Voluntary associations are organizations formed by individuals who come together based on shared interests, goals, or values without coercion. These groups play a vital role in fostering community engagement, social support, and collective action on various issues. Discover how your involvement in voluntary associations can enhance your social network and impact by reading the rest of the article.
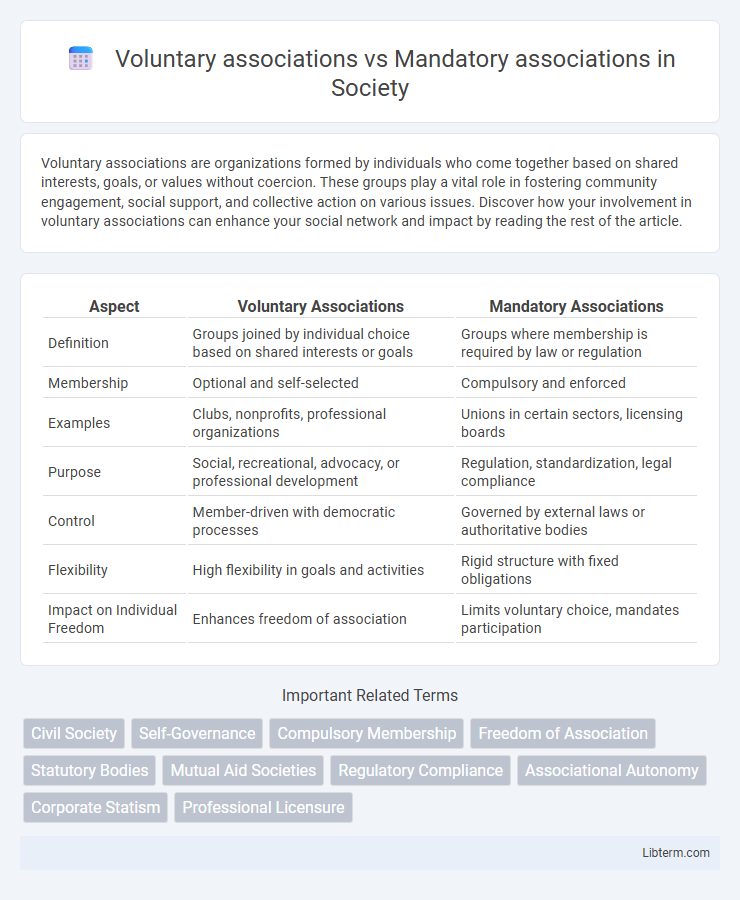
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Voluntary Associations | Mandatory Associations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Groups joined by individual choice based on shared interests or goals | Groups where membership is required by law or regulation |
| Membership | Optional and self-selected | Compulsory and enforced |
| Examples | Clubs, nonprofits, professional organizations | Unions in certain sectors, licensing boards |
| Purpose | Social, recreational, advocacy, or professional development | Regulation, standardization, legal compliance |
| Control | Member-driven with democratic processes | Governed by external laws or authoritative bodies |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in goals and activities | Rigid structure with fixed obligations |
| Impact on Individual Freedom | Enhances freedom of association | Limits voluntary choice, mandates participation |
Introduction to Voluntary and Mandatory Associations
Voluntary associations consist of individuals who join willingly based on shared interests, goals, or values, fostering collaboration without legal obligation. Mandatory associations require membership by law or regulation, compelling individuals to participate in specific groups such as professional bodies or labor unions. Understanding the distinctions between voluntary and mandatory associations highlights their different roles in social organization, legal frameworks, and individual autonomy.
Definitions: Voluntary vs Mandatory Associations
Voluntary associations are organizations formed by individuals who choose to join based on shared interests or goals, emphasizing freedom of association and personal commitment. Mandatory associations require membership by law or regulation, often to ensure compliance, standardization, or collective responsibility within a specific industry or profession. The key distinction lies in the element of choice, with voluntary associations relying on individual willingness, while mandatory associations are imposed by external authority.
Historical Development of Associations
Voluntary associations evolved during the Enlightenment as individuals sought to organize for common social, political, and economic goals without state coercion, reflecting growing values of freedom and civil society. Mandatory associations emerged later, often tied to state formation and regulatory needs, requiring membership or participation by law to ensure social order and collective responsibilities. The historical development highlights a shift from purely voluntary collective action to more structured, legally enforced associations intertwined with governance and public administration.
Key Characteristics and Structures
Voluntary associations are formed by individuals who choose to join based on shared interests, goals, or values, featuring flexible structures often governed by democratically elected officers and member participation. Mandatory associations require membership by law or regulation, typically exhibiting rigid hierarchical structures with authority centralized in formal administrative bodies. Key distinctions include the degree of member autonomy, the basis of membership, and the governance framework influencing decision-making processes.
Legal Frameworks Governing Associations
Legal frameworks governing voluntary associations typically provide flexible registration processes and allow for autonomous governance, emphasizing members' freedom of choice and voluntary participation. In contrast, mandatory associations are often subject to stricter regulations, including compulsory membership requirements and more rigorous oversight to ensure compliance with state or industry mandates. Both frameworks delineate rights and responsibilities but differ fundamentally in the scope of obligations imposed on members and the degree of governmental control.
Membership Processes and Requirements
Voluntary associations require members to actively choose participation, typically involving an application or invitation process based on shared interests or goals, with membership often contingent on acceptance criteria such as qualifications or commitment levels. Mandatory associations enforce membership by law or regulation, obligating individuals within a specific group or profession to join, frequently requiring proof of eligibility like certification or licensure. The membership process in voluntary associations emphasizes personal motivation and selective criteria, whereas mandatory associations prioritize compliance and standardized eligibility verification.
Roles and Functions in Society
Voluntary associations play a critical role in society by fostering social cohesion, enabling civic participation, and addressing community needs through self-selected membership and shared interests. Mandatory associations, often established by law or professional requirements, ensure standardized practices, regulate behavior, and maintain accountability within industries or professions. Both types of associations contribute to social order and development but differ primarily in membership criteria and the scope of their societal functions.
Advantages and Challenges of Voluntary Associations
Voluntary associations offer significant advantages such as fostering individual freedom, promoting social engagement, and enabling members to pursue shared interests voluntarily, leading to higher motivation and commitment. Challenges include potential organizational instability due to fluctuating membership, difficulties in securing consistent funding, and varying levels of member participation that can impede effective decision-making. Despite these challenges, voluntary associations remain crucial for community building and advocacy by leveraging personal investment and diverse contributions.
Advantages and Challenges of Mandatory Associations
Mandatory associations ensure consistent membership, resulting in stable funding and unified representation for collective bargaining or advocacy purposes. They improve industry standards and compliance by enforcing regulations that voluntary groups may lack the authority to implement. Challenges include potential resistance from members obligated to participate, reduced individual freedom, and the risk of bureaucratic inefficiency due to compulsory involvement.
Impact on Community Engagement and Governance
Voluntary associations foster community engagement by encouraging active participation and shared decision-making, leading to stronger social bonds and enhanced local governance responsiveness. Mandatory associations, often imposed by regulatory frameworks, ensure uniform compliance and resource pooling but may limit individual initiative and reduce grassroots involvement. The balance between voluntary commitment and mandatory structure significantly shapes the effectiveness of governance and the depth of community empowerment.
Voluntary associations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com