance to change and an inward-looking approach that challenges inclusivist efforts towards embracing diversity and broader cooperation.
Historical Roots of Inclusivism and Parochialism
Inclusivism and parochialism have distinct historical roots shaping their ideological frameworks; inclusivism traces back to ancient religious and philosophical traditions like Hinduism's Vedanta and early Christian universalism, which emphasize the integration and acceptance of diverse beliefs within a broader truth. Parochialism, rooted in localized tribalism and ethnocentrism, emerged historically through the sociopolitical structures of isolated communities prioritizing internal cohesion and distinct identity, often resistant to external influences. These contrasting origins highlight inclusivism's emphasis on universal connectivity and parochialism's focus on preserving cultural and social boundaries.
Inclusivism in Modern Societies: Advantages and Challenges
Inclusivism in modern societies promotes social cohesion by embracing cultural diversity and encouraging mutual respect among different groups, which enhances innovation and economic growth through diverse perspectives. This approach fosters equality and reduces discrimination by recognizing the value of all individuals regardless of their background, strengthening democratic participation. Challenges include balancing integration with preserving cultural identities and addressing resistance from segments of society fearful of change or perceived threats to traditional norms.
Parochialism in Contemporary Contexts: Impacts and Consequences
Parochialism in contemporary contexts often results in limited perspectives that hinder social cohesion and global cooperation. This insular mindset exacerbates conflicts by prioritizing local or group interests over broader societal or international concerns, impeding progressive policies and inclusive dialogues. The consequences include reduced innovation, increased polarization, and challenges in addressing complex global issues such as climate change and economic inequality.
Inclusivism vs Parochialism: Key Differences
Inclusivism emphasizes acceptance and integration of diverse beliefs and cultures within a broader framework, promoting mutual respect and shared values across communities. Parochialism, by contrast, centers on limited perspectives, prioritizing local or group-specific interests and often resisting external influences or diversity. The key differences lie in inclusivism's openness to plurality and parochialism's focus on exclusivity and insularity.
Cultural and Social Implications of Inclusivist Approaches
Inclusivist approaches promote cultural diversity and social cohesion by recognizing and valuing multiple cultural identities within a society, fostering mutual respect and understanding among different groups. These approaches enhance social integration and reduce conflicts by encouraging inclusive policies and intercultural dialogue, which contribute to the creation of more equitable and harmonious communities. Inclusivism supports the preservation of minority cultures while promoting shared societal values, thereby strengthening social solidarity and collective well-being.
How Parochialism Shapes Community and Identity
Parochialism shapes community and identity by fostering strong local bonds and shared traditions that create a sense of belonging and continuity within a narrowly defined group. This localized focus often results in a cohesive social fabric, where community members prioritize internal values and norms over external influences. The concentration on parochial concerns can reinforce cultural distinctiveness and a collective identity that resists broader inclusivist perspectives.
Overcoming Parochialism: Strategies for Fostering Inclusivity
Overcoming parochialism requires implementing strategies that promote inclusivity by encouraging openness to diverse perspectives and cultural understanding. Organizations can foster inclusivity through diversity training programs, inclusive leadership development, and creating environments that value and respect different backgrounds and viewpoints. Emphasizing collaboration and empathy drives collective problem-solving, reducing narrow-mindedness and enhancing social cohesion.
The Future of Inclusivism and Parochialism in a Globalized World
Inclusivism in a globalized world promotes cultural exchange and unity by recognizing diverse perspectives, fostering cooperation, and encouraging tolerance across nations. Parochialism, however, emphasizes local traditions and identities, often resisting external influences to preserve cultural uniqueness, which can lead to social fragmentation. The future likely holds a dynamic balance where inclusivism expands through digital connectivity, while parochialism persists as communities assert their distinct identities amid globalization pressures.
Inclusivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com