Groupthink occurs when a cohesive group prioritizes harmony and consensus over critical evaluation, leading to poor decision-making and suppressed dissent. This phenomenon often results in overlooking alternative solutions and ignoring potential risks, which can be detrimental in both organizational and social contexts. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to identify and prevent groupthink in your team.
Table of Comparison
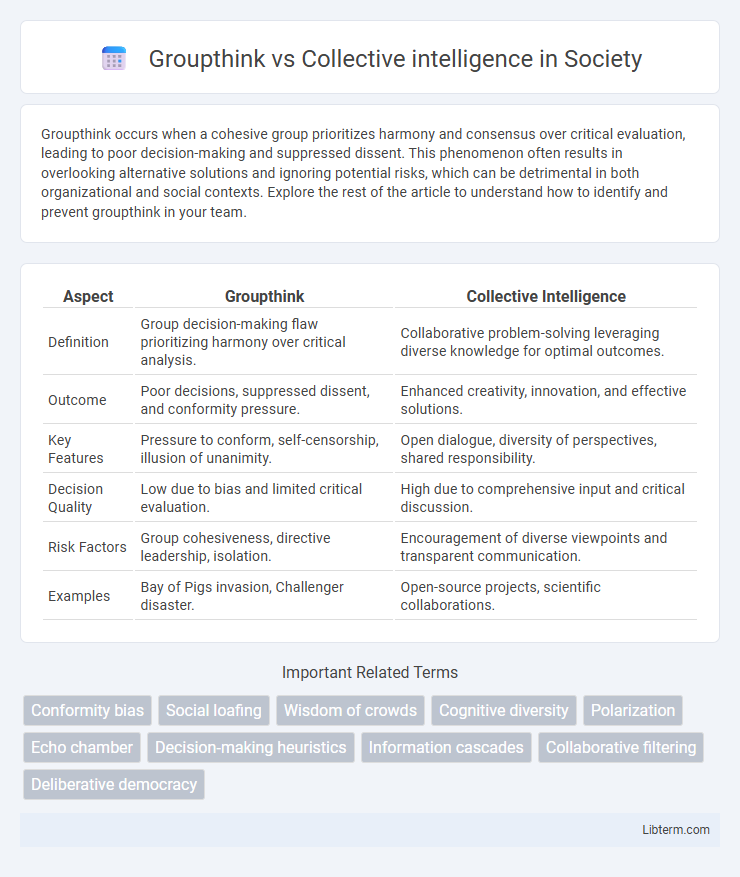
| Aspect | Groupthink | Collective Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group decision-making flaw prioritizing harmony over critical analysis. | Collaborative problem-solving leveraging diverse knowledge for optimal outcomes. |
| Outcome | Poor decisions, suppressed dissent, and conformity pressure. | Enhanced creativity, innovation, and effective solutions. |
| Key Features | Pressure to conform, self-censorship, illusion of unanimity. | Open dialogue, diversity of perspectives, shared responsibility. |
| Decision Quality | Low due to bias and limited critical evaluation. | High due to comprehensive input and critical discussion. |
| Risk Factors | Group cohesiveness, directive leadership, isolation. | Encouragement of diverse viewpoints and transparent communication. |
| Examples | Bay of Pigs invasion, Challenger disaster. | Open-source projects, scientific collaborations. |
Introduction to Groupthink and Collective Intelligence
Groupthink occurs when group members prioritize consensus over critical evaluation, often leading to poor decision-making outcomes. Collective intelligence emerges from the diverse knowledge and collaboration within a group, enhancing problem-solving and innovation. Understanding these concepts is essential for fostering effective teamwork and avoiding cognitive biases in group settings.
Defining Groupthink: Origins and Characteristics
Groupthink, first identified by Irving Janis in 1972, is a psychological phenomenon where the desire for harmony in a decision-making group leads to irrational or dysfunctional outcomes. It is characterized by members suppressing dissenting opinions, self-censorship, and an illusion of unanimity, which impairs critical thinking and fosters risk-taking behaviors. Groupthink originates from highly cohesive groups facing external threats or pressure, prioritizing consensus over realistic appraisal of alternatives.
What is Collective Intelligence? Key Concepts
Collective intelligence refers to the enhanced capacity created when individuals collaborate, share knowledge, and combine their expertise to solve problems or innovate. Key concepts include distributed cognition, where information is spread across group members, and synergy, highlighting that group performance often exceeds individual inputs. Unlike groupthink, which limits diversity of thought, collective intelligence leverages diverse perspectives to achieve better decisions and creativity.
The Psychological Mechanisms Behind Groupthink
Groupthink occurs when psychological mechanisms like conformity pressure, desire for unanimity, and self-censorship override critical thinking within a group, leading to poor decision-making outcomes. These cognitive biases suppress dissent and promote homogeneity, reducing the group's ability to evaluate alternatives objectively. In contrast, collective intelligence thrives on diverse perspectives and open communication, enhancing problem-solving and innovation.
Factors that Foster Collective Intelligence
Diverse perspectives, open communication, and psychological safety are key factors that foster collective intelligence by enabling group members to share unique insights without fear of judgment. High levels of trust and collaboration encourage the integration of individual knowledge into shared solutions, enhancing problem-solving capabilities. In contrast to groupthink, which suppresses dissent, collective intelligence thrives on critical evaluation and constructive debate.
Groupthink vs Collective Intelligence: Core Differences
Groupthink occurs when desire for harmony in a group results in irrational decision-making, suppressing dissent and critical thinking. Collective intelligence emerges from diverse perspectives and collaboration, producing more accurate solutions and innovative ideas. The core difference lies in groupthink's conformity-driven errors versus collective intelligence's dynamic integration of knowledge and expertise.
Real-World Examples: Groupthink in Action
The 1986 Challenger Space Shuttle disaster exemplifies groupthink, where NASA engineers underestimated risks due to pressure for consensus and dismissal of dissenting voices. In contrast, the Apollo 13 mission showcased collective intelligence, as diverse experts collaboratively solved critical problems under extreme pressure. Observing these events highlights how groupthink suppresses critical evaluation, while collective intelligence leverages diverse perspectives to improve decision-making outcomes.
Successful Teams Leveraging Collective Intelligence
Successful teams leveraging collective intelligence outperform those trapped in groupthink by fostering diverse perspectives, open communication, and collaborative problem-solving. Collective intelligence harnesses the combined knowledge, skills, and creativity of team members, leading to innovative solutions and higher decision-making quality. Teams that avoid groupthink actively encourage critical evaluation and constructive dissent, which strengthens overall performance and adaptability.
Strategies to Prevent Groupthink and Enhance Collective Intelligence
Implementing diverse perspectives and encouraging open dialogue are effective strategies to prevent groupthink and enhance collective intelligence. Structured decision-making techniques such as the Delphi method and nominal group technique foster independent thinking and reduce conformity pressure. Promoting psychological safety and leveraging technology for collaborative knowledge-sharing also improve critical evaluation and innovation within teams.
Conclusion: Fostering Smarter Group Dynamics
Fostering smarter group dynamics requires balancing the risks of groupthink with the benefits of collective intelligence by encouraging diverse perspectives and open dialogue. Implementing structured decision-making processes and promoting psychological safety enhances critical thinking and innovation within teams. Effective leadership that values collaboration and constructive dissent unlocks the full potential of collective intelligence while mitigating conformity pressures.
Groupthink Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com