Skills-based assessment evaluates your practical abilities and competencies directly relevant to job performance, focusing on real-world tasks rather than theoretical knowledge. This type of assessment helps employers identify candidates who possess the essential skills needed to succeed in specific roles. Explore the rest of the article to understand how skills-based assessments can enhance your hiring process and career development.
Table of Comparison
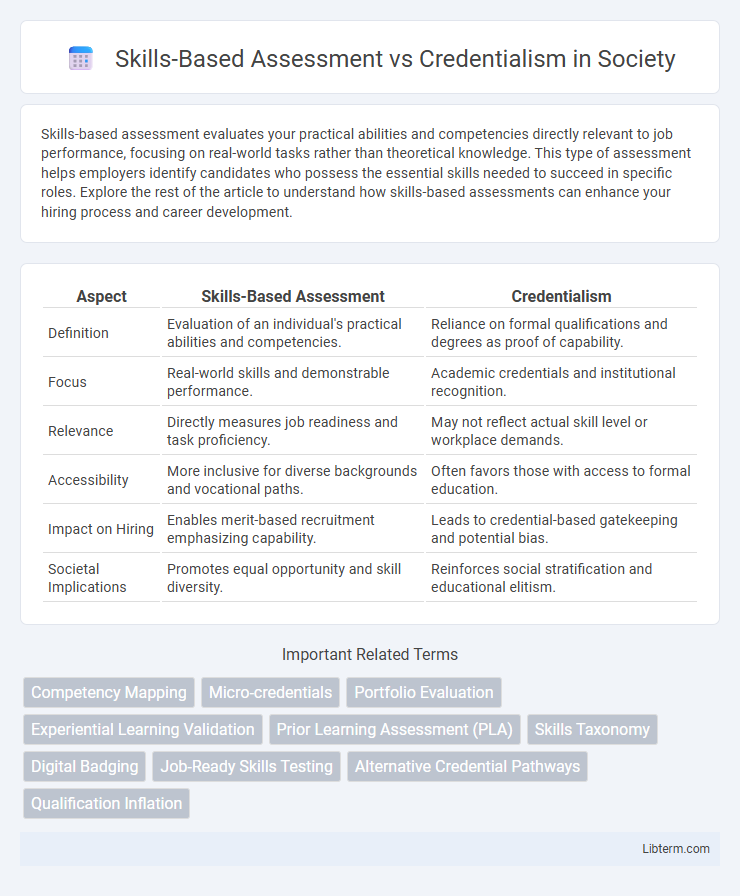
| Aspect | Skills-Based Assessment | Credentialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation of an individual's practical abilities and competencies. | Reliance on formal qualifications and degrees as proof of capability. |
| Focus | Real-world skills and demonstrable performance. | Academic credentials and institutional recognition. |
| Relevance | Directly measures job readiness and task proficiency. | May not reflect actual skill level or workplace demands. |
| Accessibility | More inclusive for diverse backgrounds and vocational paths. | Often favors those with access to formal education. |
| Impact on Hiring | Enables merit-based recruitment emphasizing capability. | Leads to credential-based gatekeeping and potential bias. |
| Societal Implications | Promotes equal opportunity and skill diversity. | Reinforces social stratification and educational elitism. |
Understanding Skills-Based Assessment
Skills-based assessment measures candidates' practical abilities and competencies directly related to job performance, offering a more accurate evaluation than traditional credentialism, which relies heavily on degrees and certifications. This approach emphasizes real-world application and continuous skill development, promoting workforce adaptability and efficiency. Organizations adopting skills-based assessments benefit from identifying talent that matches specific job requirements beyond formal qualifications.
Defining Credentialism in Modern Hiring
Credentialism in modern hiring emphasizes formal qualifications like degrees and certificates over practical skills and experience. This approach often leads employers to prioritize accredited credentials as proof of candidate competence, potentially overlooking demonstrated abilities and job-specific skills. As organizations seek to balance efficiency and talent quality, the reliance on credentialism continues to shape recruitment standards and practices.
Key Differences Between Skills-Based Assessment and Credentialism
Skills-based assessment evaluates an individual's practical abilities and competencies directly relevant to job performance, emphasizing real-world application and proficiency. Credentialism prioritizes formal qualifications, degrees, or certifications as indicators of capability, often relying on standardized educational achievements rather than hands-on skills. Key differences include the focus on demonstrated performance in skills-based assessment versus the reliance on documented credentials in credentialism, impacting hiring and advancement decisions in workplace environments.
Advantages of Skills-Based Assessment
Skills-based assessment offers a precise evaluation of a candidate's practical abilities, ensuring that individuals are proficient in the tasks relevant to the job role rather than just possessing formal qualifications. This approach reduces hiring bias by focusing on actual expertise and performance, which can lead to better job fit and increased productivity. Employers benefit from identifying talent based on demonstrated skills, promoting workforce diversity and continuous professional growth.
Limitations of Credential-Based Hiring
Credential-based hiring often overlooks the practical skills and competencies necessary for job performance, leading to mismatches between candidate qualifications and actual role requirements. This approach can perpetuate socioeconomic disparities by favoring applicants with access to higher education rather than those with relevant experience or skills. Employers may miss out on highly capable talent due to rigid credential requirements that fail to capture an individual's true potential and adaptability.
Impact on Workforce Diversity and Inclusion
Skills-based assessment emphasizes evaluating candidates on their practical abilities and competencies, leading to broader workforce diversity by prioritizing talent over traditional credentials. Credentialism often creates barriers for underrepresented groups who may lack formal degrees despite possessing relevant skills, limiting inclusion efforts. Organizations adopting skills-based hiring practices report increased representation and improved equity, fostering a more diverse and inclusive workforce environment.
Employer Perspectives: What Matters Most?
Employers prioritize skills-based assessments as they directly measure a candidate's ability to perform job-specific tasks, ensuring practical competence and reducing training costs. Credentialism often serves as a preliminary filter but may not accurately reflect current skills or work readiness, leading employers to value proven capabilities over formal qualifications. Emphasizing skill proficiency supports better hiring decisions, workforce adaptability, and aligns talent acquisition with real-world job demands.
Case Studies: Real-World Outcomes
Case studies reveal that skills-based assessment enhances workforce competency by accurately measuring practical abilities, unlike credentialism, which often prioritizes formal qualifications over actual performance. Companies implementing skills-based evaluations report higher employee productivity and reduced turnover compared to traditional credential-focused hiring practices. Real-world outcomes demonstrate that prioritizing skills aligns better with job requirements, fostering innovation and adaptability in dynamic industries.
Future Trends in Recruitment Strategies
Future recruitment strategies increasingly emphasize skills-based assessments over traditional credentialism, leveraging AI-driven platforms to evaluate candidates' competencies in real-time. Predictive analytics and virtual simulations enable employers to identify practical skills and cultural fit more accurately than relying solely on academic degrees or certifications. This shift accelerates talent acquisition efficiency and promotes diversity by valuing demonstrable abilities over formal qualifications.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Selecting between skills-based assessment and credentialism hinges on aligning evaluation methods with organizational goals and workforce needs. Skills-based assessments provide a direct measure of an individual's capabilities, fostering a candidate pool equipped with practical proficiency relevant to the role. Credentialism emphasizes formal qualifications and certifications, which may support compliance and standardization but can overlook hands-on expertise essential for job performance.
Skills-Based Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com