A market-centric approach prioritizes understanding and meeting the needs, preferences, and behaviors of target customers to create value and gain a competitive edge. It involves continuous market research, customer feedback integration, and adaptive strategies that align products and services with evolving consumer demands. Explore the rest of the article to discover how adopting a market-centric mindset can transform your business success.
Table of Comparison
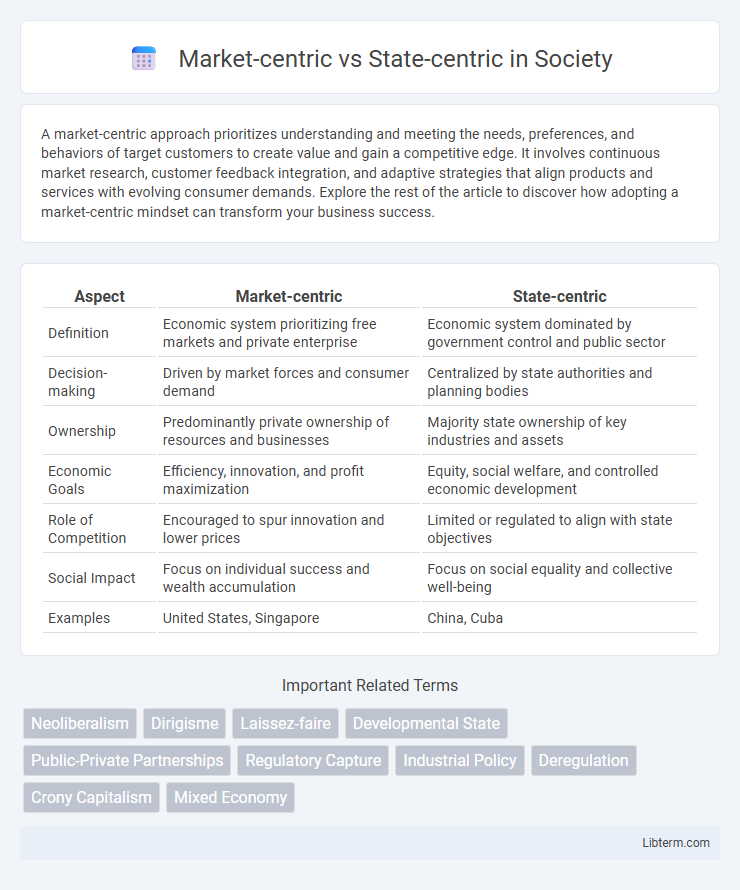
| Aspect | Market-centric | State-centric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic system prioritizing free markets and private enterprise | Economic system dominated by government control and public sector |
| Decision-making | Driven by market forces and consumer demand | Centralized by state authorities and planning bodies |
| Ownership | Predominantly private ownership of resources and businesses | Majority state ownership of key industries and assets |
| Economic Goals | Efficiency, innovation, and profit maximization | Equity, social welfare, and controlled economic development |
| Role of Competition | Encouraged to spur innovation and lower prices | Limited or regulated to align with state objectives |
| Social Impact | Focus on individual success and wealth accumulation | Focus on social equality and collective well-being |
| Examples | United States, Singapore | China, Cuba |
Introduction to Market-Centric and State-Centric Approaches
Market-centric approaches prioritize efficient resource allocation through supply and demand dynamics, emphasizing private sector roles and minimal government intervention to drive economic growth and innovation. State-centric approaches focus on government regulation and control to guide economic development, ensuring social welfare, stability, and addressing market failures through policy measures and public sector involvement. These contrasting frameworks shape economic policies by balancing market freedom with state authority to achieve sustainable development goals.
Defining Market-Centric Economies
Market-centric economies prioritize supply and demand dynamics, emphasizing decentralized decision-making by private individuals and businesses to allocate resources efficiently. Prices are determined by competitive markets, driving innovation, productivity, and consumer choice without extensive government intervention. This economic model fosters flexibility and responsiveness to market changes, relying on entrepreneurship and minimal regulatory constraints to promote growth.
Understanding State-Centric Economies
State-centric economies prioritize government control over production, distribution, and resource allocation to achieve national goals and maintain political stability. These economies rely heavily on state-owned enterprises and centralized planning, often emphasizing strategic sectors such as energy, defense, and infrastructure. Understanding state-centric models involves analyzing how regulatory policies, state intervention, and limited market competition impact economic growth, innovation, and social equity.
Historical Evolution of Economic Paradigms
The historical evolution of economic paradigms reveals a longstanding tension between market-centric and state-centric approaches, where market-centric models emphasize free trade, private enterprise, and minimal government intervention, tracing roots to Adam Smith's classical economics in the 18th century. State-centric paradigms, influenced by mercantilism and later Keynesian economics in the 20th century, argue for strategic government intervention to stabilize economies, promote industrialization, and ensure social welfare. Key events like the Great Depression and post-World War II reconstruction showcased the efficacy of state-centric policies, while neoliberal movements in the late 20th century revived market-centric frameworks emphasizing deregulation and globalization.
Key Principles of Market-Centric Models
Market-centric models prioritize decentralized decision-making, emphasizing innovation and efficiency driven by consumer demand and competition. They rely on private sector initiatives, market signals such as prices, and flexible resource allocation to optimize economic outcomes. Key principles include promoting entrepreneurship, ensuring transparency, and facilitating responsive adjustments to market changes.
Core Features of State-Centric Models
State-centric models emphasize government control over economic resources, central planning, and regulation to achieve social equity and national objectives. Core features include state ownership of key industries, centralized decision-making, and policy-driven resource allocation to stabilize markets and promote public welfare. These models prioritize collective goals over individual profit, aiming to reduce inequality and ensure sustainable development.
Impact on Economic Growth and Innovation
Market-centric systems prioritize competitive markets and private enterprise, driving economic growth through increased efficiency, entrepreneurship, and resource allocation. State-centric models emphasize government intervention and regulation, which can stabilize markets and support large-scale innovation initiatives but may slow responsiveness and reduce incentives for private innovation. Empirical studies show market-centric economies often experience higher innovation rates and faster GDP growth, while state-centric approaches can excel in infrastructure development and strategic industries.
Social Welfare: Market vs State Approaches
Market-centric approaches to social welfare prioritize individual choice and efficiency, relying on private sector solutions and competition to address social needs. State-centric models emphasize government intervention, regulation, and public funding to ensure equitable access to social services and reduce inequality. Empirical evidence suggests that hybrid systems combining market mechanisms with state oversight often achieve better social outcomes and sustainability.
Case Studies: Global Applications and Results
Market-centric models emphasize private sector efficiency and innovation, demonstrated by Singapore's economic growth driven by pro-business policies and minimal state interference. State-centric approaches prioritize government intervention and control, as seen in China's strategic state-owned enterprises fostering rapid industrialization and technological advancements. Comparative case studies reveal market-centric economies often excel in competitive global markets, while state-centric models succeed in long-term infrastructure and social development projects.
Future Trends in Economic Governance
Market-centric economic governance prioritizes decentralized decision-making, innovation, and private sector efficiency, driving global digital transformation and sustainable finance trends. State-centric models emphasize regulatory frameworks, strategic industries, and social equity, increasingly integrating technologies like AI for public policy optimization and resilient infrastructure. Future governance frameworks will likely blend these approaches, leveraging public-private partnerships to balance economic growth with social and environmental objectives.
Market-centric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com