Assimilation is a crucial process in linguistics where new information is integrated into existing cognitive schemas, enhancing comprehension and communication skills. It plays a significant role in language acquisition and cultural adaptation by blending new experiences seamlessly with prior knowledge. Explore the article to understand how assimilation shapes your learning and social interactions.
Table of Comparison
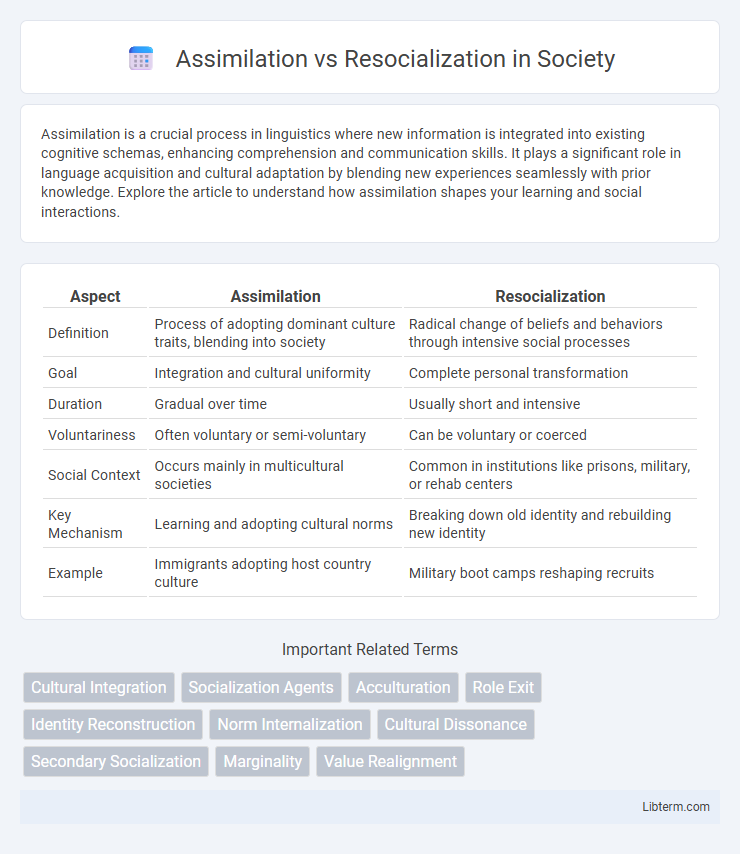
| Aspect | Assimilation | Resocialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of adopting dominant culture traits, blending into society | Radical change of beliefs and behaviors through intensive social processes |
| Goal | Integration and cultural uniformity | Complete personal transformation |
| Duration | Gradual over time | Usually short and intensive |
| Voluntariness | Often voluntary or semi-voluntary | Can be voluntary or coerced |
| Social Context | Occurs mainly in multicultural societies | Common in institutions like prisons, military, or rehab centers |
| Key Mechanism | Learning and adopting cultural norms | Breaking down old identity and rebuilding new identity |
| Example | Immigrants adopting host country culture | Military boot camps reshaping recruits |
Understanding Assimilation: Definition and Key Concepts
Assimilation involves the process by which individuals or groups absorb and integrate into a dominant culture, adopting its norms, values, and behaviors while often losing distinct cultural identities. Key concepts include cultural assimilation, where minority groups conform to the dominant society, and structural assimilation, which refers to the integration into social institutions such as education and employment. Understanding assimilation requires examining how social pressures and policies influence the gradual adaptation and potential erasure of original cultural traits.
What is Resocialization? An Overview
Resocialization is the process through which individuals undergo significant changes in their values, beliefs, and behaviors due to new social environments or life circumstances. This transformative experience often occurs in total institutions such as prisons, military boot camps, or rehabilitation centers where existing social norms are dismantled and replaced with new ones. The goal of resocialization is to facilitate adaptation and integration into a new social role or community.
Historical Perspective: Assimilation and Resocialization in Society
Assimilation historically refers to the process by which minority groups adopt the dominant culture's language, values, and norms, often erasing distinct cultural identities to achieve social cohesion. Resocialization involves deliberately replacing old behaviors and beliefs with new ones through structured social institutions, such as military training or rehabilitation programs, to adapt individuals to new social roles. Both processes have played crucial roles in shaping societal structures, with assimilation linked to nation-building and resocialization used to manage social integration and control.
Core Differences Between Assimilation and Resocialization
Assimilation involves the gradual process by which individuals adopt the cultural norms and values of a dominant society, often leading to the loss of their original cultural identity. Resocialization, on the other hand, is a deliberate and intensive process of discarding former behaviors and norms to adopt new ones, typically occurring in total institutions like prisons or military boot camps. The core difference lies in assimilation's subtle integration versus resocialization's intentional and often rapid identity transformation.
Psychological Impact of Assimilation vs Resocialization
Assimilation often leads to identity loss and increased psychological stress as individuals suppress their original cultural traits to conform to a dominant group, potentially resulting in anxiety and depression. Resocialization involves unlearning previous behaviors and adopting new norms, which can cause temporary confusion and emotional distress but may promote psychological growth and adaptation over time. Studies show that while assimilation may produce lasting internal conflicts, resocialization supports cognitive flexibility and resilience by encouraging the integration of new social roles.
Role of Institutions in Assimilation and Resocialization
Institutions play a crucial role in assimilation by promoting cultural uniformity through education, legal systems, and social norms that encourage individuals to adopt dominant societal values. In resocialization, institutions such as prisons, military, and rehabilitation centers actively facilitate the unlearning of previous behaviors and the acquisition of new social roles and identities. Both processes rely heavily on institutional frameworks to reshape individual behaviors and integrate them into new social environments.
Real-Life Examples: Assimilation and Resocialization in Action
Immigrants adopting a new country's language and cultural norms exemplify assimilation, reflecting a process where individuals gradually integrate into the dominant society by shedding previous cultural identities. Resocialization occurs in military boot camps, where recruits undergo intense training designed to replace civilian behaviors with military norms and values. Both processes highlight adaptive changes, but assimilation emphasizes blending into an existing cultural framework, while resocialization involves a complete behavioral transformation within controlled environments.
Cultural Identity and the Assimilation Process
Assimilation involves the gradual integration of individuals into a dominant culture, often leading to the loss or modification of their original cultural identity to align with prevailing societal norms. Resocialization entails a more deliberate and intense process where individuals undergo profound cultural and identity shifts, frequently in controlled environments such as institutions, resulting in the replacement of previous cultural frameworks. Both processes critically affect cultural identity, with assimilation emphasizing blending and adaptation, while resocialization focuses on systematic transformation of values, beliefs, and norms.
Resistance and Adaptation in Resocialization
Resistance in resocialization occurs when individuals reject new norms and values imposed by a total institution or social group, often due to conflicts with prior beliefs or identity. Adaptation involves gradual acceptance and internalization of these new norms, facilitated by mechanisms such as role modeling, reinforcement, and immersion in the resocialization environment. The balance between resistance and adaptation significantly influences the success of resocialization efforts in transforming behavior and social identity.
Assimilation vs Resocialization: Implications for Modern Communities
Assimilation involves individuals integrating into a dominant culture by adopting its norms, values, and behaviors, often leading to a loss of original cultural identity. Resocialization, by contrast, entails a fundamental restructuring of an individual's social identity through new norms and roles, typically occurring in isolated environments like military training or rehabilitation centers. The implications for modern communities include challenges in balancing cultural preservation with social cohesion, as assimilation may promote unity but risks eroding diversity, while resocialization facilitates adaptation to new social contexts but can disrupt established community ties.
Assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com