Ideology shapes beliefs, values, and behaviors, influencing social and political systems worldwide. Understanding the core principles of various ideologies can help you critically analyze current events and societal trends. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your insight into how ideology impacts everyday life.
Table of Comparison
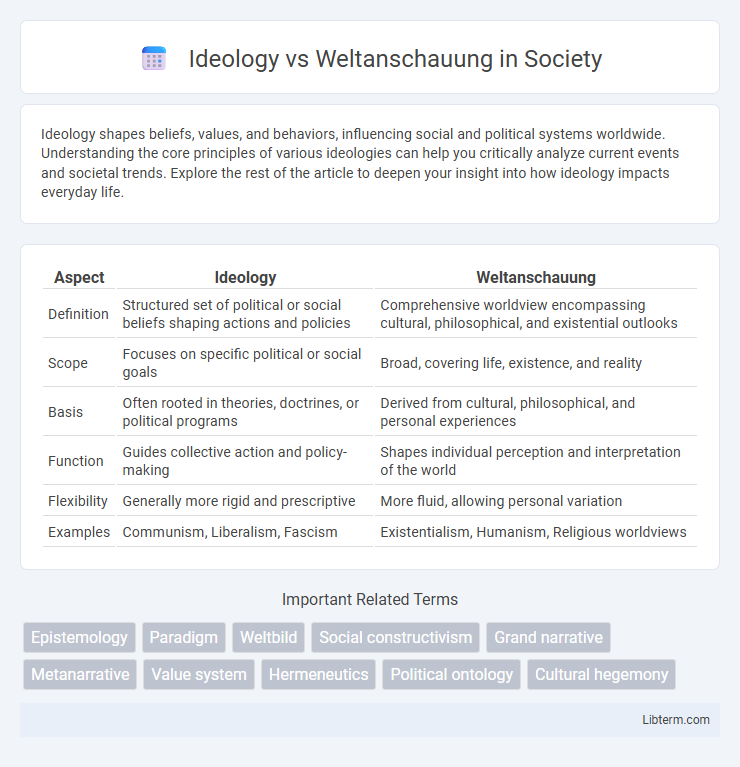
| Aspect | Ideology | Weltanschauung |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured set of political or social beliefs shaping actions and policies | Comprehensive worldview encompassing cultural, philosophical, and existential outlooks |
| Scope | Focuses on specific political or social goals | Broad, covering life, existence, and reality |
| Basis | Often rooted in theories, doctrines, or political programs | Derived from cultural, philosophical, and personal experiences |
| Function | Guides collective action and policy-making | Shapes individual perception and interpretation of the world |
| Flexibility | Generally more rigid and prescriptive | More fluid, allowing personal variation |
| Examples | Communism, Liberalism, Fascism | Existentialism, Humanism, Religious worldviews |
Defining Ideology: Foundations and Functions
Ideology constitutes a structured set of beliefs and values that guide political behavior and social organization, serving as a blueprint for collective action. It functions by providing coherence to social experiences, legitimizing power structures, and motivating political mobilization. Its foundations lie in shared assumptions about society, economy, and governance, which shape individual and group identities within a cultural context.
Unpacking Weltanschauung: Meaning and Origins
Weltanschauung, a German term meaning "worldview," encapsulates the comprehensive framework through which individuals interpret reality, encompassing beliefs, values, and cultural experiences. Originating from 19th-century German philosophy, particularly the works of Wilhelm Dilthey and Johann Gottfried Herder, Weltanschauung extends beyond rigid ideological systems by integrating historical context and personal perspective. This concept emphasizes a holistic understanding of human existence, contrasting with ideology's often prescriptive nature and highlighting the depth of cultural and existential interpretation.
Historical Development of Ideology and Weltanschauung
The historical development of ideology can be traced back to the Enlightenment era, where it emerged as a systematic framework for political and social beliefs, emphasizing structured doctrines and rational analysis. In contrast, weltanschauung, a German term meaning "worldview," evolved through philosophical and cultural traditions as a more holistic, subjective interpretation of reality reflecting individual or collective consciousness. Both concepts diverged as ideology became linked to political movements and social theories, while weltanschauung maintained a broader intellectual and existential significance across various disciplines.
Key Differences Between Ideology and Weltanschauung
Ideology refers to a structured set of political or social beliefs aimed at influencing collective behavior, often linked to specific movements or parties, whereas Weltanschauung denotes a broader, comprehensive world view encompassing cultural, philosophical, and existential perspectives that shape an individual's interpretation of reality. Ideologies are typically prescriptive and goal-oriented, providing strategies for social change, while Weltanschauung is descriptive, reflecting an overarching framework of meaning and values. The key difference lies in ideology's focus on organized systems targeting societal transformation compared to Weltanschauung's encompassing, intrinsic worldview guiding personal or cultural identity.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Weltanschauung
Weltanschauung, a comprehensive worldview, is deeply influenced by culture, embodying the collective beliefs, values, and norms that shape how individuals perceive reality. Unlike ideology, which often serves specific political or social agendas, Weltanschauung reflects the underlying cultural context that informs a society's interpretive framework. This cultural foundation influences not only personal identity but also communal understanding and behaviors, highlighting the pervasive role of cultural heritage in shaping human experience.
Political Influence and Power of Ideologies
Ideologies shape political influence by providing structured frameworks that guide policy-making and mobilize collective action, directly impacting governance and social order. Weltanschauung, representing a broad worldview, influences political thought indirectly by framing individuals' and groups' perceptions of reality and values, thereby shaping ideological adherence. The power of ideologies lies in their ability to unify diverse populations under common goals and justify authority, often driving political movements and institutional power dynamics.
Intersections: Where Ideology Meets Weltanschauung
Ideology and Weltanschauung intersect in their function as frameworks for understanding social and cultural realities, with ideology often providing structured political or economic doctrines while Weltanschauung encompasses broader philosophical worldviews. Both influence individual and collective behavior by shaping perceptions, values, and interpretations of existence, linking personal beliefs with societal norms. This intersection highlights how dynamic worldviews inform ideological commitments, allowing for the integration of abstract, cultural, and practical dimensions in human thought.
Social Identity and Worldview Formation
Ideology shapes social identity by providing structured beliefs and values that align individuals with specific political or social groups, influencing behavior and group cohesion. Weltanschauung, as a broader worldview, encompasses not only political but also cultural, philosophical, and existential perspectives, shaping how individuals interpret their place in the world. Both concepts contribute to worldview formation, but ideology offers a targeted framework for group identity, while Weltanschauung forms a comprehensive lens through which people make sense of reality.
Ideology and Weltanschauung in Modern Society
Ideology in modern society functions as a structured set of political and social beliefs that guide collective action and policy making, often emphasizing power dynamics and institutional goals. Weltanschauung, by contrast, represents a broader, more holistic worldview encompassing culture, existential values, and personal identity beyond political frameworks. Understanding the interplay between ideology and weltanschauung is essential for analyzing contemporary social movements, cultural conflicts, and identity politics within diverse global contexts.
Toward a Deeper Understanding: Implications for Thought and Action
Ideology and Weltanschauung shape thought and action by framing how individuals interpret reality and prioritize values, with ideology often reflecting systematic political or social doctrines, while Weltanschauung encompasses a broader, existential worldview. Analyzing these concepts reveals how ideology can drive collective movements rooted in specific agendas, whereas Weltanschauung influences deeper, more personalized meaning-making processes. Understanding their distinctions and interplay enhances critical reflection on motivations behind behaviors and societal structures, informing more nuanced approaches to social and philosophical inquiry.
Ideology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com