Social assistance programs provide vital support to individuals and families facing financial hardship, ensuring access to essential resources like food, housing, and healthcare. These initiatives are designed to promote social equity and improve overall community well-being by reducing poverty and vulnerability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how social assistance can impact your life and the broader society.
Table of Comparison
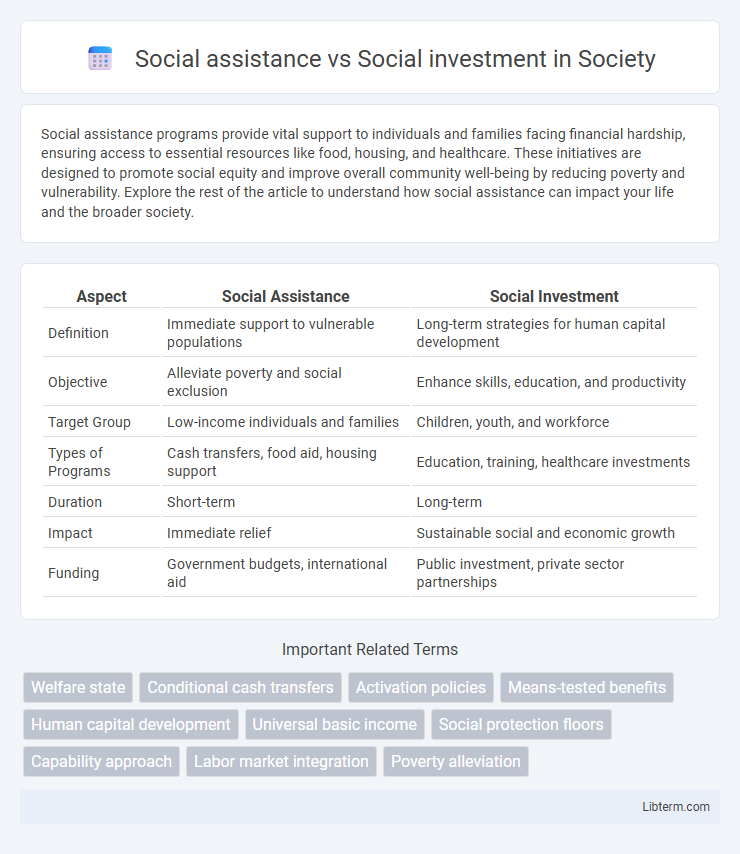
| Aspect | Social Assistance | Social Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate support to vulnerable populations | Long-term strategies for human capital development |
| Objective | Alleviate poverty and social exclusion | Enhance skills, education, and productivity |
| Target Group | Low-income individuals and families | Children, youth, and workforce |
| Types of Programs | Cash transfers, food aid, housing support | Education, training, healthcare investments |
| Duration | Short-term | Long-term |
| Impact | Immediate relief | Sustainable social and economic growth |
| Funding | Government budgets, international aid | Public investment, private sector partnerships |
Understanding Social Assistance: Definition and Purpose
Social assistance refers to government programs designed to provide immediate financial support and basic needs to vulnerable individuals and families facing poverty or hardship. Its primary purpose is to reduce economic insecurity by offering cash transfers, food aid, or housing support without requiring repayment. Unlike social investment, which aims to enhance long-term human capital and self-sufficiency, social assistance focuses on meeting urgent welfare needs and preventing deprivation.
What is Social Investment? Key Principles
Social investment refers to the strategic allocation of resources to generate long-term social and economic benefits, emphasizing prevention, capacity building, and sustainable outcomes. Key principles include fostering empowerment, promoting equality, and ensuring measurable impact through evidence-based approaches. It prioritizes proactive interventions over reactive aid, aiming to reduce dependency and enhance community resilience.
Historical Evolution: Social Assistance and Social Investment
Social assistance historically emerged as a reactive system aimed at providing immediate relief to vulnerable populations through welfare programs and cash transfers, often rooted in post-industrial revolution welfare states of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Social investment evolved later, particularly from the 1990s onwards, emphasizing proactive strategies like education, healthcare, and skill development to promote long-term economic productivity and social inclusion. This shift reflects a growing recognition of human capital as a pivotal asset for sustainable development in modern welfare policies.
Core Differences Between Social Assistance and Social Investment
Social assistance primarily provides immediate financial aid and basic support to individuals facing economic hardship, targeting poverty alleviation through direct transfers or subsidies. Social investment focuses on long-term human capital development by funding education, health, and training programs that enhance productivity and economic participation. Core differences lie in the goals of social assistance addressing short-term needs, whereas social investment aims to generate sustainable growth and reduce dependency over time.
Target Populations: Who Benefits Most from Each Approach?
Social assistance primarily benefits vulnerable populations such as low-income families, the elderly, and people with disabilities by providing immediate relief through cash transfers and basic services. Social investment targets groups with long-term growth potential, including children, youth, and marginalized communities, by focusing on education, health, and skill development to enhance future economic productivity. Both approaches aim to reduce poverty but differ in their temporal focus, with social assistance addressing urgent needs and social investment promoting sustainable human capital development.
Impact on Poverty Reduction: Comparative Effectiveness
Social assistance primarily provides immediate relief to poverty through cash transfers and subsidies, effectively reducing short-term hardship. Social investment, by funding education, healthcare, and skill development, targets long-term poverty reduction by enhancing human capital and economic productivity. Studies show that social investments yield more sustainable poverty alleviation, while social assistance is crucial for urgent needs, highlighting the importance of integrating both for comprehensive impact.
Economic Implications: Short-term Relief vs Long-term Growth
Social assistance programs provide immediate economic relief by addressing basic needs and stabilizing consumption during crises, reducing poverty and social exclusion in the short term. Social investment focuses on enhancing human capital through education, health, and skills development, fostering sustainable long-term economic growth and productivity. Balancing these approaches is crucial for promoting both economic resilience and inclusive development over time.
Social Inclusion: Promoting Equity and Empowerment
Social assistance provides immediate support to vulnerable populations by offering financial aid and basic services, while social investment focuses on long-term strategies like education, skills development, and job creation to foster social inclusion. Emphasizing social inclusion through social investment promotes equity by empowering marginalized groups to participate fully in economic and social life. Effective policies integrate both approaches to reduce poverty sustainably and enhance opportunities for all citizens.
Policy Challenges: Implementing Social Assistance and Social Investment
Implementing social assistance faces challenges such as targeting accuracy, administrative capacity, and ensuring timely delivery to vulnerable populations. Social investment policies require long-term commitment, effective coordination across sectors, and evaluation mechanisms to maximize returns in education, health, and employment. Balancing immediate relief from social assistance with sustainable outcomes from social investment poses significant policy dilemmas for governments.
Future Trends: Integrating Social Assistance and Social Investment Strategies
Future trends in social policy emphasize the integration of social assistance and social investment to enhance long-term economic resilience and social equity. Combining direct support for vulnerable populations with proactive investments in education, healthcare, and skills development can drive sustainable growth and reduce dependency on welfare. Policymakers increasingly adopt data-driven approaches and cross-sector collaborations to optimize resource allocation and maximize societal impact.
Social assistance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com