Individualism emphasizes personal freedom, self-reliance, and the importance of individual rights over collective control, fostering creativity and innovation. It encourages you to pursue your unique path and express your authentic self without undue societal pressure. Explore the rest of the article to understand how individualism shapes cultures and impacts social dynamics.
Table of Comparison
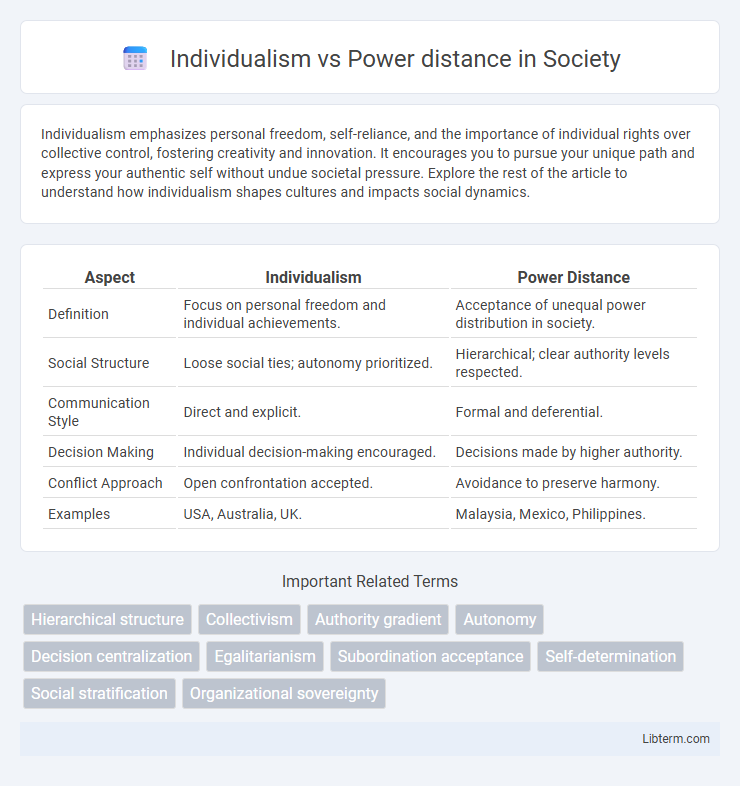
| Aspect | Individualism | Power Distance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on personal freedom and individual achievements. | Acceptance of unequal power distribution in society. |
| Social Structure | Loose social ties; autonomy prioritized. | Hierarchical; clear authority levels respected. |
| Communication Style | Direct and explicit. | Formal and deferential. |
| Decision Making | Individual decision-making encouraged. | Decisions made by higher authority. |
| Conflict Approach | Open confrontation accepted. | Avoidance to preserve harmony. |
| Examples | USA, Australia, UK. | Malaysia, Mexico, Philippines. |
Understanding Individualism: Core Concepts
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and the prioritization of individual goals over group objectives. Cultures with high individualism encourage independent decision-making and value personal achievements and rights. This contrasts with power distance, where hierarchical structures and unequal power distribution affect social interactions and acceptance of authority.
Defining Power Distance in Society
Power distance in society measures the extent to which less powerful members accept and expect unequal power distribution within institutions and organizations. High power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical structures and authority, while low power distance societies promote equality and participative decision-making. Understanding power distance is crucial for analyzing social dynamics, leadership styles, and communication patterns across different cultural contexts.
Historical Roots of Individualism and Power Distance
Individualism traces its historical roots to Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke who emphasized personal freedom and self-reliance, shaping Western cultures with a strong focus on individual rights and autonomy. Power distance originates from hierarchical social structures evident in feudal and caste systems across Asia and Africa, where authority and unequal power distribution were institutionalized. These divergent historical foundations explain why low power distance correlates with individualistic societies valuing equality, while high power distance aligns with collectivist cultures respecting authority and rank.
Individualism vs Power Distance: Key Differences
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, self-reliance, and individual goals, while Power Distance reflects the acceptance of hierarchical order and unequal power distribution within a society. In individualistic cultures, people value independence and expect equal treatment, whereas high power distance cultures prioritize authority, obedience, and clear social ranks. These fundamental differences shape communication styles, workplace dynamics, and decision-making processes across diverse cultural contexts.
Cultural Impacts on Individualism and Power Distance
Cultural impacts on individualism and power distance significantly influence social behavior and organizational dynamics across societies. High individualism cultures prioritize personal autonomy and self-expression, fostering innovation and open communication, whereas low individualism cultures emphasize collective goals and conformity, reinforcing group cohesion. Conversely, cultures with high power distance accept hierarchical structures and unequal power distribution, shaping leadership styles and decision-making processes, while low power distance cultures promote egalitarianism and participative management.
Workplace Dynamics: Individualism and Power Distance
Workplace dynamics are significantly influenced by the cultural dimensions of individualism and power distance, affecting communication styles and decision-making processes. In individualistic cultures, employees prioritize personal goals and autonomy, fostering innovation and self-reliance, while low power distance encourages open dialogue and egalitarian relationships between management and staff. Conversely, high power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical structures and respect for authority, with collective goals often taking precedence over individual desires, leading to centralized decision-making and formal communication channels.
Leadership Styles Across Different Cultures
Leadership styles fluctuate significantly between cultures with varying levels of individualism and power distance; in individualistic societies like the United States, leaders tend to adopt participative and democratic approaches that empower employees. Conversely, in high power distance cultures such as India and Malaysia, authoritarian or paternalistic leadership is more prevalent, emphasizing hierarchical structures and obedience. Understanding these cultural dimensions is crucial for multinational organizations to tailor leadership strategies that enhance motivation and productivity across diverse global teams.
Decision-Making in Individualistic vs Hierarchical Societies
Decision-making in individualistic societies prioritizes personal autonomy and independent judgment, encouraging individuals to assert their opinions and challenge authority. In contrast, hierarchical societies with high power distance emphasize centralized decision-making, where deference to authority and group consensus are key to maintaining social order. The contrast shapes organizational dynamics, with individualistic cultures fostering innovation through personal initiative, while hierarchical cultures rely on structured communication and respect for established roles.
Social Relationships and Authority Structures
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and prioritizes direct, egalitarian social relationships, fostering open communication and equal participation. Power distance reflects acceptance of hierarchical authority structures where unequal power distribution shapes social interactions, promoting respect for authority and formal roles. Societies with low power distance and high individualism encourage independent decision-making and challenge traditional power dynamics.
The Future of Individualism and Power Distance in a Globalized World
The future of individualism and power distance in a globalized world will be shaped by increasing cross-cultural interactions and digital connectivity, fostering a complex blend of personal autonomy and hierarchical respect. Emerging economies may experience shifts towards lower power distance as access to information empowers individuals, while established societies might reinforce individualistic values through technological innovation and social mobility. Organizations navigating this dynamic must balance cultural sensitivity with adaptive leadership to thrive in an interconnected global market.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com