Individualism emphasizes personal freedom, self-expression, and the importance of autonomy in shaping one's identity. It fosters innovation and creativity by encouraging individuals to think independently and pursue their unique goals. Explore the rest of this article to understand how individualism impacts society and your personal development.
Table of Comparison
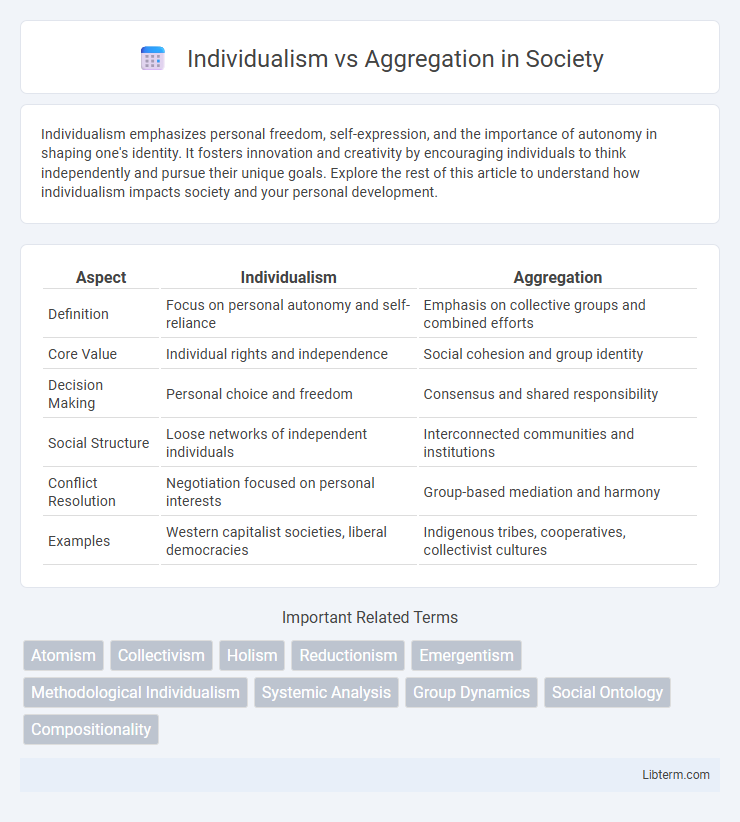
| Aspect | Individualism | Aggregation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on personal autonomy and self-reliance | Emphasis on collective groups and combined efforts |
| Core Value | Individual rights and independence | Social cohesion and group identity |
| Decision Making | Personal choice and freedom | Consensus and shared responsibility |
| Social Structure | Loose networks of independent individuals | Interconnected communities and institutions |
| Conflict Resolution | Negotiation focused on personal interests | Group-based mediation and harmony |
| Examples | Western capitalist societies, liberal democracies | Indigenous tribes, cooperatives, collectivist cultures |
Understanding Individualism: Core Principles
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy, prioritizing individual rights, self-expression, and independent decision-making as fundamental values. Core principles include self-reliance, personal responsibility, and the belief that individuals should pursue their own goals without undue interference from collective forces. This philosophy supports innovation and creativity by valuing unique perspectives over group conformity.
Aggregation Defined: Collective Approaches Explained
Aggregation refers to the process of combining individual data points or entities into a collective whole to analyze broader patterns and trends. This collective approach enhances decision-making by leveraging the power of combined information rather than isolated data, improving accuracy and insights in fields like economics, sociology, and big data analytics. Aggregation facilitates understanding of group behaviors and outcomes that individual analysis might overlook, highlighting the importance of holistic data integration.
Historical Perspectives on Individualism and Aggregation
Historical perspectives on individualism emphasize autonomy and self-reliance, rooted in Renaissance humanism and Enlightenment philosophy, championing personal freedom and moral responsibility. Aggregation, historically linked to collectivist traditions and social contract theories, underscores the importance of social cohesion and shared values for societal stability. Debates between these viewpoints shaped political ideologies and economic systems, influencing modern concepts of governance and community.
The Psychology Behind Individual and Collective Mindsets
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, highlighting the psychological need for independence and unique identity formation. Aggregation reflects a collective mindset where social harmony, cooperation, and group identity drive decision-making and behavior. Psychological research links individualistic cultures to higher levels of personal agency, while collectivist cultures foster interconnectedness and group-oriented values.
Social Impacts: Benefits and Challenges of Individualism
Individualism promotes personal freedom and self-expression, leading to increased innovation and creativity within societies. It encourages responsibility and autonomy but can also result in social fragmentation and weakened community bonds. Balancing individual rights with collective well-being remains a key challenge for maintaining social cohesion.
Aggregation in Practice: Societal Case Studies
Aggregation in practice manifests through collective decision-making and resource pooling, enhancing efficiency in societal systems such as public health and urban planning. Case studies of successful aggregation include cooperative farming initiatives that improve food security and community-based disaster response teams that optimize emergency management. These examples demonstrate how aggregating individual efforts leads to scalable solutions addressing complex social challenges.
Economic Implications: Individualism vs Aggregation
Individualism in economics emphasizes personal responsibility, innovation, and entrepreneurial freedom, often leading to increased productivity and diverse market outcomes. Aggregation prioritizes collective decision-making and resource pooling, which can enhance risk-sharing and equity but may reduce incentives for individual initiative. The balance between these approaches impacts economic growth, wealth distribution, and market efficiency across different economic systems.
Technology and Data: Aggregating Individual Behaviors
Aggregating individual behaviors through advanced data analytics and machine learning enables technology platforms to uncover patterns that enhance personalized experiences and predictive modeling. Big data technologies such as Hadoop and Spark process vast amounts of user-generated information, transforming discrete individual actions into comprehensive insights that drive business intelligence and innovation. This fusion of individualism and aggregation in technology accelerates decision-making by leveraging collective behavioral data while respecting individual privacy through differential privacy techniques and anonymization.
Finding a Balance: Integrating Individualism and Aggregation
Finding a balance between individualism and aggregation involves recognizing the value of personal autonomy while leveraging collective insights for enhanced decision-making. Integrating individual perspectives with aggregated data fosters innovation and comprehensive understanding in diverse fields such as business, technology, and social sciences. Effective strategies emphasize collaboration frameworks that respect unique contributions yet promote unified goals for optimal outcomes.
Future Trends: Evolving Attitudes Toward Individual and Collective Action
Future trends indicate a dynamic shift in individualism vs aggregation with growing emphasis on cooperative frameworks that balance personal autonomy and collective responsibility. Technological advancements, such as blockchain and decentralized networks, enhance aggregation capabilities without compromising individual rights, fostering trust and transparency. Societal movements increasingly advocate for hybrid approaches where individual innovation drives progress within collaborative ecosystems to address global challenges.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com