Environmental audit evaluates a company's compliance with environmental regulations, identifies potential risks, and helps implement sustainable practices to reduce ecological impact. This process enhances operational efficiency, minimizes waste, and ensures adherence to legal requirements, fostering a positive corporate reputation. Discover how your organization can benefit from an environmental audit by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
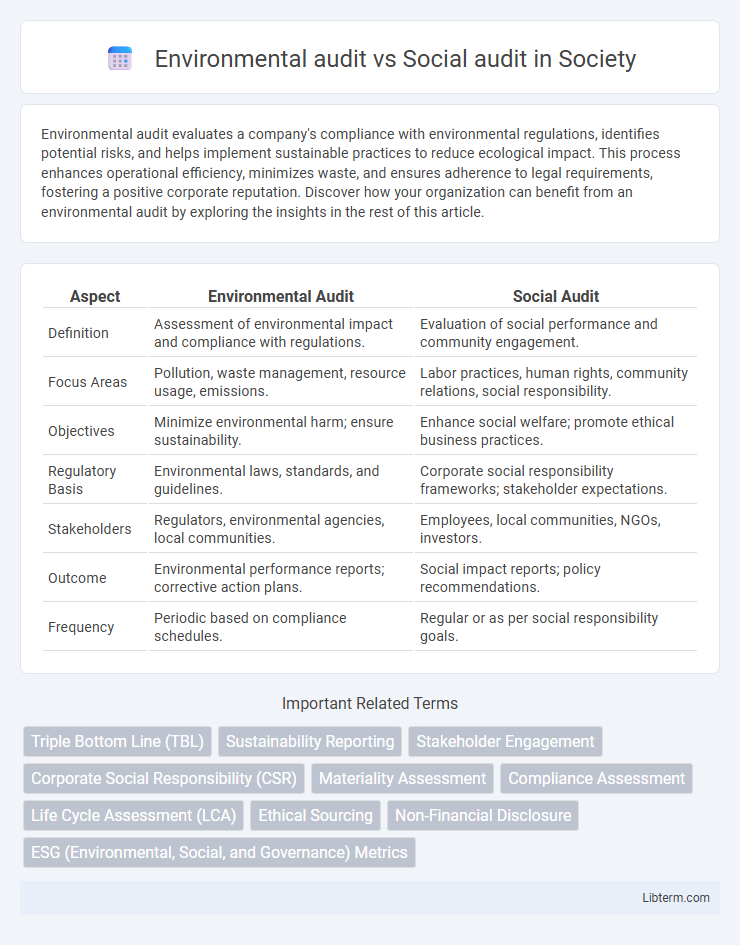
| Aspect | Environmental Audit | Social Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment of environmental impact and compliance with regulations. | Evaluation of social performance and community engagement. |
| Focus Areas | Pollution, waste management, resource usage, emissions. | Labor practices, human rights, community relations, social responsibility. |
| Objectives | Minimize environmental harm; ensure sustainability. | Enhance social welfare; promote ethical business practices. |
| Regulatory Basis | Environmental laws, standards, and guidelines. | Corporate social responsibility frameworks; stakeholder expectations. |
| Stakeholders | Regulators, environmental agencies, local communities. | Employees, local communities, NGOs, investors. |
| Outcome | Environmental performance reports; corrective action plans. | Social impact reports; policy recommendations. |
| Frequency | Periodic based on compliance schedules. | Regular or as per social responsibility goals. |
Introduction to Environmental and Social Audits
Environmental audits evaluate an organization's compliance with environmental regulations, assessing factors like waste management, pollution control, and resource conservation to minimize ecological impact. Social audits examine a company's social responsibility practices, including labor conditions, community engagement, and ethical standards, ensuring alignment with social values and stakeholder expectations. Both audits promote sustainability and accountability by identifying risks and opportunities for improved environmental and social performance.
Defining Environmental Audits
Environmental audits systematically assess an organization's compliance with environmental regulations, focusing on resource usage, waste management, and pollution control. These audits identify environmental risks and opportunities for sustainable practices, helping companies reduce ecological impact and enhance regulatory adherence. By evaluating air emissions, water discharges, and hazardous substances, environmental audits support proactive environmental management and corporate responsibility.
Understanding Social Audits
Social audits evaluate an organization's social performance by assessing its impact on stakeholders such as employees, communities, and consumers, measuring factors like labor practices, human rights, and community engagement. Unlike environmental audits that focus on sustainability metrics and ecological compliance, social audits emphasize transparency, accountability, and ethical responsibility in social dimensions. Understanding social audits involves analyzing qualitative and quantitative data to ensure corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals align with stakeholder expectations and regulatory standards.
Key Objectives of Environmental Audits
Environmental audits primarily target the assessment of an organization's impact on natural resources, evaluating compliance with environmental laws, and identifying areas for reducing pollution and waste. These audits aim to promote sustainable practices by monitoring energy use, emissions, and resource conservation to minimize ecological harm. Social audits, in contrast, focus on evaluating an organization's social responsibility and ethical practices, such as labor conditions and community engagement.
Main Goals of Social Audits
Social audits primarily focus on evaluating an organization's adherence to social responsibilities, including labor rights, community impact, and stakeholder engagement. They aim to ensure transparency, accountability, and alignment with ethical standards while measuring the actual social performance against commitments. This process helps identify gaps in social equity, human rights compliance, and community welfare initiatives.
Differences Between Environmental and Social Audits
Environmental audits assess an organization's compliance with environmental regulations, impact on natural resources, waste management, and pollution control, focusing on sustainability and ecological footprint. Social audits evaluate a company's social responsibility, stakeholder engagement, labor practices, community impact, and human rights adherence, emphasizing ethical standards and social accountability. The primary difference lies in environmental audits targeting ecological factors while social audits concentrate on social and ethical dimensions of business operations.
Methods and Tools Used in Environmental Audits
Environmental audits utilize systematic methods such as site inspections, compliance checklists, and environmental impact assessments to evaluate adherence to environmental regulations and sustainability goals. Common tools include Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for spatial analysis, monitoring equipment like air and water quality sensors, and life cycle assessment software to measure environmental footprints. These methods provide quantitative data that support decision-making for reducing ecological damage and improving resource management strategies.
Techniques Applied in Social Audits
Social audits employ participatory techniques such as community meetings, interviews, and surveys to assess an organization's social impact, ensuring transparency and accountability. These methods facilitate stakeholder engagement and collect qualitative data on issues like labor rights, community development, and ethical practices. Unlike environmental audits that prioritize scientific measurements and compliance checks, social audits emphasize human-centered approaches to evaluate social performance and governance.
Integration of Environmental and Social Auditing Processes
Integrating environmental and social auditing processes enhances the comprehensive assessment of a company's sustainability performance, enabling organizations to identify risks and opportunities across ecological and social dimensions simultaneously. Combined audits utilize shared data collection methods and aligned indicators such as carbon footprint, labor practices, and community engagement, improving efficiency and providing a holistic view for stakeholders. This integration supports regulatory compliance with frameworks like ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria and fosters transparent reporting that drives sustainable business strategies.
Benefits of Conducting Environmental and Social Audits
Environmental audits identify compliance with ecological regulations, reduce waste, and improve resource efficiency, leading to cost savings and enhanced corporate sustainability. Social audits evaluate workplace conditions, labor practices, and community impact, fostering transparency, stakeholder trust, and improved employee relations. Together, these audits help organizations mitigate risks, strengthen brand reputation, and align operations with environmental and social governance (ESG) standards.
Environmental audit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com