Diaspora networks play a crucial role in connecting migrants with their home countries, facilitating economic, social, and cultural exchanges. These networks enhance business opportunities, support community development, and strengthen the identity of dispersed populations. Discover how your engagement with diaspora networks can unlock new possibilities by reading the full article.
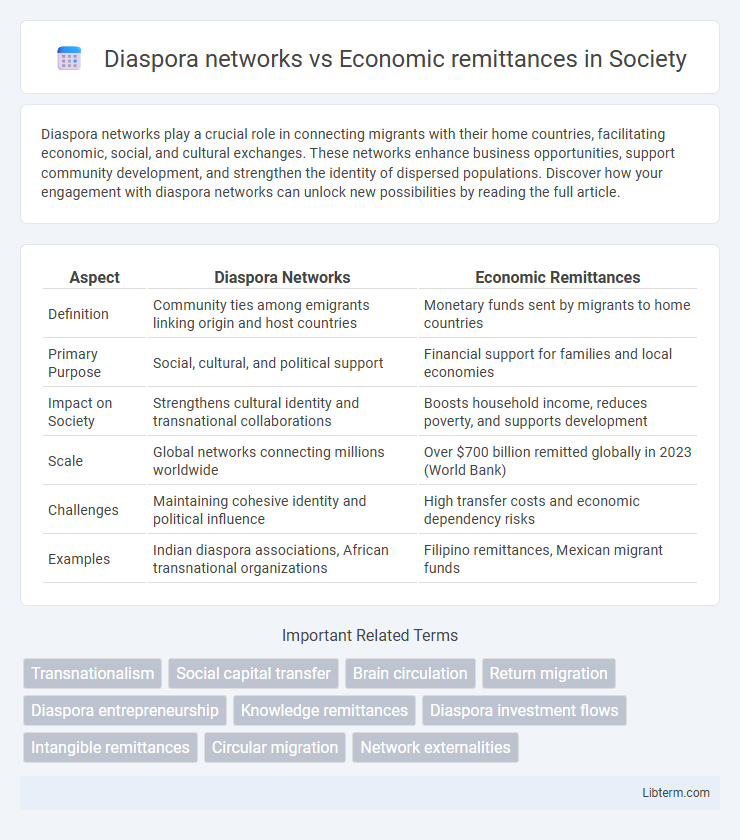
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Diaspora Networks | Economic Remittances |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Community ties among emigrants linking origin and host countries | Monetary funds sent by migrants to home countries |
| Primary Purpose | Social, cultural, and political support | Financial support for families and local economies |
| Impact on Society | Strengthens cultural identity and transnational collaborations | Boosts household income, reduces poverty, and supports development |
| Scale | Global networks connecting millions worldwide | Over $700 billion remitted globally in 2023 (World Bank) |
| Challenges | Maintaining cohesive identity and political influence | High transfer costs and economic dependency risks |
| Examples | Indian diaspora associations, African transnational organizations | Filipino remittances, Mexican migrant funds |
Introduction to Diaspora Networks and Economic Remittances
Diaspora networks are social and professional connections maintained by migrants across borders, facilitating information exchange, cultural ties, and business opportunities. Economic remittances refer to the funds that migrants send back to their home countries, contributing significantly to household income and national GDP in many developing economies. These two phenomena interact closely, as diaspora networks often enhance the efficiency and frequency of remittance flows, driving economic development.
Defining Diaspora Networks: Beyond Financial Transfers
Diaspora networks encompass social, cultural, and professional connections that transcend mere economic remittances, facilitating knowledge exchange, innovation, and political influence across borders. These networks play a crucial role in fostering transnational entrepreneurship, strengthening trade links, and enhancing human capital development in home countries. Unlike financial remittances, which primarily address immediate economic needs, diaspora networks contribute to long-term socio-economic transformation through sustained collaboration and resource sharing.
Understanding Economic Remittances: Scale and Impact
Economic remittances constitute a significant financial flow from diaspora networks to home countries, often surpassing foreign direct investments and official development aid in scale. These funds directly improve household income, drive consumption, and support entrepreneurship, fostering economic stability and growth in emerging economies. Understanding the volume and allocation of remittances is crucial for policymakers to design effective strategies that maximize their developmental impact and reduce dependency.
Comparative Mechanisms: Networks vs. Remittances
Diaspora networks facilitate knowledge exchange, social capital formation, and business opportunities through trust-based relationships and transnational connections, whereas economic remittances primarily involve monetary transfers sent by migrants to support household consumption, investments, and community projects in the home country. Networks leverage social interaction and collective action to enhance economic and social development by fostering entrepreneurship and innovation, while remittances directly inject financial resources that alleviate poverty and improve living standards. Comparative analysis shows diaspora networks generate long-term sustainable impacts through collaborative mechanisms, whereas remittances provide immediate financial relief and economic stability.
Socioeconomic Benefits of Diaspora Networks
Diaspora networks enhance socioeconomic development by facilitating knowledge transfer, investment, and trade between host and home countries, thereby boosting economic growth and innovation. These networks create opportunities for entrepreneurship and access to international markets, which often surpass the direct financial inflows of economic remittances. By fostering social capital and collaborative ventures, diaspora networks contribute to sustainable development and job creation in origin communities.
The Economic Influence of Remittance Flows
Remittance flows from diaspora networks significantly boost the GDP of developing countries by increasing household incomes and fueling local consumption. These economic remittances create financial stability and enable investments in education, healthcare, and small businesses, which drive sustainable development. The multiplier effect of remittance inflows enhances economic growth by improving credit access and fostering entrepreneurship in recipient communities.
Diaspora Networks in Knowledge and Skills Transfer
Diaspora networks serve as crucial channels for knowledge and skills transfer, enabling the flow of expertise, innovation, and best practices across borders that economic remittances alone cannot provide. These networks facilitate collaborative projects, entrepreneurship, and capacity building in home countries through mentoring, remote consultations, and investment in human capital. By leveraging social capital and professional connections, diaspora networks significantly enhance development outcomes beyond the financial benefits of economic remittances.
Remittances: Household Welfare and Economic Stability
Remittances from diaspora networks play a crucial role in enhancing household welfare by providing a consistent source of income that supports food security, education, and healthcare expenditures. These financial inflows contribute to economic stability in recipient countries by bolstering foreign exchange reserves and enabling investments in local infrastructure and small businesses. Empirical studies highlight that remittances often counteract economic shocks, smoothing consumption and reducing poverty levels among vulnerable populations.
Policy Implications: Leveraging Networks and Remittances
Diaspora networks enhance economic development by facilitating business connections, knowledge transfer, and investment opportunities across borders, creating a multiplier effect on local economies. Economic remittances provide direct financial inflows that bolster household consumption, education, and entrepreneurship, contributing significantly to poverty alleviation and economic stability. Effective policy frameworks should integrate the mobilization of diaspora networks with the efficient use of remittances, promoting financial inclusion, incentivizing diaspora investments, and establishing regulatory environments to maximize their socioeconomic impact.
Conclusion: Synergies and Future Prospects
Diaspora networks and economic remittances create powerful synergies that boost development through knowledge transfer, investment, and sustained financial flows. Leveraging diaspora expertise alongside remittance capital fosters innovation and entrepreneurship in origin countries. Future prospects emphasize integrated policies that harness these synergistic impacts for inclusive economic growth and resilience.
Diaspora networks Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com