Social structure shapes the organization of society by defining roles, relationships, and hierarchies that influence behavior and interactions. Understanding these frameworks reveals how power, status, and resources are distributed within communities. Explore the article to uncover how social structure impacts your daily life and societal dynamics.
Table of Comparison
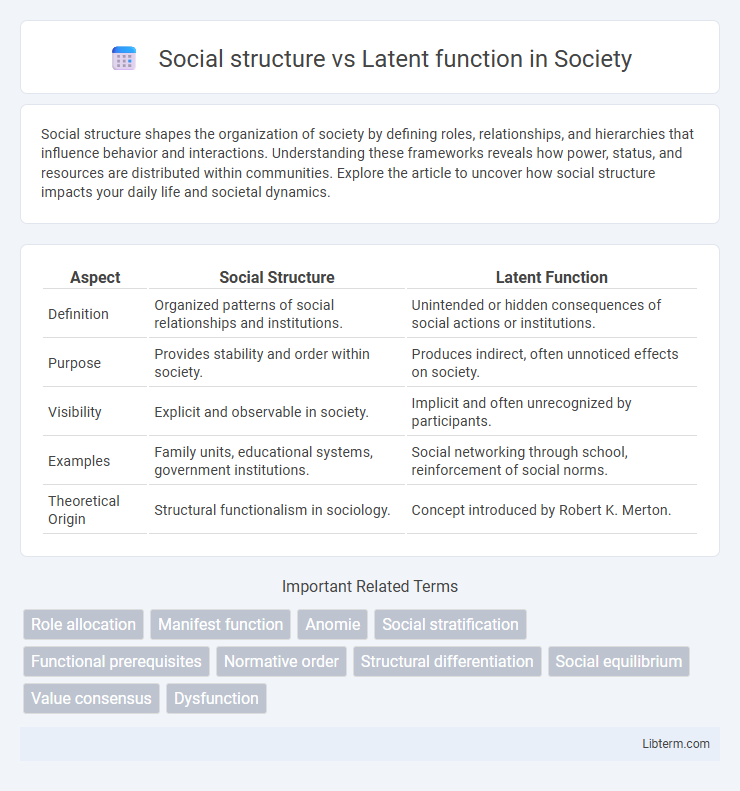
| Aspect | Social Structure | Latent Function |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized patterns of social relationships and institutions. | Unintended or hidden consequences of social actions or institutions. |
| Purpose | Provides stability and order within society. | Produces indirect, often unnoticed effects on society. |
| Visibility | Explicit and observable in society. | Implicit and often unrecognized by participants. |
| Examples | Family units, educational systems, government institutions. | Social networking through school, reinforcement of social norms. |
| Theoretical Origin | Structural functionalism in sociology. | Concept introduced by Robert K. Merton. |
Understanding Social Structure: Foundations and Frameworks
Social structure refers to the organized patterns of relationships and institutions that shape society, providing a framework for social behavior and interaction. Latent functions are the unintended, often unrecognized consequences of social institutions that contribute to social stability and cohesion. Understanding social structure involves analyzing both manifest functions and latent functions to grasp how underlying frameworks sustain societal order.
Defining Latent Function in Sociology
Latent function in sociology refers to the unintended and often unrecognized consequences of social structures or actions that contribute to the stability or change of society. Unlike manifest functions, which are deliberate and obvious, latent functions operate beneath the surface, influencing social behavior and relationships in subtle ways. Understanding latent functions helps sociologists uncover hidden social patterns and the underlying dynamics within institutions and social systems.
Comparative Analysis: Social Structure vs. Latent Function
Social structure refers to the organized pattern of social relationships and institutions that shape society, while latent functions are the unintended, unrecognized consequences of social actions or institutions. Comparative analysis reveals that social structures provide the framework within which latent functions emerge, often stabilizing or disrupting the social system in ways not initially perceived. Understanding the dynamic interplay between formal structures and latent functions is essential for comprehending how societies adapt and evolve over time.
Manifest Functions vs. Latent Functions: Key Distinctions
Manifest functions refer to the intended and recognized consequences of social institutions or actions, such as education providing knowledge and skills. Latent functions are the unintended, hidden, or secondary effects, like schools fostering social networks or reinforcing social norms. Understanding the distinction between manifest and latent functions helps reveal how social structures operate beyond their overt purposes.
Impact of Social Structure on Societal Behavior
Social structure provides the organized framework of social institutions and relationships that shape individual and group behaviors within society. Latent functions, often unintended and unrecognized, emerge from these structures, subtly influencing social norms and interactions. The impact of social structure on societal behavior manifests through the establishment of roles, hierarchy, and expectations that guide how individuals act and relate within a community.
Unintended Consequences: Exploring Latent Functions
Latent functions represent the unintended, often hidden consequences of social structures that influence societal behavior beyond their explicit purposes. These outcomes can reinforce existing social patterns or generate new social dynamics without deliberate planning by individuals or institutions. Understanding latent functions reveals how social institutions contribute to stability or change in unanticipated ways, highlighting the complexity of societal organization.
Examples of Latent Functions within Social Structures
Latent functions within social structures refer to the unintended and often unrecognized consequences of social activities, such as schools inadvertently serving as matchmaking venues or workplaces fostering social networks beyond professional relationships. These hidden functions contribute to social stability by promoting social cohesion and cultural transmission outside the formal objectives of institutions. Understanding latent functions helps sociologists uncover deeper layers of social interaction, revealing how social systems adapt and persist over time.
Theoretical Perspectives: Functionalism and Beyond
Social structure refers to the organized patterns of relationships and institutions that form the foundation of society, while latent functions are the unintended, hidden consequences of social actions within this structure. Functionalism emphasizes how social structures contribute to societal stability by fulfilling both manifest and latent functions, ensuring cohesion and order. Contemporary perspectives extend beyond functionalism to explore how latent functions may also perpetuate inequality and social change by revealing underlying power dynamics.
Contemporary Relevance of Social Structures and Latent Functions
Contemporary relevance of social structures lies in their role as organized frameworks shaping societal behavior, institutional interactions, and hierarchy formations. Latent functions reveal the hidden, unintended consequences of these social structures, influencing social cohesion, cultural norms, and systemic inequalities. Understanding the dynamic interplay between social structures and latent functions aids in addressing modern challenges such as social stratification, policy impacts, and technological integration within communities.
Implications for Social Policy and Research
Social structure shapes the predictable patterns of behavior within a society, while latent functions refer to the unintended, often hidden consequences of social actions that influence social stability. Understanding latent functions aids policymakers and researchers in identifying unforeseen outcomes of laws or programs, allowing for more adaptive and effective social policies. Research focusing on both dimensions encourages comprehensive analyses that account for both overt and covert social dynamics, improving intervention strategies and societal well-being.
Social structure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com