Information equity ensures that all individuals have fair access to accurate, relevant, and timely information regardless of socioeconomic, geographic, or cultural barriers. Achieving information equity involves addressing digital divides, improving information literacy, and creating inclusive technologies that serve diverse communities. Explore the rest of this article to learn how information equity can empower Your decisions and foster a more just society.
Table of Comparison
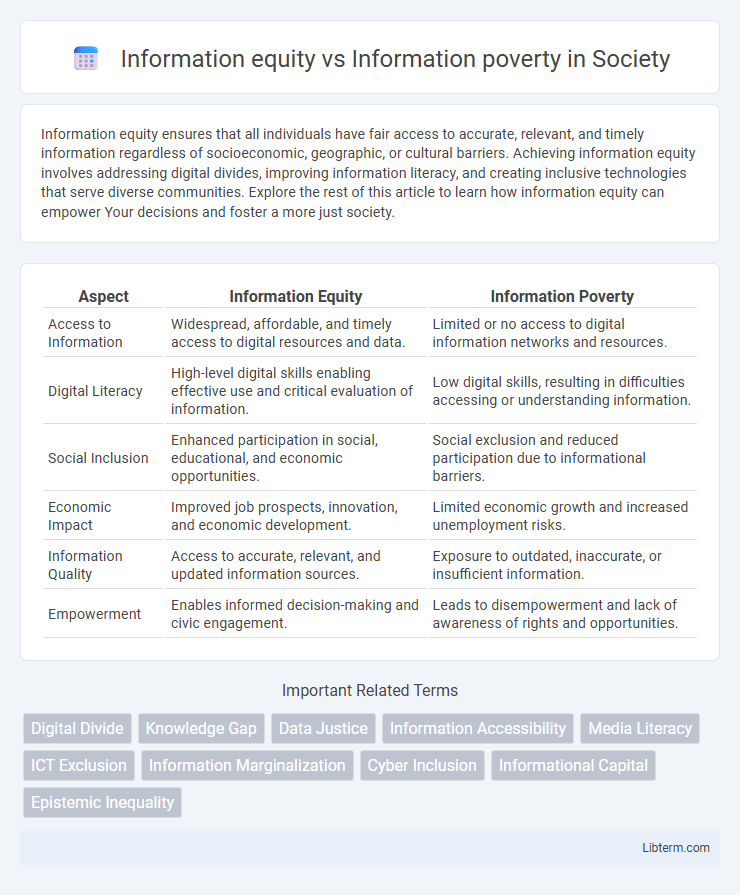
| Aspect | Information Equity | Information Poverty |
|---|---|---|
| Access to Information | Widespread, affordable, and timely access to digital resources and data. | Limited or no access to digital information networks and resources. |
| Digital Literacy | High-level digital skills enabling effective use and critical evaluation of information. | Low digital skills, resulting in difficulties accessing or understanding information. |
| Social Inclusion | Enhanced participation in social, educational, and economic opportunities. | Social exclusion and reduced participation due to informational barriers. |
| Economic Impact | Improved job prospects, innovation, and economic development. | Limited economic growth and increased unemployment risks. |
| Information Quality | Access to accurate, relevant, and updated information sources. | Exposure to outdated, inaccurate, or insufficient information. |
| Empowerment | Enables informed decision-making and civic engagement. | Leads to disempowerment and lack of awareness of rights and opportunities. |
Understanding Information Equity
Understanding information equity involves recognizing that all individuals should have fair access to accurate, timely, and relevant information regardless of socioeconomic status, geographic location, or education level. Information equity addresses disparities caused by digital divides, language barriers, and resource limitations, promoting inclusive participation in the information society. Achieving information equity requires investment in infrastructure, digital literacy programs, and policies that support open access to information resources for marginalized communities.
Defining Information Poverty
Information poverty refers to the lack of access to, use of, or skills to effectively utilize information, resulting in significant barriers to education, economic opportunities, and social participation. It is characterized by limited access to digital technologies, reliable internet, and information literacy, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. Addressing information poverty is crucial for fostering information equity, which ensures fair and equal access to information resources for all individuals.
The Digital Divide: Causes and Consequences
Information equity ensures equal access to digital resources and technology, bridging gaps created by socioeconomic status, geographic location, and education disparities. Information poverty arises when marginalized communities lack reliable internet, digital literacy, and affordable devices, deepening the digital divide. The digital divide perpetuates social inequality by limiting access to essential services, education, and economic opportunities for underserved populations.
Social Impacts of Unequal Information Access
Unequal information access exacerbates social disparities by limiting educational and economic opportunities for marginalized communities, resulting in information poverty. Information equity ensures that diverse populations have equal access to digital resources and knowledge, which fosters social inclusion and empowerment. Addressing this gap improves civic participation, reduces misinformation, and promotes equitable development across societies.
Barriers to Achieving Information Equity
Barriers to achieving information equity include limited access to digital technologies, socio-economic disparities, and inadequate digital literacy, which disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Geographic isolation and linguistic differences further restrict equitable access to reliable information sources. Overcoming these challenges requires targeted investment in infrastructure, inclusive educational programs, and policies promoting affordable internet access.
Role of Technology in Bridging Information Gaps
Technology plays a pivotal role in addressing information equity by providing widespread access to digital resources, educational content, and communication tools, thereby reducing information poverty in underserved communities. Innovations such as affordable internet connectivity, mobile devices, and open-source platforms empower marginalized populations to gain knowledge and participate actively in the information society. Bridging these information gaps through technology enhances social inclusion, economic development, and informed decision-making processes globally.
Education and Information Literacy as Solutions
Information equity ensures all individuals have access to quality educational resources and effective information literacy skills, bridging gaps in knowledge acquisition and critical thinking. Information poverty limits educational opportunities, hindering intellectual growth and socioeconomic mobility due to inadequate access to relevant data and digital tools. Promoting robust information literacy programs and expanding digital infrastructure in underserved communities are key solutions to overcoming information poverty and achieving equitable education outcomes.
Government Policies Promoting Information Equity
Government policies promoting information equity focus on expanding broadband infrastructure, subsidizing internet access for low-income populations, and supporting digital literacy programs. Initiatives like the U.S. Federal Communications Commission's Lifeline program and the Digital India campaign address information poverty by reducing barriers to technology and enhancing access to reliable information. These policies aim to create an inclusive digital environment that fosters equal opportunities for education, healthcare, and economic participation.
Community Initiatives Against Information Poverty
Community initiatives against information poverty focus on bridging the digital divide by providing equitable access to digital resources, educational programs, and reliable internet connectivity. These initiatives empower marginalized populations through technology literacy workshops, public Wi-Fi access points, and library-based digital hubs that enhance information equity. Effective programs leverage local partnerships and data-driven strategies to address barriers, promoting inclusive knowledge sharing and socioeconomic development.
Future Strategies for Inclusive Information Access
Future strategies for inclusive information access must address the persistent gap between information equity and information poverty by investing in affordable digital infrastructure and expanding broadband connectivity in underserved regions. Empowering communities through digital literacy programs ensures equitable participation in the information society and combats disparities rooted in socioeconomic status or geographic isolation. Policy frameworks should prioritize open access initiatives and diverse content representation to foster a more inclusive and democratic information ecosystem.
Information equity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com