An institutional framework defines the structures, rules, and processes that govern organizations and systems within a society, ensuring stability and promoting economic development. It shapes interactions between individuals, businesses, and governments, influencing regulatory environments and policy implementation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your actions and decisions are impacted within this framework.
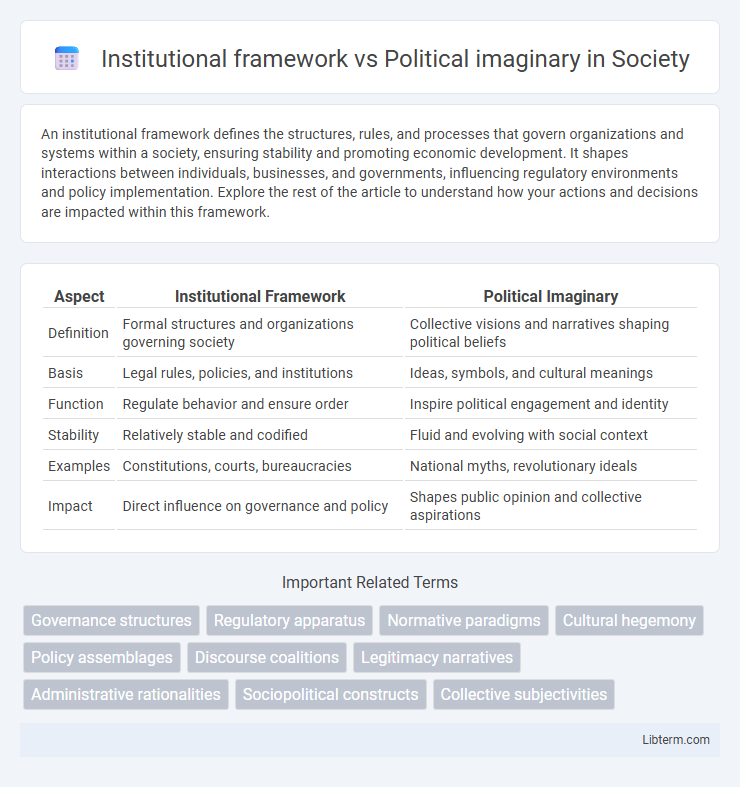
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Institutional Framework | Political Imaginary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal structures and organizations governing society | Collective visions and narratives shaping political beliefs |
| Basis | Legal rules, policies, and institutions | Ideas, symbols, and cultural meanings |
| Function | Regulate behavior and ensure order | Inspire political engagement and identity |
| Stability | Relatively stable and codified | Fluid and evolving with social context |
| Examples | Constitutions, courts, bureaucracies | National myths, revolutionary ideals |
| Impact | Direct influence on governance and policy | Shapes public opinion and collective aspirations |
Defining Institutional Frameworks
Defining institutional frameworks involves establishing codified structures, rules, and norms that govern political and social interactions within a society, ensuring predictable and stable processes. These frameworks dictate the formal organization of governments, legal systems, and bureaucracies, directly influencing policy-making and implementation. Political imaginary, by contrast, encompasses the collective visions and narratives that shape citizens' perceptions and expectations of institutions, often guiding informal practices beyond formal frameworks.
Understanding the Political Imaginary
Understanding the political imaginary involves grasping the collective narratives, symbols, and myths that shape a society's perception of power and governance beyond formal institutional frameworks. While institutional frameworks provide the structured legal and organizational basis for political operation, the political imaginary frames how citizens envision their political reality and legitimacy. This interplay influences civic engagement, policy acceptance, and the potential for political change within a given institutional context.
Historical Roots of Institutional Structures
Institutional frameworks originated from codified laws, governance systems, and administrative practices that evolved through historical processes such as state formation and legal codification, providing formal structures for societal regulation. Political imaginaries, by contrast, derive from collective beliefs, myths, and cultural narratives that shape citizens' perceptions of political legitimacy and social order, often preceding or influencing institutional development. Understanding the historical roots of institutional structures requires analyzing how these formal frameworks emerged within the context of dominant political imaginaries that justified and sustained authority over time.
Political Imaginaries: Origins and Influence
Political imaginaries originate from collective beliefs, cultural narratives, and social values that shape how communities envision governance and power structures. These imaginaries influence institutional frameworks by guiding the legitimacy, purpose, and functioning of political systems through shared symbols and ideological foundations. The interplay between political imaginaries and institutional frameworks determines policy priorities, citizen engagement, and the evolution of state authority over time.
Interactions Between Institutions and Imaginaries
Institutional frameworks establish formal rules and structures governing political behavior, while political imaginaries shape collective perceptions and ideologies influencing those structures. Interactions between institutions and imaginaries involve reciprocal shaping, where institutions codify prevailing imaginaries, and shifting imaginaries prompt institutional reforms. Understanding this dynamic reveals how governance adapts to evolving social meanings and legitimizes authority through symbolic narratives embedded in institutional practices.
Power Dynamics: Institutional vs Imaginary
Institutional frameworks codify power dynamics through formal rules, regulations, and hierarchies, granting authority based on legal and organizational structures. In contrast, political imaginaries shape power by influencing collective beliefs, values, and narratives that define legitimacy and social norms beyond institutional boundaries. The interplay between institutional mechanisms and political imaginaries determines the distribution and exercise of power within societies.
Role in Policy-Making and Governance
The institutional framework establishes formal rules, procedures, and organizational structures that guide policy-making and governance, ensuring legal authority and accountability in decision-making processes. The political imaginary shapes the collective beliefs, narratives, and ideologies influencing how societies envision governance roles, public priorities, and legitimacy, thereby driving informal norms and public engagement. Together, they interact to balance codified institutional mandates with culturally embedded visions that shape policy agendas and governance outcomes.
Case Studies: Institutional Frameworks in Practice
Case studies on institutional frameworks reveal how formal rules, regulations, and organizational structures shape governance outcomes and public policy effectiveness across different regions. The contrast with political imaginaries highlights how collective beliefs and shared visions influence institutional design and reform processes. Empirical examples demonstrate that institutional frameworks grounded in local social realities tend to yield more sustainable and legitimate governance models.
The Impact of Political Imaginaries on Societal Change
Political imaginaries shape societal change by influencing collective perceptions of governance, identity, and power beyond formal institutional frameworks. These shared visions frame public discourse, guide policy preferences, and mobilize social movements, often driving transformative shifts that formal institutions struggle to initiate. Understanding the dynamic interplay between institutional structures and political imaginaries reveals how cultural narratives and symbolic meanings affect political legitimacy and innovation.
Bridging Institutional Frameworks and Political Imaginaries
Bridging institutional frameworks and political imaginaries requires integrating formal governance structures with the collective visions and cultural narratives that shape political engagement. Effective policy design depends on aligning institutional mechanisms with the societal values and aspirations embedded in political imaginaries. This synergy enhances democratic legitimacy and fosters adaptive governance capable of addressing complex social challenges.
Institutional framework Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com