Advocacy coalitions are networks of individuals and organizations that share common policy goals and collaborate to influence decision-making processes. These coalitions leverage collective expertise and resources to shape public policy, often through strategic advocacy and lobbying efforts. Explore the rest of the article to learn how your participation in advocacy coalitions can drive meaningful policy change.
Table of Comparison
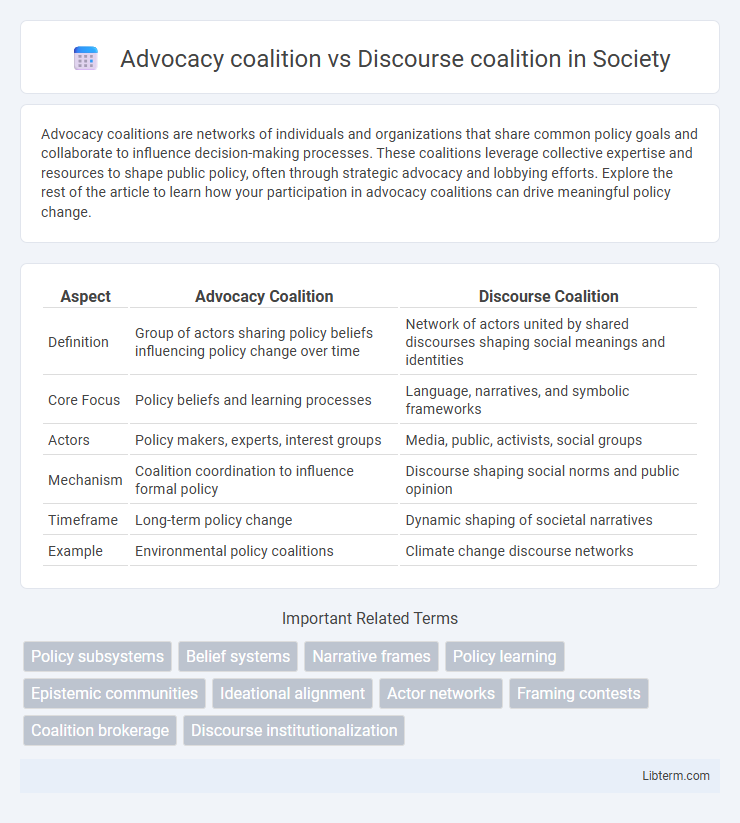
| Aspect | Advocacy Coalition | Discourse Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group of actors sharing policy beliefs influencing policy change over time | Network of actors united by shared discourses shaping social meanings and identities |
| Core Focus | Policy beliefs and learning processes | Language, narratives, and symbolic frameworks |
| Actors | Policy makers, experts, interest groups | Media, public, activists, social groups |
| Mechanism | Coalition coordination to influence formal policy | Discourse shaping social norms and public opinion |
| Timeframe | Long-term policy change | Dynamic shaping of societal narratives |
| Example | Environmental policy coalitions | Climate change discourse networks |
Introduction to Advocacy and Discourse Coalitions
Advocacy coalitions consist of groups of actors who share core beliefs and collaborate to influence public policy within a specific domain over time. Discourse coalitions form around shared narratives and language that shape how policy issues are framed and understood by diverse stakeholders. Understanding the dynamics between advocacy and discourse coalitions is crucial for analyzing the power of belief systems and communication strategies in policy-making processes.
Defining Advocacy Coalitions
Advocacy coalitions consist of groups of individuals and organizations that share policy beliefs and collaborate over time to influence public policy within a specific subsystem. These coalitions actively coordinate strategies and resources to promote their shared policy objectives, differentiating them from discourse coalitions, which focus on the shared use of language and framing rather than coordinated actions. Defining advocacy coalitions involves identifying their shared core beliefs, coordinated efforts, and persistent engagement within policy processes.
Understanding Discourse Coalitions
Discourse coalitions consist of diverse actors who share common storylines and narratives that frame policy issues, shaping public perception and influencing decision-making processes. Unlike advocacy coalitions, which prioritize policy-oriented beliefs and formal strategies, discourse coalitions emphasize the power of language, symbols, and communication in constructing social realities. Understanding discourse coalitions reveals how shared meanings mobilize stakeholders and drive policy debates beyond formal advocacy networks.
Theoretical Frameworks: ACF vs. Discourse Analysis
The Advocacy Coalition Framework (ACF) emphasizes the role of belief systems and policy-oriented learning among coalitions of actors within policy subsystems, highlighting how shared values drive coordinated advocacy over time. Discourse Analysis, in contrast, focuses on the power of language, narratives, and social constructs to shape policy debates and influence meaning-making processes within discourse coalitions. Both frameworks analyze policy change but differ fundamentally in their approach: ACF centers on structured belief-driven actor networks while Discourse Analysis prioritizes the interpretive and communicative dimensions of policy formation.
Key Characteristics of Advocacy Coalitions
Advocacy coalitions consist of groups of actors from various institutions who share a set of normative and causal beliefs and engage in a non-trivial degree of coordinated activity over time to influence policy processes. These coalitions are characterized by their stable belief systems, long-term commitment, and strategic use of resources such as expertise, political influence, and networks to affect policy decisions. Unlike discourse coalitions that focus on shared narratives and language, advocacy coalitions prioritize belief systems and active coordination among members within complex policy subsystems.
Core Features of Discourse Coalitions
Discourse coalitions center on shared storylines and narratives that shape actors' perceptions and policy preferences, emphasizing language, symbols, and interpretative frames as core features. Unlike advocacy coalitions that rely on formal organizational ties and stable beliefs, discourse coalitions highlight fluid alliances formed through communicative practices and mutual understanding. These coalitions influence policy processes by constructing dominant discourses and enabling collective meaning-making across diverse stakeholders.
Formation and Dynamics: How Coalitions Emerge
Advocacy coalitions emerge through the alignment of actors who share similar policy beliefs and coordinate efforts within a specific policy subsystem, often maintaining formal networks for collective influence. Discourse coalitions form around shared narratives and language that shape how issues are framed, with participants united by common storytelling rather than formal agreements. While advocacy coalitions emphasize stable, belief-driven collaboration, discourse coalitions dynamically evolve through shifting discursive practices and contested meanings within political discourse.
Influence on Policy Change: Mechanisms and Impact
Advocacy coalitions influence policy change primarily through coordinated strategies, shared belief systems, and leveraging technical expertise to mobilize political support over extended periods. Discourse coalitions shape policy by framing narratives, controlling language, and constructing dominant storylines that define problem perceptions and legitimate policy solutions in public debates. The impact of advocacy coalitions hinges on resource mobilization and coalition stability, while discourse coalitions rely on discursive power and the ability to shift societal norms and values.
Comparative Analysis: Advocacy vs. Discourse Coalitions
Advocacy coalitions consist of groups of actors united by shared policy beliefs and actively engage in coordinated efforts to influence policy change over long periods. Discourse coalitions, by contrast, are formed around shared narratives and language, emphasizing the power of framing and communication rather than formal organization or sustained action. Advocacy coalitions rely on belief systems and policy-oriented learning, whereas discourse coalitions focus on shaping meanings and public perception within policy debates.
Implications for Policy Studies and Future Research
Advocacy coalitions emphasize shared beliefs and coordinated strategies among actors influencing policy change over time, providing a structured framework for analyzing political learning and policy subsystem dynamics. Discourse coalitions focus on the role of language, narratives, and shared storylines in shaping policy debates, highlighting how meaning and interpretation influence policy outcomes. Future research should integrate both approaches to capture the interplay between belief systems and discursive practices, enriching policy analysis with deeper insights into power, identity, and the evolution of policy paradigms.
Advocacy coalition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com