The Global South encompasses regions primarily in Latin America, Africa, and Asia, characterized by shared experiences of colonial history, economic challenges, and development disparities compared to the Global North. Understanding the social, political, and economic dynamics of the Global South is essential for addressing global inequality and promoting sustainable development. Explore the rest of the article to learn how these factors shape your world and the future of international relations.
Table of Comparison
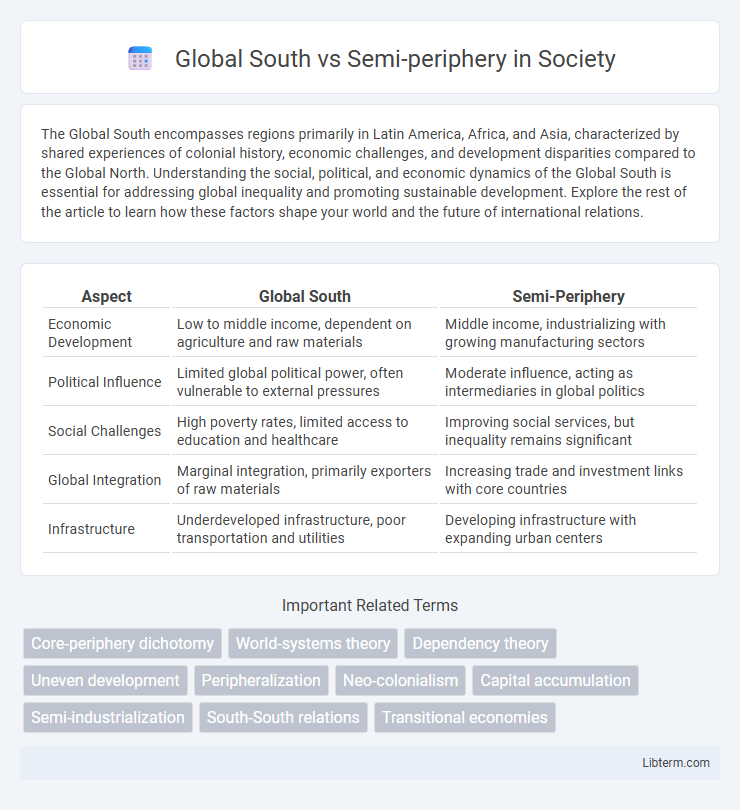
| Aspect | Global South | Semi-Periphery |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Development | Low to middle income, dependent on agriculture and raw materials | Middle income, industrializing with growing manufacturing sectors |
| Political Influence | Limited global political power, often vulnerable to external pressures | Moderate influence, acting as intermediaries in global politics |
| Social Challenges | High poverty rates, limited access to education and healthcare | Improving social services, but inequality remains significant |
| Global Integration | Marginal integration, primarily exporters of raw materials | Increasing trade and investment links with core countries |
| Infrastructure | Underdeveloped infrastructure, poor transportation and utilities | Developing infrastructure with expanding urban centers |
Defining the Global South and Semi-Periphery
The Global South encompasses developing nations primarily in Africa, Latin America, and Asia, characterized by lower income levels, limited industrialization, and post-colonial economic challenges. The semi-periphery refers to countries that act as intermediaries between the Global North and Global South, exhibiting moderate industrialization and economic development, such as Brazil, South Africa, and Mexico. These semi-peripheral states play a crucial role in global trade and industrial networks, balancing exploitation and development within the world-systems theory framework.
Historical Origins and Development
The Global South, encompassing regions primarily in Latin America, Africa, and Asia, has historically experienced colonial exploitation and resource extraction that shaped its socio-economic conditions. The semi-periphery, a concept in world-systems theory, represents countries with intermediate levels of industrialization and development, often transitioning from peripheral dependency to more autonomous economic roles. Both categories emerged from the geopolitical and economic legacies of imperialism, with the semi-periphery serving as a buffer zone facilitating trade and political stability between the core and the periphery.
Economic Structures and Growth Patterns
The Global South primarily comprises low- to middle-income countries characterized by agrarian-based economies and limited industrialization, leading to slower and more volatile growth patterns. Semi-periphery nations exhibit diversified economic structures with emerging industrial sectors and increased integration into global trade networks, fostering more stable and moderate growth rates. These differences in economic complexity and global economic roles significantly influence development trajectories and resilience to external shocks.
Political Influence and International Relations
The Global South encompasses developing countries with limited political influence in major international organizations such as the United Nations Security Council, whereas semi-periphery nations like Brazil, India, and South Africa hold more strategic positions, often acting as regional power brokers. Semi-periphery states leverage their intermediary status to negotiate favorable economic and political terms in global governance, balancing between core powers and the Global South. This dynamic shapes international relations by creating a layered geopolitical landscape where semi-periphery countries play critical roles in multilateral agreements, trade blocs, and diplomatic alliances.
Social Inequality and Development Indicators
The Global South often experiences higher levels of social inequality characterized by disparities in income, education, and healthcare access compared to Semi-periphery regions, which show moderate development indicators due to partial industrialization and more diversified economies. Development metrics such as the Human Development Index (HDI), Gini coefficient, and access to basic services reveal that Semi-periphery countries typically outperform Global South nations in economic stability and social mobility. Despite progress, both regions face challenges in reducing poverty and enhancing equitable growth, with social inequality remaining a persistent barrier to sustainable development.
Case Studies: Examples from Each Category
The Global South includes countries such as India, Brazil, and South Africa, which exemplify developing economies with significant challenges in infrastructure and social equity. Semi-periphery nations like Mexico, Malaysia, and Turkey demonstrate transitional characteristics with moderate industrialization and emerging markets driving regional influence. Case studies reveal that India's IT sector highlights the Global South's potential for growth, while Mexico's automotive industry typifies semi-periphery economic diversification.
The Role in Globalization and Trade
The Global South, comprising emerging economies primarily in Africa, Latin America, and parts of Asia, plays a crucial role in globalization by supplying raw materials and serving as growing consumer markets. Semi-periphery countries like Brazil, India, and South Africa bridge the Global South and Global North by engaging in both manufacturing and resource extraction, facilitating trade flows and technology transfer. These semi-peripheral nations actively participate in global value chains, enhancing regional integration and reshaping trade dynamics within the global economy.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
The Global South faces challenges including limited infrastructure, economic dependency, and social inequalities, while the semi-periphery holds a strategic position between core and periphery nations with potential for industrial growth and political influence. Opportunities for the Global South lie in leveraging demographic dividends, natural resources, and digital innovation to drive sustainable development. Semi-peripheral countries can capitalize on their transitional status to attract foreign investment, diversify economies, and facilitate technology transfer, fostering regional integration and economic resilience.
Transition: Movement Between Categories
The transition from the Global South to the semi-periphery involves complex economic and political shifts characterized by industrialization, infrastructural development, and increased integration into global trade networks. Countries moving into the semi-periphery often exhibit rising middle-income status, diversification of their economies, and growing influence in regional geopolitics. This movement reflects dynamic processes where states balance dependency on core countries with strategies to enhance autonomy and economic resilience.
Implications for Global Policy and Future Research
The distinction between the Global South and semi-periphery regions shapes global policy by highlighting diverse developmental challenges and opportunities, necessitating tailored approaches in trade, investment, and climate strategy frameworks. Understanding the economic and political dynamics within semi-periphery countries offers critical insights for policies aimed at reducing inequality and fostering sustainable growth. Future research must prioritize interdisciplinary analysis of these regions' roles in global value chains and geopolitical shifts to inform inclusive international cooperation and equity-driven development agendas.
Global South Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com