Ethnic groups are communities of people who share a common cultural heritage, language, ancestry, or social experience that distinguishes them from other groups. Understanding the dynamics of ethnic identity can provide deeper insights into social cohesion, conflict, and diversity within societies. Explore this article to learn how ethnic groups influence cultural landscapes and your role in fostering inclusivity.
Table of Comparison
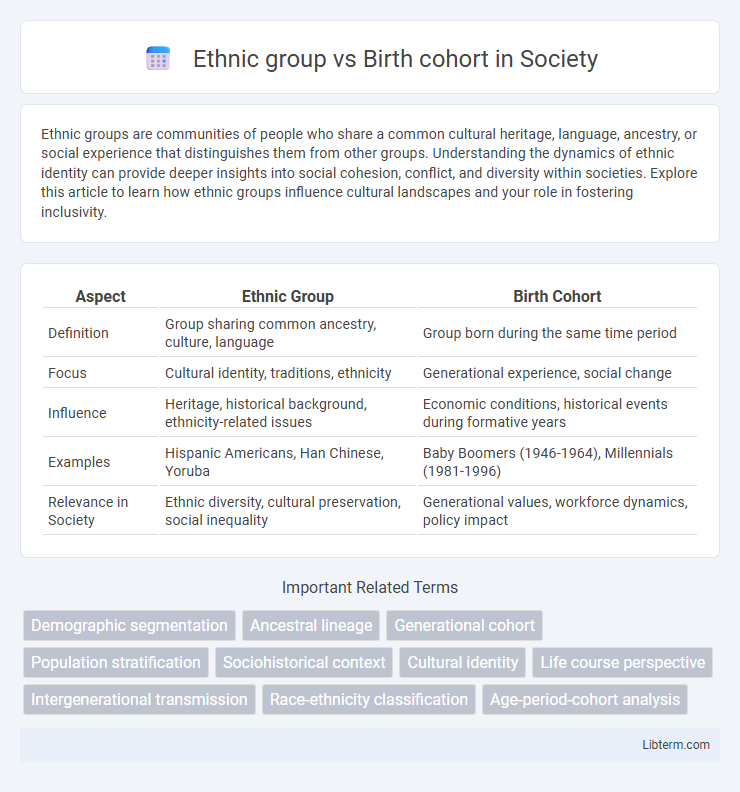
| Aspect | Ethnic Group | Birth Cohort |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group sharing common ancestry, culture, language | Group born during the same time period |
| Focus | Cultural identity, traditions, ethnicity | Generational experience, social change |
| Influence | Heritage, historical background, ethnicity-related issues | Economic conditions, historical events during formative years |
| Examples | Hispanic Americans, Han Chinese, Yoruba | Baby Boomers (1946-1964), Millennials (1981-1996) |
| Relevance in Society | Ethnic diversity, cultural preservation, social inequality | Generational values, workforce dynamics, policy impact |
Definition of Ethnic Group
An ethnic group is a community of people who share common cultural traits, language, ancestry, and often a shared history or geographic origin, distinguishing them from other groups. Unlike birth cohorts, which classify individuals based on their year or period of birth to analyze generational characteristics, ethnic groups emphasize cultural identity and social connections. Understanding the definition of ethnic group is essential for interpreting social dynamics, migration patterns, and demographic research in multicultural societies.
Understanding Birth Cohort
Understanding birth cohort involves analyzing groups of individuals born within the same time period to identify patterns in social, economic, and health outcomes that reflect shared historical and environmental influences. Unlike ethnic group classifications, which focus on cultural, linguistic, and ancestral attributes, birth cohort analysis highlights generational experiences and temporal trends that impact behaviors and life trajectories. This approach enables researchers to track changes across generations and assess how specific events or policies uniquely affect each cohort's development.
Key Differences Between Ethnic Groups and Birth Cohorts
Ethnic groups represent populations defined by shared cultural, linguistic, or ancestral traits, influencing social identity and historical experiences, while birth cohorts consist of individuals born within the same time period, shaping collective attitudes and behaviors due to shared generational events. Key differences lie in the basis of classification--ethnicity is rooted in inherited cultural heritage, whereas birth cohorts are temporal groups influenced by socio-historical contexts during formative years. Understanding these distinctions allows for targeted analysis of demographic trends, social patterns, and policy impacts across diverse populations.
Cultural Identity vs Generational Identity
Ethnic group shapes cultural identity through shared language, traditions, and heritage that persist across time, anchoring individuals to their ancestral roots. Birth cohort influences generational identity by reflecting the unique social, economic, and political experiences of people born during the same period, creating a sense of collective belonging. Cultural identity emphasizes long-standing ethnic customs, while generational identity highlights temporal experiences defining a specific age group's worldview.
Social Dynamics within Ethnic Groups
Social dynamics within ethnic groups are profoundly shaped by the interactions between different birth cohorts, reflecting shifts in cultural values, traditions, and social norms over time. Older cohorts often serve as custodians of heritage and collective memory, influencing identity preservation, while younger cohorts introduce new perspectives and adaptations in response to contemporary challenges. Intergenerational dialogue and conflict within ethnic groups drive social change, impacting cohesion, transmission of knowledge, and the evolution of group identity.
Historical Context Shaping Birth Cohorts
Historical context shapes birth cohorts by influencing shared experiences, cultural norms, and socioeconomic conditions during formative years. Ethnic groups often experience distinct historical events such as migration, segregation, or policy changes that differentially impact their birth cohorts. These collective experiences create unique generational identities tied to both ethnicity and time period, affecting attitudes, behaviors, and opportunities across lifespans.
Impact on Health and Behavioral Studies
Ethnic group and birth cohort are critical variables influencing health and behavioral studies, as ethnic group captures genetic, cultural, and environmental factors affecting disease prevalence, while birth cohort reflects shared historical and social experiences shaping health behaviors. Variations in health outcomes, such as incidence of chronic diseases or mental health disorders, often emerge from the intersection of ethnic group distinctions and cohort-specific exposures to risk factors. Understanding these dimensions enables researchers to identify targeted interventions and address health disparities effectively.
Interplay of Ethnicity and Generational Change
Ethnic group and birth cohort significantly influence social dynamics, with ethnicity shaping cultural identity and birth cohorts reflecting generational experiences. The interplay between these factors reveals how generational change affects ethnic group behaviors, attitudes, and socioeconomic outcomes across time. Examining longitudinal data highlights shifts in intergenerational mobility, assimilation patterns, and identity negotiation within diverse ethnic populations.
Policy Implications and Social Research
Understanding the distinctions between ethnic groups and birth cohorts is crucial for effective policy design and social research, as each category captures different dimensions of identity and experience that influence social outcomes. Ethnic group analysis informs targeted policies addressing cultural, linguistic, and systemic inequalities, while birth cohort analysis highlights generational shifts in behavior, attitudes, and socioeconomic conditions. Integrating both frameworks enables more nuanced assessments of inequality and social dynamics, improving the precision of interventions and the robustness of social science methodologies.
Future Trends in Ethnic and Cohort Analysis
Future trends in ethnic group and birth cohort analysis will increasingly leverage big data and machine learning to uncover nuanced patterns in demographic shifts and health disparities. Researchers focus on integrating genetic, environmental, and socioeconomic variables to predict how ethnic compositions and cohort-specific behaviors evolve over time. Enhanced predictive models aim to inform public policy and healthcare strategies, addressing the complex interplay of ethnicity and generational experiences in diverse populations.
Ethnic group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com