Foundations are essential structural elements that distribute the load of a building to the ground, ensuring stability and durability over time. Choosing the right foundation type depends on soil conditions, building design, and environmental factors to prevent shifting or settling that could compromise your structure. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to select and maintain foundations for a safe and lasting construction.
Table of Comparison
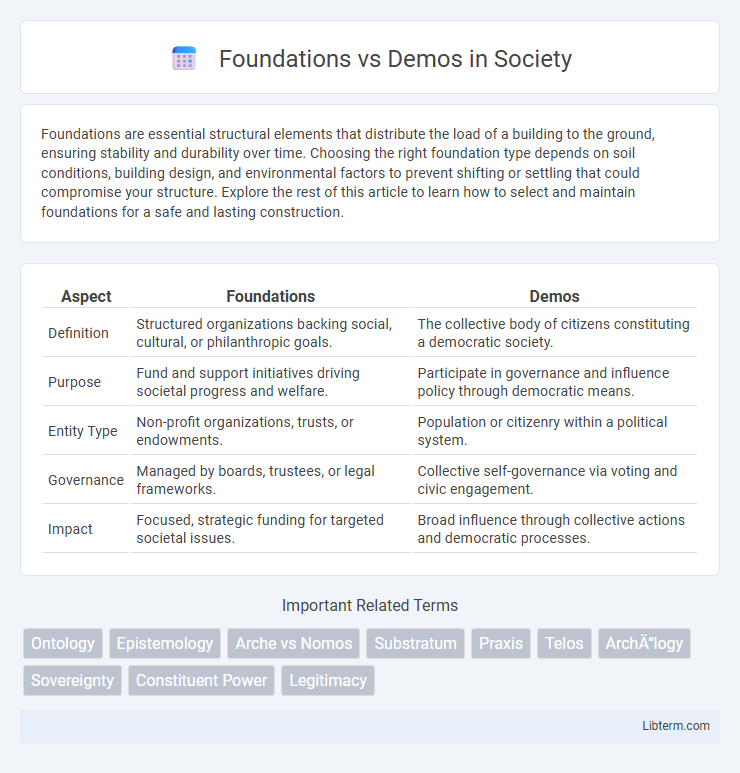
| Aspect | Foundations | Demos |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured organizations backing social, cultural, or philanthropic goals. | The collective body of citizens constituting a democratic society. |
| Purpose | Fund and support initiatives driving societal progress and welfare. | Participate in governance and influence policy through democratic means. |
| Entity Type | Non-profit organizations, trusts, or endowments. | Population or citizenry within a political system. |
| Governance | Managed by boards, trustees, or legal frameworks. | Collective self-governance via voting and civic engagement. |
| Impact | Focused, strategic funding for targeted societal issues. | Broad influence through collective actions and democratic processes. |
Understanding Foundations and Demos
Foundations provide the essential principles and core concepts that form the basis of a subject, enabling deeper comprehension and long-term retention. Demos illustrate these concepts in action, offering practical examples that clarify complex ideas through real-world application. Understanding the relationship between foundations and demos enhances learning efficiency by bridging theory with practice, fostering a more comprehensive grasp of the material.
Core Differences Between Foundations and Demos
Foundations provide the essential principles, structures, and frameworks that support a concept or system, emphasizing underlying theories and long-term stability. Demos focus on practical implementations or demonstrations that showcase functionalities and real-world applications to validate concepts quickly. The core difference lies in foundations establishing the groundwork and theoretical basis, while demos illustrate and test those ideas through applied examples.
Purpose and Objectives of Foundations
Foundations establish the fundamental principles and core structures that guide the development and sustainability of a project or organization, aiming to ensure long-term stability and consistent value delivery. Their objectives include creating a robust framework for governance, fostering community engagement, and supporting ongoing innovation through resource allocation and strategic partnerships. By setting clear standards and providing continuous support, foundations enable scalable growth and resilient ecosystems.
Key Goals of Demos
Demos primarily aim to showcase product capabilities, highlighting real-world applications and user benefits to engage potential customers effectively. They serve as interactive experiences designed to demonstrate functionality, answer specific use-case questions, and build trust in the product's value. By focusing on user interaction and problem-solving, demos drive informed decision-making and accelerate the sales cycle.
Structure and Organization: Foundations vs Demos
Foundations emphasize a robust, scalable structure with clear organizational principles that support long-term development and maintainability, ensuring components are reusable and modular. Demos prioritize rapid implementation and visual appeal to showcase features or concepts quickly, often sacrificing detailed organization for immediacy. The contrast lies in Foundations fostering systematic, well-documented frameworks, while Demos aim for concise, illustrative presentations with less emphasis on underlying structure.
Funding Models: Foundations vs Demos
Foundations typically rely on endowments, grants, and philanthropic donations to sustain their funding, ensuring long-term financial stability for their initiatives. In contrast, demos often depend on government allocations, crowdfunding, or volunteer contributions, making their funding more variable and project-specific. This fundamental difference impacts the scalability and sustainability of both foundations and demos in executing their missions.
Contribution and Participation Mechanisms
Foundations typically establish formal governance structures and well-defined contribution guidelines to manage participation in open-source projects, ensuring transparency and accountability. Demos often rely on informal or ad-hoc participation mechanisms centered around community engagement and iterative feedback to foster innovation. The contribution process in foundations involves rigorous code reviews and compliance checks, while demos emphasize rapid prototyping and collaborative experimentation.
Impact and Influence Comparison
Foundations provide a structured base with long-term impact through sustained support and financial resources, enabling systemic change in societies and sectors. Demos, as practical demonstrations, influence immediate perceptions and behavior by showcasing tangible applications and outcomes. The combination of foundations' overarching strategies and demos' real-world examples amplifies overall effectiveness in driving both policy reform and public engagement.
Case Studies: Successful Foundations and Demos
Case studies of successful foundations reveal their long-term impact on societal change through sustained funding and strategic grantmaking, exemplified by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation's role in global health initiatives. Demo projects, such as Tesla's early electric vehicle prototypes, demonstrate the value of practical, real-world testing to validate innovative technologies and attract investment. These cases highlight how foundations leverage resources for systemic solutions while demos prove concepts, accelerating adoption and scaling.
Choosing Between Foundations and Demos for Your Project
Choosing between foundations and demos depends on the project's scope and development stage; foundations provide a stable, reusable base ideal for long-term scalability, while demos offer quick, functional prototypes to validate concepts early. Foundations emphasize robust architecture and modular components, making them essential for complex applications requiring maintainability. Demos prioritize speed and simplicity, facilitating user feedback and iterative improvements during initial design phases.
Foundations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com