Homophobia manifests as prejudice, discrimination, or aversion toward individuals based on their sexual orientation, often resulting in social exclusion and mental health challenges. Understanding the deep-rooted causes and societal impacts of homophobia is crucial in fostering a more inclusive environment for everyone. Explore the rest of this article to learn how you can contribute to combating homophobia and promoting equality.
Table of Comparison
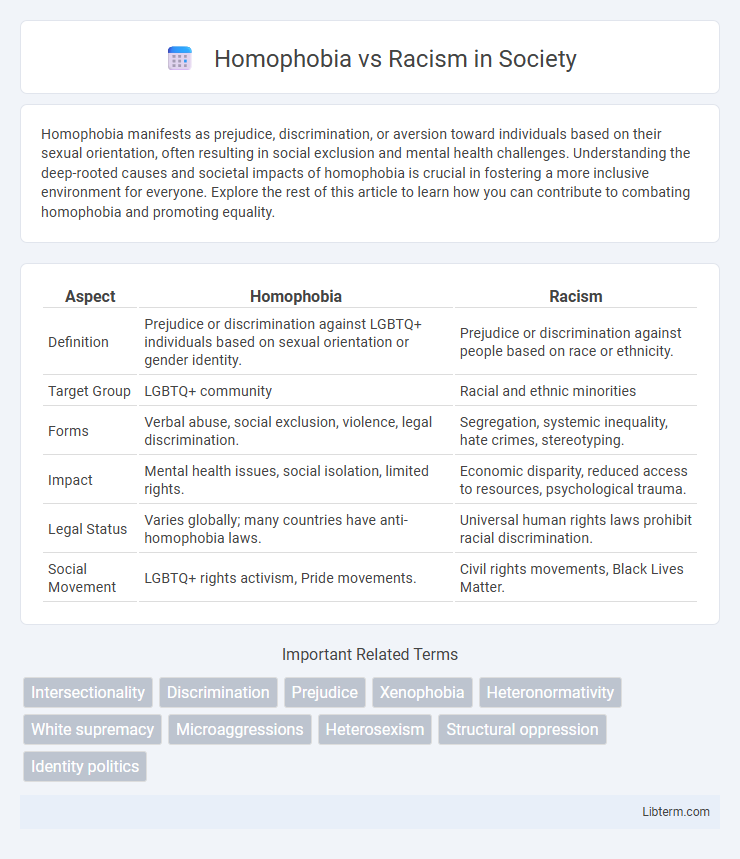
| Aspect | Homophobia | Racism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prejudice or discrimination against LGBTQ+ individuals based on sexual orientation or gender identity. | Prejudice or discrimination against people based on race or ethnicity. |
| Target Group | LGBTQ+ community | Racial and ethnic minorities |
| Forms | Verbal abuse, social exclusion, violence, legal discrimination. | Segregation, systemic inequality, hate crimes, stereotyping. |
| Impact | Mental health issues, social isolation, limited rights. | Economic disparity, reduced access to resources, psychological trauma. |
| Legal Status | Varies globally; many countries have anti-homophobia laws. | Universal human rights laws prohibit racial discrimination. |
| Social Movement | LGBTQ+ rights activism, Pride movements. | Civil rights movements, Black Lives Matter. |
Understanding Homophobia: Definition and Origins
Homophobia refers to the irrational fear, hatred, or discrimination against individuals based on their sexual orientation, particularly towards those who identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual. This prejudice often stems from cultural, religious, and societal norms that promote heteronormativity and stigmatize non-heterosexual identities. Understanding homophobia requires examining historical contexts, such as legal restrictions and social marginalization, that have perpetuated negative attitudes towards LGBTQ+ communities.
What is Racism? Historical Context and Meaning
Racism is the systemic oppression and discrimination based on race, rooted in historical contexts such as colonialism, slavery, and segregation that have shaped societal hierarchies. It perpetuates inequality by privileging one racial group over others through institutional practices and cultural norms. Understanding racism requires analyzing its impact on social, economic, and political structures across different periods and regions.
Similarities Between Homophobia and Racism
Both homophobia and racism involve systemic discrimination rooted in prejudice against marginalized groups, perpetuating social inequality and exclusion. These forms of bias manifest through harmful stereotypes, institutional policies, and acts of violence that limit access to opportunities and resources. Understanding their intersectionality reveals how overlapping identities face compounded oppression in society.
Key Differences: Homophobia vs Racism
Homophobia targets individuals based on their sexual orientation, often resulting in discrimination against LGBTQ+ communities, while racism involves prejudice and systemic inequality directed at people based on their race or ethnicity. Homophobia manifests through exclusion, hate crimes, and denial of rights related to sexual identity, whereas racism includes segregation, unequal access to resources, and institutional bias affecting racial minorities. Both forms of discrimination perpetuate social injustice but differ fundamentally in the identities they target and the historical contexts shaping their impact.
Social Consequences of Homophobia and Racism
Homophobia and racism both perpetuate systemic inequality and social exclusion, leading to increased discrimination, mental health issues, and reduced access to opportunities for marginalized groups. Social consequences of homophobia include stigmatization and violence against LGBTQ+ individuals, resulting in higher rates of depression and suicide. Racism fosters segregation and economic disparities, reinforcing cycles of poverty and limited educational attainment in affected communities.
Impact on Mental Health: Comparative Analysis
Homophobia and racism both significantly impact mental health by increasing risks of depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among affected individuals. Research indicates that experiences of homophobic discrimination often lead to higher rates of internalized stigma and social isolation, while racial discrimination is strongly linked to chronic stress and trauma-related symptoms. The intersectionality of these identities can exacerbate mental health challenges, highlighting the need for targeted interventions addressing both homophobia and racism concurrently.
Intersectionality: Experiencing Both Homophobia and Racism
Experiences of homophobia and racism intersect to create unique challenges for individuals who belong to both marginalized groups, significantly impacting their mental health and social inclusion. Intersectionality reveals how the compounded discrimination affects access to resources, support networks, and legal protections differently than when facing a single form of bias. Addressing these overlapping oppressions requires targeted policies and inclusive frameworks that recognize the complex identities and lived realities of affected individuals.
Legal Responses to Homophobia and Racism
Legal responses to homophobia and racism vary globally but increasingly involve anti-discrimination laws designed to protect individuals based on sexual orientation and race. Countries like Canada and the United Kingdom have enacted comprehensive legislation that penalizes hate crimes motivated by both homophobia and racism, ensuring equal protection in employment, housing, and public services. Enforcement agencies and courts play critical roles in upholding these laws, promoting social justice and reducing systemic discrimination through consistent legal precedents.
Strategies for Combating Homophobia and Racism
Effective strategies for combating homophobia and racism include comprehensive education programs that promote empathy, diversity, and inclusion from an early age. Implementing robust anti-discrimination laws paired with consistent enforcement helps protect marginalized communities and hold perpetrators accountable. Supporting grassroots organizations and community-led initiatives fosters safe spaces and amplifies voices fighting against systemic prejudice.
Creating Inclusive Communities: Moving Beyond Hate
Creating inclusive communities requires addressing both homophobia and racism as interconnected forms of discrimination that harm social cohesion and individual well-being. Effective strategies include education on diversity, implementing policies that protect LGBTQ+ individuals and racial minorities, and fostering open dialogues that challenge stereotypes and biases. Emphasizing empathy and shared humanity promotes unity, reducing hate and building resilient, supportive environments for all marginalized groups.
Homophobia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com