Participatory democracy empowers citizens to actively engage in decision-making processes beyond just voting, fostering greater transparency and accountability in governance. This approach enhances civic responsibility and ensures that diverse voices influence policies affecting their communities. Discover how participatory democracy can transform Your role in shaping a more inclusive political landscape by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
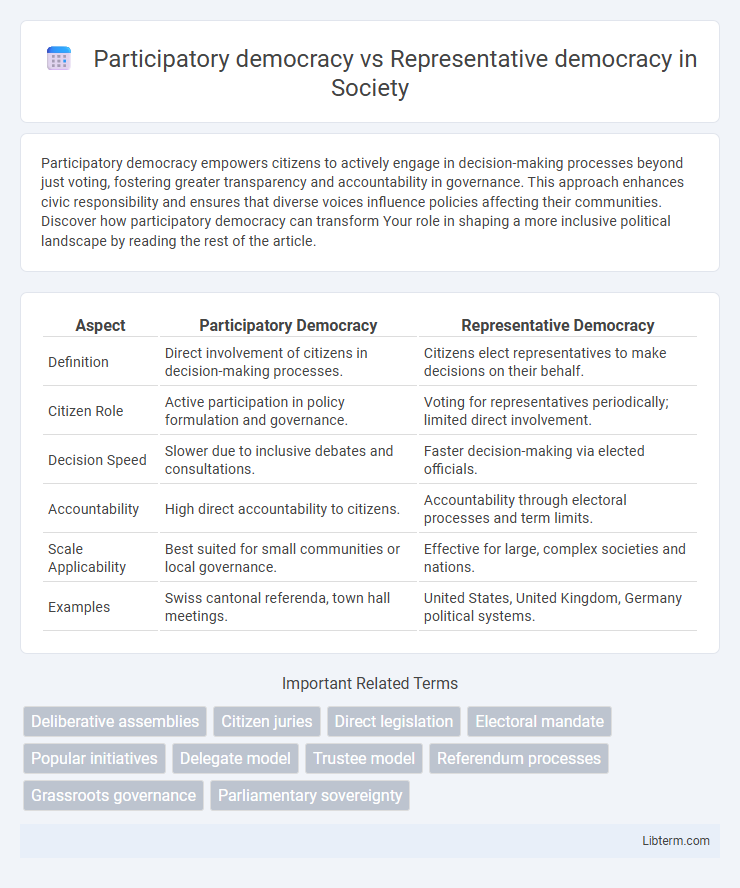
| Aspect | Participatory Democracy | Representative Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes. | Citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. |
| Citizen Role | Active participation in policy formulation and governance. | Voting for representatives periodically; limited direct involvement. |
| Decision Speed | Slower due to inclusive debates and consultations. | Faster decision-making via elected officials. |
| Accountability | High direct accountability to citizens. | Accountability through electoral processes and term limits. |
| Scale Applicability | Best suited for small communities or local governance. | Effective for large, complex societies and nations. |
| Examples | Swiss cantonal referenda, town hall meetings. | United States, United Kingdom, Germany political systems. |
Understanding Participatory Democracy
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes, empowering individuals to actively shape policies and community outcomes. It contrasts with representative democracy, where elected officials make decisions on behalf of constituents, potentially limiting public engagement. Understanding participatory democracy involves recognizing the importance of inclusive deliberation, grassroots participation, and collective responsibility in fostering responsive governance.
Defining Representative Democracy
Representative democracy is a system where citizens elect officials to make decisions and create laws on their behalf, emphasizing indirect participation in governance. This form of democracy relies on elected representatives to reflect the public's interests, balancing efficiency and public accountability in political processes. It contrasts with participatory democracy, which encourages direct citizen involvement in decision-making at all levels.
Historical Contexts of Both Systems
Participatory democracy, with roots in ancient Athens, emphasizes direct citizen involvement in decision-making processes, reflecting the political ideals of classical Greece from around the 5th century BCE. Representative democracy emerged prominently in the 17th and 18th centuries during the Enlightenment, influenced by thinkers like John Locke and Montesquieu, as a practical system to govern larger, more complex societies through elected officials. The evolution of these systems is shaped by the scale of populations and technological advancements, leading to representative democracy's dominance in modern nation-states while participatory elements persist in local governance and civic engagement movements.
Key Principles and Values Compared
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct citizen involvement in decision-making, valuing active engagement, transparency, and collective responsibility to enhance political equality. Representative democracy relies on elected officials to make decisions on behalf of citizens, prioritizing efficiency, accountability, and the protection of minority rights within a structured institutional framework. Both systems uphold democratic legitimacy but differ in the balance between direct public participation and delegated authority.
Role of Citizens: Direct vs. Delegated Power
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct citizen involvement in decision-making processes, allowing individuals to have a hands-on role in shaping policies and laws. Representative democracy relies on elected officials to delegate decision-making authority, where citizens participate mainly through voting to choose these representatives. The primary difference lies in the immediacy of power exercise: direct in participatory systems versus delegated in representative systems.
Accountability and Transparency Differences
Participatory democracy enhances accountability and transparency by directly involving citizens in decision-making processes, ensuring their voices influence policy outcomes and reducing intermediaries. Representative democracy relies on elected officials to make decisions, which can create layers between the public and policymakers, potentially decreasing transparency and complicating accountability due to delegation. The direct engagement in participatory systems fosters more immediate feedback and clearer mechanisms for holding leaders responsible compared to the more indirect accountability structures characteristic of representative democracy.
Strengths of Participatory Democracy
Participatory democracy empowers citizens to actively engage in decision-making processes, fostering enhanced transparency and accountability in governance. It promotes civic education and social cohesion by encouraging diverse voices and community involvement, leading to policies that better reflect the public's needs and values. This direct engagement often results in increased political legitimacy and improved responsiveness compared to representative democracy systems.
Advantages of Representative Democracy
Representative democracy offers the advantage of efficient decision-making by electing skilled officials to manage complex governance tasks on behalf of the population. It ensures stability and continuity in government while allowing citizens to influence policies through periodic elections. This system also enables broader participation by accommodating large and diverse populations that would find direct involvement impractical.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Models
Participatory democracy faces challenges such as scalability issues, where direct citizen involvement becomes impractical in large populations, and the risk of decision-making dominated by highly vocal minorities rather than a broad consensus. Representative democracy is criticized for potential disconnects between elected officials and constituents, leading to voter apathy and lack of accountability, as well as susceptibility to influence from interest groups and political elites. Both models struggle with ensuring equitable participation and maintaining transparency, which are essential for legitimacy and effective governance.
The Future of Democratic Governance
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct citizen involvement in decision-making processes, promoting transparency and accountability, while representative democracy relies on elected officials to make policy decisions on behalf of the populace, ensuring efficiency and scalability in governance. The future of democratic governance likely involves a hybrid model leveraging digital technologies, such as e-democracy platforms and blockchain voting systems, to enhance citizen engagement without sacrificing the benefits of representative structures. Innovations in civic tech and deliberative forums can bridge gaps between participation and representation, fostering more inclusive, resilient, and adaptive democratic institutions.
Participatory democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com