Social integration fosters a sense of belonging and community by connecting individuals across diverse backgrounds and promoting mutual respect and understanding. It helps reduce social inequalities and enhances cohesion, leading to healthier, more resilient societies. Explore the rest of the article to discover how social integration can positively impact your life and community.
Table of Comparison
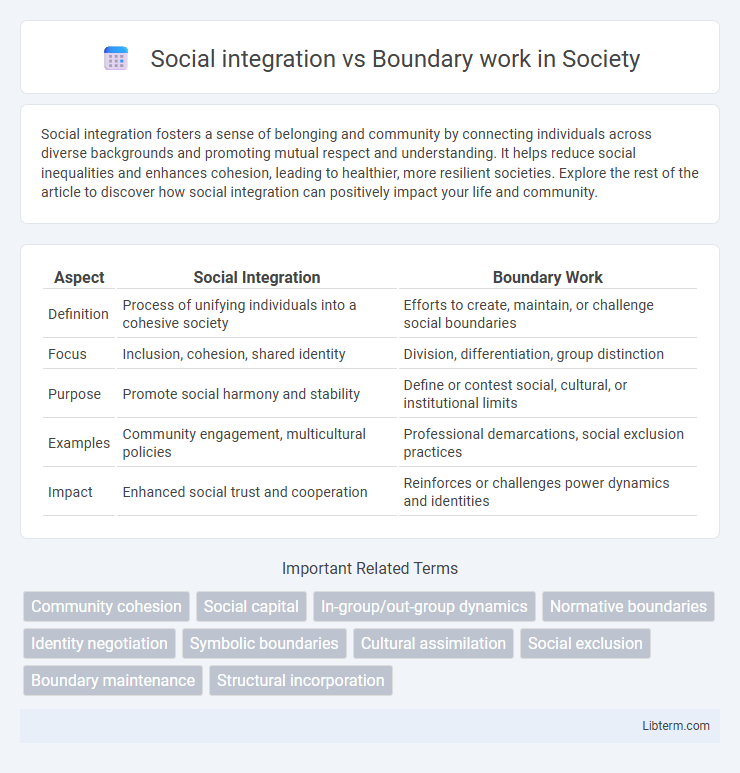
| Aspect | Social Integration | Boundary Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of unifying individuals into a cohesive society | Efforts to create, maintain, or challenge social boundaries |
| Focus | Inclusion, cohesion, shared identity | Division, differentiation, group distinction |
| Purpose | Promote social harmony and stability | Define or contest social, cultural, or institutional limits |
| Examples | Community engagement, multicultural policies | Professional demarcations, social exclusion practices |
| Impact | Enhanced social trust and cooperation | Reinforces or challenges power dynamics and identities |
Understanding Social Integration
Social integration involves the process through which individuals or groups are incorporated into the social structure, strengthening social cohesion and fostering a sense of belonging. It emphasizes shared norms, values, and social networks that facilitate cooperation and collective identity. Understanding social integration requires analyzing how social bonds and institutional support reduce marginalization and enable inclusive participation in society.
Defining Boundary Work
Boundary work refers to the processes through which social groups and individuals create, maintain, and negotiate distinctions between different categories, identities, or social domains, often to establish legitimacy or control resources. It involves actively managing social, cultural, or professional boundaries to delineate in-groups and out-groups, influencing social integration by either enabling inclusion or reinforcing exclusion. Understanding boundary work sheds light on how social integration is shaped by power dynamics and identity politics within complex social structures.
Historical Perspectives on Inclusion and Exclusion
Social integration involves the process by which marginalized groups become incorporated into mainstream society, reducing social barriers and promoting inclusion through policies and cultural shifts. Boundary work, historically examined in sociology, refers to the mechanisms that maintain distinctions between groups, often reinforcing exclusion based on race, class, or ethnicity during periods of social change. Historical perspectives reveal how these dynamics played out during movements such as the Civil Rights era, where efforts toward social integration challenged entrenched boundary work sustaining segregation and discrimination.
Key Theories in Social Integration
Key theories in social integration emphasize mechanisms through which individuals and groups connect within society, highlighting Durkheim's concept of collective conscience and Parsons' structural functionalism that stress social cohesion and shared norms. Boundary work, in contrast, involves processes identified by Lamont and Molnar that delineate social distinctions and reinforce group identities through symbolic and material boundaries. Understanding both social integration theories and boundary work elucidates how social order and differentiation coexist within complex societies.
Mechanisms of Boundary Construction
Social integration involves processes that create cohesion by blending diverse group identities, whereas boundary work focuses on mechanisms of boundary construction that maintain distinctions between social groups. These mechanisms include symbolic practices, language use, and rituals that reinforce in-group norms and exclude outsiders, thus preserving social boundaries. Understanding how boundary work operates through these mechanisms reveals the dynamic tension between inclusion and exclusion in social interactions.
Factors Influencing Social Integration
Factors influencing social integration include shared values, communication practices, and social networks that foster a sense of belonging and cooperation among group members. Economic stability, cultural compatibility, and institutional support also play critical roles in enhancing participation and reducing social exclusion. Boundary work, which defines and negotiates group identities, can either facilitate or hinder integration by clarifying group norms and managing inclusion or exclusion dynamics.
The Role of Identity in Boundary Work
Identity plays a crucial role in boundary work by shaping how individuals and groups define, maintain, or challenge social distinctions and categorizations. Social integration often involves negotiating these boundaries to foster inclusion while preserving core identity traits that reinforce group solidarity. By actively managing identity markers, boundary work facilitates the dynamic processes through which social cohesion and differentiation coexist.
Impacts of Integration and Boundaries on Communities
Social integration fosters community cohesion by encouraging shared values and cooperative interactions, which enhance social support networks and collective identity. Boundary work, by defining distinctions between groups, helps maintain cultural diversity and group identity but can also lead to social exclusion or conflict when boundaries become rigid. The balance between integration and boundary work critically impacts community resilience, social trust, and the capacity for inclusive collaboration.
Case Studies: Integration vs Boundary Work in Practice
Case studies on social integration versus boundary work reveal contrasting approaches to managing group identities and interactions within organizations. Social integration emphasizes the blending of diverse groups to foster collaboration and shared goals, while boundary work involves maintaining distinctions and managing differences to protect group identity and control resources. Practical examples include multinational corporations promoting inclusive cultures for integration versus professional guilds using boundary work to assert expertise and regulate membership.
Navigating Toward Inclusive Societies
Social integration fosters cohesion by promoting shared norms, values, and equal access within diverse communities, enhancing social harmony and inclusion. Boundary work involves defining and negotiating social, cultural, or institutional divisions that may hinder inclusion, highlighting the dynamics of in-group and out-group interactions. Navigating toward inclusive societies requires balancing social integration efforts with boundary work to address exclusion mechanisms and create environments that support diversity, equity, and mutual respect.
Social integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com